Chem Curr - New Haven Science
... 6. Define and contrast physical, chemical, and nuclear changes. 7. Determine whether a substance is a mixture, element, or compound. 8. Use properties of matter to separate mixtures. ...
... 6. Define and contrast physical, chemical, and nuclear changes. 7. Determine whether a substance is a mixture, element, or compound. 8. Use properties of matter to separate mixtures. ...
No Slide Title
... Reading and Writing Think of a memory chip as a grid or array of capacitors located at specific rows and columns. If we choose to read the memory cell located at row 3, column 5, we will retrieve information from a specific capacitor. Every time we go to row 3, column 5, we will access or address ...
... Reading and Writing Think of a memory chip as a grid or array of capacitors located at specific rows and columns. If we choose to read the memory cell located at row 3, column 5, we will retrieve information from a specific capacitor. Every time we go to row 3, column 5, we will access or address ...
Electrochemistry
... 7. Spontaneous redox reactions (unlike electrolysis/electroplating) can simply occur (as in the ornament lab) or can be separated so the oxidation and reduction occur in different containers (half-cells). In this way, the electrons must move through an outside wire (this is an electrochemical cell—a ...
... 7. Spontaneous redox reactions (unlike electrolysis/electroplating) can simply occur (as in the ornament lab) or can be separated so the oxidation and reduction occur in different containers (half-cells). In this way, the electrons must move through an outside wire (this is an electrochemical cell—a ...
(electrons).
... many times smaller than the diameter of the atom. In this model, the electrons move randomly around the nucleus ...
... many times smaller than the diameter of the atom. In this model, the electrons move randomly around the nucleus ...
chapter5
... He proposed a planetary model of the atom with the electrons orbiting around the nucleus in a specific circular paths. Each electron has an energy level. Each energy level of the electron can be thought of as rungs on a ladder. The energy levels closest to the nucleus are like rungs of a ladder clos ...
... He proposed a planetary model of the atom with the electrons orbiting around the nucleus in a specific circular paths. Each electron has an energy level. Each energy level of the electron can be thought of as rungs on a ladder. The energy levels closest to the nucleus are like rungs of a ladder clos ...
Microbiology: A Systems Approach
... atoms electrons unequally due to differences in electronegativities. This is seen in water (H2O). More electronegative atoms tend to pull electrons toward them creating a polar molecule. ...
... atoms electrons unequally due to differences in electronegativities. This is seen in water (H2O). More electronegative atoms tend to pull electrons toward them creating a polar molecule. ...
History of Atomic Theory - Reading Community Schools
... move in definite orbits around the nucleus, much like planets circle the sun. These orbits, or energy levels, are located at ...
... move in definite orbits around the nucleus, much like planets circle the sun. These orbits, or energy levels, are located at ...
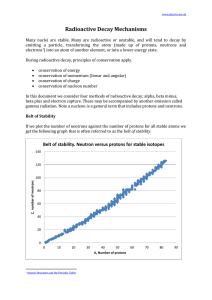
Radioactive Decay Mechanisms
... Note that 1. there are no stable nuclei with an atomic number of 84 or greater. 2. for smaller atoms the ratio neutrons:protons is 1:1 3. for larger atoms the ratio of neutrons:protons approaches about 1.5:1 Since the strong nuclear force weakens significantly with distance, as the atom gets bigger. ...
... Note that 1. there are no stable nuclei with an atomic number of 84 or greater. 2. for smaller atoms the ratio neutrons:protons is 1:1 3. for larger atoms the ratio of neutrons:protons approaches about 1.5:1 Since the strong nuclear force weakens significantly with distance, as the atom gets bigger. ...
P2 Topic 3 - The Polesworth School
... P2 4.3/4 Current – potential difference graphs When we experiment to measure the current that flows through different components as we change the potential difference, we find that each component produces a different shape graph that is characteristic of that component. The simplest is for a resist ...
... P2 4.3/4 Current – potential difference graphs When we experiment to measure the current that flows through different components as we change the potential difference, we find that each component produces a different shape graph that is characteristic of that component. The simplest is for a resist ...
Lecture 9
... Oxidation number is a property of a single atom. We cannot define the oxidation number for a molecule or a polyatomic ion. The sum of oxidation numbers of the atoms in a polyatomic ion or molecule can be calculated. This is not the oxidation number of the molecule or ion. Polyatomic ions have an ov ...
... Oxidation number is a property of a single atom. We cannot define the oxidation number for a molecule or a polyatomic ion. The sum of oxidation numbers of the atoms in a polyatomic ion or molecule can be calculated. This is not the oxidation number of the molecule or ion. Polyatomic ions have an ov ...
Atomic structure - Don`t Trust Atoms
... The atoms of any particular element always contain the same number of protons. For example: hydrogen atoms always contain 1 proton; carbon atoms always contain 6 protons; magnesium atoms always contain 12 protons, The number of protons in an atom is known as its atomic number or proton number. ...
... The atoms of any particular element always contain the same number of protons. For example: hydrogen atoms always contain 1 proton; carbon atoms always contain 6 protons; magnesium atoms always contain 12 protons, The number of protons in an atom is known as its atomic number or proton number. ...
Sommerfeld-Drude model Ground state of ideal electron gas
... At energies that are farther than a few times kBT from the chemical potential , states within the Fermi sphere continue to be completely filled, as if they were frozen in, while states outside the Fermi sphere remain empty. Thus, the majority of the electrons are frozen in states well below the Fer ...
... At energies that are farther than a few times kBT from the chemical potential , states within the Fermi sphere continue to be completely filled, as if they were frozen in, while states outside the Fermi sphere remain empty. Thus, the majority of the electrons are frozen in states well below the Fer ...
Atoms Template
... Law of Conservation of Mass • In 1774, Antoine Lavoisier used a new chemical balance to weigh the chemicals he used in his experiments. He found that if the reactions take place in a sealed container, then the mass of the chemicals that were there before the reaction took place was exactly the same ...
... Law of Conservation of Mass • In 1774, Antoine Lavoisier used a new chemical balance to weigh the chemicals he used in his experiments. He found that if the reactions take place in a sealed container, then the mass of the chemicals that were there before the reaction took place was exactly the same ...
Chapter 2 Atoms and Ions
... Rutherford's partner in the initial phase of this work was Hans Geiger, who later developed the Geiger counter to detect and count fast particles. Many hours of staring at the tiny zinc sulphide screen in the dark must have focused his mind on finding a better way! In 1909, an undergraduate, Ernest ...
... Rutherford's partner in the initial phase of this work was Hans Geiger, who later developed the Geiger counter to detect and count fast particles. Many hours of staring at the tiny zinc sulphide screen in the dark must have focused his mind on finding a better way! In 1909, an undergraduate, Ernest ...
Atomic Structure Notes file
... The atoms of an element can differ in mass from each other because they have differing numbers of neutrons. Those with more neutrons will weigh more and be more massive. The atomic mass (often referred to as atomic weight) of an element is calculated by adding together the number of protons and the ...
... The atoms of an element can differ in mass from each other because they have differing numbers of neutrons. Those with more neutrons will weigh more and be more massive. The atomic mass (often referred to as atomic weight) of an element is calculated by adding together the number of protons and the ...
Chemistry Name_______________________ Chapter 4
... Democritus believed these atoms could move through empty space. Aristotle did not believe in empty space ...
... Democritus believed these atoms could move through empty space. Aristotle did not believe in empty space ...
File
... While all the protons and neutrons are packed tightly together in the central nucleus, the electrons are arranged in a very specific pattern, according to a set of rules. 1. The electrons can orbit (go around) the nucleus as if they are on rings or shells around the nucleus 2. Only two electrons can ...
... While all the protons and neutrons are packed tightly together in the central nucleus, the electrons are arranged in a very specific pattern, according to a set of rules. 1. The electrons can orbit (go around) the nucleus as if they are on rings or shells around the nucleus 2. Only two electrons can ...
Matter and Measurement
... At the equivalence point, all the HCl has reacted. Addition of a very small amount of NaOH results in a dramatic color change of the indicator. This is called the END POINT of the titration. Based on the volume of NaOH that must be added to reach the end point we can determine the concentration of t ...
... At the equivalence point, all the HCl has reacted. Addition of a very small amount of NaOH results in a dramatic color change of the indicator. This is called the END POINT of the titration. Based on the volume of NaOH that must be added to reach the end point we can determine the concentration of t ...
Gizmo Lab Bohr Models 2014
... Student Exploration: Element Builder Investigating Atoms and Drawing Bohr Models Vocabulary: atom, atomic number, electron, element, energy level, mass number, neutron, nucleus, Periodic Table, proton, valence electrons Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.) 1. What are some of ...
... Student Exploration: Element Builder Investigating Atoms and Drawing Bohr Models Vocabulary: atom, atomic number, electron, element, energy level, mass number, neutron, nucleus, Periodic Table, proton, valence electrons Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.) 1. What are some of ...
ATOMIC STRUCTURE Democritus, ancient Greece: “All matter is
... An atom with its electrons in the lowest possible energy levels is said to be in its .............. state. 23. What happens to an electron when energy is supplied? The atom that has more energy than in its ground state is said to be in an .................... state. There are many possible excited s ...
... An atom with its electrons in the lowest possible energy levels is said to be in its .............. state. 23. What happens to an electron when energy is supplied? The atom that has more energy than in its ground state is said to be in an .................... state. There are many possible excited s ...
ATOMIC STRUCTURE Democritus, ancient Greece: “All matter is
... An atom with its electrons in the lowest possible energy levels is said to be in its .............. state. 23. What happens to an electron when energy is supplied? The atom that has more energy than in its ground state is said to be in an .................... state. There are many possible excited s ...
... An atom with its electrons in the lowest possible energy levels is said to be in its .............. state. 23. What happens to an electron when energy is supplied? The atom that has more energy than in its ground state is said to be in an .................... state. There are many possible excited s ...