CMC Chapter 04
... • The figure shown below is a nuclear equation showing the radioactive decay of radium-226 to radon-222. ...
... • The figure shown below is a nuclear equation showing the radioactive decay of radium-226 to radon-222. ...
Chapter 2
... The different states of potential energy that the electrons of an atom can have are called electron shells. o The first shell, closest to the nucleus, has the lowest potential energy. o Electrons in outer shells have higher potential energy. o Electrons can change their position only if they absorb ...
... The different states of potential energy that the electrons of an atom can have are called electron shells. o The first shell, closest to the nucleus, has the lowest potential energy. o Electrons in outer shells have higher potential energy. o Electrons can change their position only if they absorb ...
Answers to Final Exam Review
... 26. Arrange the following elements in order of increasing electronegativity, from lowest to highest: F, K, Si, and S. a. F < K < S < Si c. Si < F < K < S d. S < Si < F < K b. K < Si < S < F 27. Does potassium (K) have more similar properties to sodium (Na) or calcium (Ca)? Justify your answer. Sodiu ...
... 26. Arrange the following elements in order of increasing electronegativity, from lowest to highest: F, K, Si, and S. a. F < K < S < Si c. Si < F < K < S d. S < Si < F < K b. K < Si < S < F 27. Does potassium (K) have more similar properties to sodium (Na) or calcium (Ca)? Justify your answer. Sodiu ...
AtomsHandout - mrsgaschoscience
... The Bohr Model of the Atom One of the scientists that helped to develop the ______________ of the atom that we use today was a ______________ physicist named ________________________. He suggested that there were ______________ to the position and motion of _______________. Bohr believed the followi ...
... The Bohr Model of the Atom One of the scientists that helped to develop the ______________ of the atom that we use today was a ______________ physicist named ________________________. He suggested that there were ______________ to the position and motion of _______________. Bohr believed the followi ...
Lesson 5: Current Atomic Model
... During the 1930’s protons and neutrons discovered. Charges are the same magnitude but opposite sign for protons and electrons, neutrons have no charge. ...
... During the 1930’s protons and neutrons discovered. Charges are the same magnitude but opposite sign for protons and electrons, neutrons have no charge. ...
Test - Regents
... 56 As the volume of a fixed mass of a gas increases at constant temperature, the pressure of the gas ...
... 56 As the volume of a fixed mass of a gas increases at constant temperature, the pressure of the gas ...
Physical Science
... mixtures of isotopes. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that differ in the number of neutrons. ...
... mixtures of isotopes. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that differ in the number of neutrons. ...
Early Atomic Theory - Cinnaminson School
... an electron. He also determined that there was a smallest 'unit' charge, or that charge is 'quantized'. He received the Nobel Prize for his work. ...
... an electron. He also determined that there was a smallest 'unit' charge, or that charge is 'quantized'. He received the Nobel Prize for his work. ...
SC71 Chemistry
... Determine the atomic number and mass number of an element from the periodic table. Determine the correct number of electrons, protons and neutrons for any given element. Identify what an isotope is. ...
... Determine the atomic number and mass number of an element from the periodic table. Determine the correct number of electrons, protons and neutrons for any given element. Identify what an isotope is. ...
Chapter 19 part 1
... These are the most common oxidation states. However, other oxidation states are also possible. ...
... These are the most common oxidation states. However, other oxidation states are also possible. ...
Practice MSL Multiple Choice 1. Compared to the charge and mass
... lose electrons and form negative ions lose electrons and form positive ions gain electrons and from negative ions gain electrons and form positive ions ...
... lose electrons and form negative ions lose electrons and form positive ions gain electrons and from negative ions gain electrons and form positive ions ...
Chemistry I Exams and Answer Keys 2015 Season
... A pure metal is made up of atoms that are held together by all valence electrons that are not held exclusively by any particular atoms, but move freely around them. This statement is best described as A. a correct definition of a chemical term or expression, either in terms of experimental behavior ...
... A pure metal is made up of atoms that are held together by all valence electrons that are not held exclusively by any particular atoms, but move freely around them. This statement is best described as A. a correct definition of a chemical term or expression, either in terms of experimental behavior ...
File
... 15. Explain basic character and reducing character of hydrides of the 15th group elements. 16. What are enantiomers? How can they be identified? 17. What are the micro-alloys? Explain with two examples. 18. Half-life period of a radioactive element is 100 seconds. Calculate the disintegration const ...
... 15. Explain basic character and reducing character of hydrides of the 15th group elements. 16. What are enantiomers? How can they be identified? 17. What are the micro-alloys? Explain with two examples. 18. Half-life period of a radioactive element is 100 seconds. Calculate the disintegration const ...
b. Elements as Mixtures - Isotopes
... Elements are made from atoms having the same atomic number, protons Are all atoms of one particular atom the same or are they mixtures? 1) All atom nuclei for an element have the same number of protons. 2) Every atom in an element has the same number of protons & electrons 3) However, elements are ...
... Elements are made from atoms having the same atomic number, protons Are all atoms of one particular atom the same or are they mixtures? 1) All atom nuclei for an element have the same number of protons. 2) Every atom in an element has the same number of protons & electrons 3) However, elements are ...
electron configuration
... (less reactive) • In addition to full outer EL’s, there are other econfigurations of high relative stability: filled ...
... (less reactive) • In addition to full outer EL’s, there are other econfigurations of high relative stability: filled ...
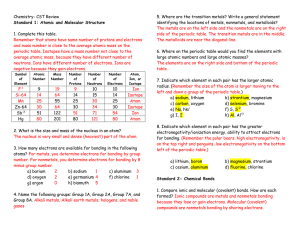
Chemistry- CST Review
... 4. What atoms does carbon commonly form bonds with? Hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, and another carbon commonly form bonds with carbon. Standard 11- Nuclear Processes 1. What elements have radioactive isotopes? Elements with atomic number 84 and above are radioisotopes. There are more like carbon which ...
... 4. What atoms does carbon commonly form bonds with? Hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, and another carbon commonly form bonds with carbon. Standard 11- Nuclear Processes 1. What elements have radioactive isotopes? Elements with atomic number 84 and above are radioisotopes. There are more like carbon which ...
gp - fc2009goran
... radioisotopes were used in what is now called nuclear medicine. The most common, stable form of iodine has an atomic number of 53 (protons) and an atomic weight of 127 (53 protons plus 74 neutrons). Because its nucleus has the "correct" number of neutrons, it is stable and is not radioactive. A less ...
... radioisotopes were used in what is now called nuclear medicine. The most common, stable form of iodine has an atomic number of 53 (protons) and an atomic weight of 127 (53 protons plus 74 neutrons). Because its nucleus has the "correct" number of neutrons, it is stable and is not radioactive. A less ...
The Modern Atomic Model
... • Every atom of an element will always have the same number of protons • Carbon will always have 6 protons, oxygen will always have 8 protons, and iron will always have 26 protons. ...
... • Every atom of an element will always have the same number of protons • Carbon will always have 6 protons, oxygen will always have 8 protons, and iron will always have 26 protons. ...
Build an Atom
... What happens when you add protons, neutrons, or electrons? To start over, click Show the symbol, atomic mass, and charge by clicking on the ...
... What happens when you add protons, neutrons, or electrons? To start over, click Show the symbol, atomic mass, and charge by clicking on the ...
Reaction Predictions
... Hydrolysis: The reaction of a salt with water to form molecular species. Salts of a strong acid + a weak base will always hydrolyze to give an acidic solution. Neutralization: Acid and base react to form a salt and water. Catalyst: A molecule that speeds that speeds a reaction but that does not appe ...
... Hydrolysis: The reaction of a salt with water to form molecular species. Salts of a strong acid + a weak base will always hydrolyze to give an acidic solution. Neutralization: Acid and base react to form a salt and water. Catalyst: A molecule that speeds that speeds a reaction but that does not appe ...
weighted average - Effingham County Schools
... definition of an element as a substance that cannot be further broken down by ordinary chemical means. •It was also clear that elements combine to form compounds that have different physical and chemical properties than those of the elements that form them. Na + Cl → NaCl ...
... definition of an element as a substance that cannot be further broken down by ordinary chemical means. •It was also clear that elements combine to form compounds that have different physical and chemical properties than those of the elements that form them. Na + Cl → NaCl ...