Practice questions
... The average atomic mass of Eu is 151.96 amu. There are only two naturally occurring isotopes of europium, 151Eu with a mass of 151.0 amu and 153Eu with a mass of 153.0 amu. The natural abundance of the 131Eu isotope must be approximately a) ...
... The average atomic mass of Eu is 151.96 amu. There are only two naturally occurring isotopes of europium, 151Eu with a mass of 151.0 amu and 153Eu with a mass of 153.0 amu. The natural abundance of the 131Eu isotope must be approximately a) ...
Atomic Structure - Teach-n-Learn-Chem
... 2. Atoms of the same element are exactly alike; in particular, they have the same mass. 3. Compounds are formed by the joining of atoms of two or more elements in fixed, whole ...
... 2. Atoms of the same element are exactly alike; in particular, they have the same mass. 3. Compounds are formed by the joining of atoms of two or more elements in fixed, whole ...
Unit 2 Atomic Structure
... 2. Atoms of the same element are exactly alike; in particular, they have the same mass. 3. Compounds are formed by the joining of atoms of two or more elements in fixed, whole ...
... 2. Atoms of the same element are exactly alike; in particular, they have the same mass. 3. Compounds are formed by the joining of atoms of two or more elements in fixed, whole ...
Chapter 3 - WordPress.com
... particles at a very thin sheet of gold foil. • Based on Thomson’s model of the atom he expected the alpha particles to pass through the foil but not all did! ...
... particles at a very thin sheet of gold foil. • Based on Thomson’s model of the atom he expected the alpha particles to pass through the foil but not all did! ...
Chapter 2: The Composition and Structure of the Atom • 2.1 Matter
... o Ground state – the lowest possible energy state an electron can occupy. o The orbits are also identified using “quantum numbers”: 1, 2, 3, … o When the electron relaxes (c) the energy released is observed as a single wavelength of light. 2.6 Modern Atomic Theory o Bohr’s model of the atom when app ...
... o Ground state – the lowest possible energy state an electron can occupy. o The orbits are also identified using “quantum numbers”: 1, 2, 3, … o When the electron relaxes (c) the energy released is observed as a single wavelength of light. 2.6 Modern Atomic Theory o Bohr’s model of the atom when app ...
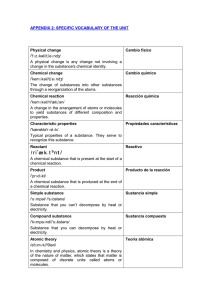
specific vocabulary of the unit
... The order of an element in Mendeleyev's table of the elements; equal to the number of protons in the nucleus or electrons in the neutral state of an atom of an element. Mass number Número másico /mæs//'nʌmbər / The sum of the number of neutrons and protons in an atomic nucleus. Atomic mass ...
... The order of an element in Mendeleyev's table of the elements; equal to the number of protons in the nucleus or electrons in the neutral state of an atom of an element. Mass number Número másico /mæs//'nʌmbər / The sum of the number of neutrons and protons in an atomic nucleus. Atomic mass ...
Grade 11 Chemistry E.. - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... 2. Classify the following changes as physical or chemical: a) food spoils b) an icicle melts c) a nail rusts d) oil is pumped out of a well f) salt dissolves in water g) a window is broken ...
... 2. Classify the following changes as physical or chemical: a) food spoils b) an icicle melts c) a nail rusts d) oil is pumped out of a well f) salt dissolves in water g) a window is broken ...
Atoms
... The mass of a proton is 1836 times that of an electron, and the mass of a neutron is 1839 times that of an electron. Thus the vast majority of the mass of an atom is in the nucleus. ...
... The mass of a proton is 1836 times that of an electron, and the mass of a neutron is 1839 times that of an electron. Thus the vast majority of the mass of an atom is in the nucleus. ...
Atoms - Images
... 1.673 x 10-27 kg. The mass of a neutron is 1.675 x 10-27 kg. The mass of an electron is about 1836 times less than that of a proton, so they are usually neglected when calculating mass. ...
... 1.673 x 10-27 kg. The mass of a neutron is 1.675 x 10-27 kg. The mass of an electron is about 1836 times less than that of a proton, so they are usually neglected when calculating mass. ...
Chapter 2 Atoms, Molecules and Ions
... atoms present and subscripts are used to indicate the relative numbers of atoms. CO2 indicates each molecule contains 1 atom of carbon and 2 atoms of oxygen. Structural Formula: In which the individual bonds are shown by lines. It may or may not indicates the actual shape of the molecules. O=C=O ...
... atoms present and subscripts are used to indicate the relative numbers of atoms. CO2 indicates each molecule contains 1 atom of carbon and 2 atoms of oxygen. Structural Formula: In which the individual bonds are shown by lines. It may or may not indicates the actual shape of the molecules. O=C=O ...
Gateway Chemistry Review (Answer Key) Structure and Properties
... How many protons and neutrons does one atom of the following elements contain? Element ...
... How many protons and neutrons does one atom of the following elements contain? Element ...
Lesson 4 - 5.1: Models of the atom
... in the nucleus of an atom (by Chadwick) Both these particles provided the evidence needed by Rutherford to account for the mass of the nucleus ...
... in the nucleus of an atom (by Chadwick) Both these particles provided the evidence needed by Rutherford to account for the mass of the nucleus ...
Electrons in Atoms
... some what like energy levels. (a) In an ordinary ladder, the rungs are equally spaced. (b) The energy levels in atoms are unequally spaced, like the rungs in this ladder. The higher energy levels are closer together so the amount of energy is not always the same as you move. ...
... some what like energy levels. (a) In an ordinary ladder, the rungs are equally spaced. (b) The energy levels in atoms are unequally spaced, like the rungs in this ladder. The higher energy levels are closer together so the amount of energy is not always the same as you move. ...
Nuclear Fission sim
... amounts of energy, there have to be a LOT of them. How can we do that? • Some fissionable materials have the property that, while they require one neutron to fission, they produce more than one neutron. This means that, if you have enough atoms (a CRITICAL MASS), the one neutron you started with qui ...
... amounts of energy, there have to be a LOT of them. How can we do that? • Some fissionable materials have the property that, while they require one neutron to fission, they produce more than one neutron. This means that, if you have enough atoms (a CRITICAL MASS), the one neutron you started with qui ...
Atoms, Molecules and Ions
... of each element in a given compound is always the same. 3. Chemical reactions only involve the rearrangement of atoms. Atoms are not created or destroyed in chemical reactions. ...
... of each element in a given compound is always the same. 3. Chemical reactions only involve the rearrangement of atoms. Atoms are not created or destroyed in chemical reactions. ...
Preview from Notesale.co.uk Page 2 of 12
... usual in the order of their atomic number, from 2 to 20. The red numbers below each chemical symbol show its electronic structure. Moving across each period, you can see that the number of occupie ...
... usual in the order of their atomic number, from 2 to 20. The red numbers below each chemical symbol show its electronic structure. Moving across each period, you can see that the number of occupie ...
NAME - Partners4results
... ____ 23. The atomic mass of an atom of carbon is 12, and the atomic mass of an atom of oxygen is 16. To produce CO, 16g of oxygen can be combined with 12g of carbon. According to the Law of Multiple Proportions, the ratio of oxygen to carbon when 32g of oxygen combine with 12g of carbon is a. 1:1 b. ...
... ____ 23. The atomic mass of an atom of carbon is 12, and the atomic mass of an atom of oxygen is 16. To produce CO, 16g of oxygen can be combined with 12g of carbon. According to the Law of Multiple Proportions, the ratio of oxygen to carbon when 32g of oxygen combine with 12g of carbon is a. 1:1 b. ...
Chemistry of Life
... Chemistry of Life – the SMALLEST particle that can exist and still be considered matter ...
... Chemistry of Life – the SMALLEST particle that can exist and still be considered matter ...
19.1 Notes - Trimble County Schools
... surrounded by electrons http://www.cfo.doe.gov/me70/manhattan/images/AtomLabeled.gif ...
... surrounded by electrons http://www.cfo.doe.gov/me70/manhattan/images/AtomLabeled.gif ...
Chemistry (B) Final Exam Study Guide 1
... ____ 50. How does the energy of an electron change when the electron moves closer to the nucleus? a. It decreases. c. It stays the same. b. It increases. d. It doubles. ____ 51. What is the shape of the 3p atomic orbital? a. sphere c. bar b. dumbbell d. two perpendicular dumbbells ____ 52. What is ...
... ____ 50. How does the energy of an electron change when the electron moves closer to the nucleus? a. It decreases. c. It stays the same. b. It increases. d. It doubles. ____ 51. What is the shape of the 3p atomic orbital? a. sphere c. bar b. dumbbell d. two perpendicular dumbbells ____ 52. What is ...
Blue File
... Over the years Many Scientists have put forward ‘models’ that they have arrived at from their research of what they understand an atom to look like……. Firstly came : ‘J.J Thompson’s ‘Plum Pudding ‘ model which showed that ‘atoms were tiny balls of positive charge with tiny negative particles stuck i ...
... Over the years Many Scientists have put forward ‘models’ that they have arrived at from their research of what they understand an atom to look like……. Firstly came : ‘J.J Thompson’s ‘Plum Pudding ‘ model which showed that ‘atoms were tiny balls of positive charge with tiny negative particles stuck i ...