Thomson`s Atomic Model
... • Physicists began to wrestle with explaining the unpredictable nature of electrons. • The unconventional solution was to understand electrons not as particles, but as waves. ...
... • Physicists began to wrestle with explaining the unpredictable nature of electrons. • The unconventional solution was to understand electrons not as particles, but as waves. ...
Development of Atomic Theory: Rutherford to Modern Theory
... Electron clouds exist at a certain Energy Level. Therefore the energy that an electron has is based on what? Explain how the bookshelves in Fig. 9 can help you understand the movement of electrons in an atom. Atoms are very small. How many atoms could fit inside a ...
... Electron clouds exist at a certain Energy Level. Therefore the energy that an electron has is based on what? Explain how the bookshelves in Fig. 9 can help you understand the movement of electrons in an atom. Atoms are very small. How many atoms could fit inside a ...
chemistry
... 88 Based on Reference Table L, the Ka of H2S is 9.5 ¥ 10–8. This value indicates that H2S is a ...
... 88 Based on Reference Table L, the Ka of H2S is 9.5 ¥ 10–8. This value indicates that H2S is a ...
Development of Atomic Theory: Rutherford to Modern Theory
... Electron clouds exist at a certain Energy Level. Therefore the energy that an electron has is based on what? Explain how the bookshelves in Fig. 9 can help you understand the movement of electrons in an atom. Atoms are very small. How many atoms could fit inside a ...
... Electron clouds exist at a certain Energy Level. Therefore the energy that an electron has is based on what? Explain how the bookshelves in Fig. 9 can help you understand the movement of electrons in an atom. Atoms are very small. How many atoms could fit inside a ...
Notes - Learner
... Arrangement of electrons in the space around nucleus in an atom known as electronic configuration Pauli Exclusion Principle It states, no two electrons in an atom can have identical set of four quantum numbers. The maximum number of electrons in s subshell is 2, p subshell is 6 d subshell is 10 and ...
... Arrangement of electrons in the space around nucleus in an atom known as electronic configuration Pauli Exclusion Principle It states, no two electrons in an atom can have identical set of four quantum numbers. The maximum number of electrons in s subshell is 2, p subshell is 6 d subshell is 10 and ...
Structure of an Atom
... The atom is made up of several parts. It has a center part called the nucleus. The nucleus is made up of a positively charged particle called a proton and a particle that does not have a charge called a neutron. The nucleus is surrounded by negatively charged particles called electrons that move in ...
... The atom is made up of several parts. It has a center part called the nucleus. The nucleus is made up of a positively charged particle called a proton and a particle that does not have a charge called a neutron. The nucleus is surrounded by negatively charged particles called electrons that move in ...
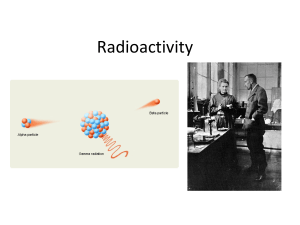
Radioactivity2015
... • Radioisotopes decay from one element to another until they are transformed into stable, non-radioactive isotopes. • For example, 238U decays 11 times, shedding mass and energy each time, eventually becoming 206Pb, a stable isotope. • Radioactive decay is spontaneous – it does not require an input ...
... • Radioisotopes decay from one element to another until they are transformed into stable, non-radioactive isotopes. • For example, 238U decays 11 times, shedding mass and energy each time, eventually becoming 206Pb, a stable isotope. • Radioactive decay is spontaneous – it does not require an input ...
Defining the Atom Guided Reading WS
... a. All elements are composed of tiny, indivisible particles called atoms. b. An element is composed of several types of atoms. c. Atoms of different elements can physically mix together, or can chemically combine in simple, whole-number ratios to form compounds. d. Chemical reactions occur when atom ...
... a. All elements are composed of tiny, indivisible particles called atoms. b. An element is composed of several types of atoms. c. Atoms of different elements can physically mix together, or can chemically combine in simple, whole-number ratios to form compounds. d. Chemical reactions occur when atom ...
Introduction to Chemistry
... Ionic- Two elements bond by transferring electrons to create ions that attract together (+ is attracted to - after an electron is transferred) ...
... Ionic- Two elements bond by transferring electrons to create ions that attract together (+ is attracted to - after an electron is transferred) ...
Chapter 2
... – absorb energy by excitation of electrons to higher energy levels – release energy by relaxation of electrons to lower energy levels ...
... – absorb energy by excitation of electrons to higher energy levels – release energy by relaxation of electrons to lower energy levels ...
Chapter 11 Chemical Reactions
... 2 substances combine to make one compound (also called “synthesis”) Ca + O2 CaO SO3 + H2O H2SO4 We can predict the products, especially if the reactants are two elements. Mg3N2 (symbols, charges, cross) Mg + N2 _______ ...
... 2 substances combine to make one compound (also called “synthesis”) Ca + O2 CaO SO3 + H2O H2SO4 We can predict the products, especially if the reactants are two elements. Mg3N2 (symbols, charges, cross) Mg + N2 _______ ...
Periodic Table Notes
... • All neutral atoms have the same number electrons as protons. The atomic number tells us the number of protons, and it also tells us the total number of electrons. • The number of electrons surrounding the nucleus of an atom is equal to the number of protons in its nucleus. • How many electrons do ...
... • All neutral atoms have the same number electrons as protons. The atomic number tells us the number of protons, and it also tells us the total number of electrons. • The number of electrons surrounding the nucleus of an atom is equal to the number of protons in its nucleus. • How many electrons do ...
Chapter 11 Chemical Reactions
... 2 substances combine to make one compound (also called “synthesis”) Ca + O2 CaO SO3 + H2O H2SO4 We can predict the products, especially if the reactants are two elements. Mg3N2 (symbols, charges, cross) Mg + N2 _______ ...
... 2 substances combine to make one compound (also called “synthesis”) Ca + O2 CaO SO3 + H2O H2SO4 We can predict the products, especially if the reactants are two elements. Mg3N2 (symbols, charges, cross) Mg + N2 _______ ...
No Slide Title
... • 3. the center or nucleus of the atom must consist of a dense positive charge. ...
... • 3. the center or nucleus of the atom must consist of a dense positive charge. ...
atomic number
... You know that neutrons are found in the nucleus of an atom. Under normal conditions, protons and neutrons stick together in the nucleus. During radioactive decay, they may be knocked out of there. Neutron numbers are able to change the mass of atoms, because they weigh about as much as a proton and ...
... You know that neutrons are found in the nucleus of an atom. Under normal conditions, protons and neutrons stick together in the nucleus. During radioactive decay, they may be knocked out of there. Neutron numbers are able to change the mass of atoms, because they weigh about as much as a proton and ...
February Homework Packet
... 8. How do the energy and the most probable location of an electron in the third shell of an atom compare to the energy and the most probable location of an electron in the first shell of the same atom? (1) In the third shell, an electron has more energy and is closer to the nucleus. (2) In the third ...
... 8. How do the energy and the most probable location of an electron in the third shell of an atom compare to the energy and the most probable location of an electron in the first shell of the same atom? (1) In the third shell, an electron has more energy and is closer to the nucleus. (2) In the third ...
Alpha Decay Alpha decay can most simply be described like this: 1
... 1. An electron from the closest energy level falls into the nucleus, which causes a proton to become a neutron. 2. A neutrino is emitted from the nucleus. 3. Another electron falls into the empty energy level and so on causing a cascade of electrons falling. One free electron, moving about in space, ...
... 1. An electron from the closest energy level falls into the nucleus, which causes a proton to become a neutron. 2. A neutrino is emitted from the nucleus. 3. Another electron falls into the empty energy level and so on causing a cascade of electrons falling. One free electron, moving about in space, ...
Science 9 - Ms. J Reed
... Draw a circle and put the symbol and number of protons and neutrons inside of it ◦ Number of protons equals the atomic number ◦ Number of neutrons equals the atomic mass – the number of protons number of protons + number of neutrons = atomic mass ...
... Draw a circle and put the symbol and number of protons and neutrons inside of it ◦ Number of protons equals the atomic number ◦ Number of neutrons equals the atomic mass – the number of protons number of protons + number of neutrons = atomic mass ...
Chapter 5 - U of L Class Index
... Temperature. Raising the temperature will increase the number of collisions between molecules and also provide the collisions with the required energy of activation. Raising the temperature almost always increases the rate of reaction. Conversely, lowering the temperature will reduce the rate of rea ...
... Temperature. Raising the temperature will increase the number of collisions between molecules and also provide the collisions with the required energy of activation. Raising the temperature almost always increases the rate of reaction. Conversely, lowering the temperature will reduce the rate of rea ...
The History of the Atom
... Almost always occurs with alpha or beta decay. Does not change mass number or atomic number. No new element is created ...
... Almost always occurs with alpha or beta decay. Does not change mass number or atomic number. No new element is created ...
LIST OF TOPICS COVERED DURING THIS COURSE
... The following should serve as a checklist for your notebook. The topics below include all topics that have been covered this semester and are testable on your final exam. These topics should be studied from a variety of source including inclass notes, homework questions, lab questions, assignments, ...
... The following should serve as a checklist for your notebook. The topics below include all topics that have been covered this semester and are testable on your final exam. These topics should be studied from a variety of source including inclass notes, homework questions, lab questions, assignments, ...
double-replacement reaction
... Classifying Chemical Reactions Combination Reactions Decomposition Reactions Single-Replacement Reactions The Activity Series Double-Replacement Reactions Solubility Rules Neutralization Reactions H+ + OH- H2O(l) ...
... Classifying Chemical Reactions Combination Reactions Decomposition Reactions Single-Replacement Reactions The Activity Series Double-Replacement Reactions Solubility Rules Neutralization Reactions H+ + OH- H2O(l) ...