Day 5 Intro-to-Chem
... oxide reacts with water to form sodium hydroxide (NaOH). If you evaporate the water, you will have solid NaOH not Na2O. S Sodium oxide has different chemical properties compared to salt, and so it reacts differently. S We write the reaction as ...
... oxide reacts with water to form sodium hydroxide (NaOH). If you evaporate the water, you will have solid NaOH not Na2O. S Sodium oxide has different chemical properties compared to salt, and so it reacts differently. S We write the reaction as ...
AToms
... charged subatomic particle. They are much smaller than protons. Protons and neutrons have nearly 2000 times the mass of an electron. Electrons are in constant motion around the nucleus, acting like a cloud. The flow of electrons from one atom to another is electricity. ...
... charged subatomic particle. They are much smaller than protons. Protons and neutrons have nearly 2000 times the mass of an electron. Electrons are in constant motion around the nucleus, acting like a cloud. The flow of electrons from one atom to another is electricity. ...
Empirical Formula
... • Count the number of atoms of each element in the reactants and in the products, and record the results in a table. • Identify elements that appear in only one reactant and in only one product, and balance the atoms of those elements first. Delay the balancing of atoms (often hydrogen and oxygen) t ...
... • Count the number of atoms of each element in the reactants and in the products, and record the results in a table. • Identify elements that appear in only one reactant and in only one product, and balance the atoms of those elements first. Delay the balancing of atoms (often hydrogen and oxygen) t ...
2013 Final Exam Answers
... A 1.0 L and 10.0 L contain the same number of gaseous He atoms. The flasks are at 25°C. Which of the following statements is false? ...
... A 1.0 L and 10.0 L contain the same number of gaseous He atoms. The flasks are at 25°C. Which of the following statements is false? ...
Development of Atomic Theory
... particles with either a negative or positive charge form at least part of the structure of an atom. Thomson won the Nobel Prize in physics in 1906. While Thomson was director of the Cavendish Laboratory at Cambridge University in Cambridge England, one of his graduate students was Ernest Rutherfor ...
... particles with either a negative or positive charge form at least part of the structure of an atom. Thomson won the Nobel Prize in physics in 1906. While Thomson was director of the Cavendish Laboratory at Cambridge University in Cambridge England, one of his graduate students was Ernest Rutherfor ...
Chapter 4 - Early at..
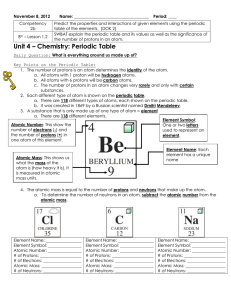
... • If an element has an atomic number of 34 and a mass number of 78 what is the: • number of protons in the atom? • number of neutrons in the atom? • number of electrons in the atom? • complete symbol of the atom? ...
... • If an element has an atomic number of 34 and a mass number of 78 what is the: • number of protons in the atom? • number of neutrons in the atom? • number of electrons in the atom? • complete symbol of the atom? ...
Lesson 1 - St John Brebeuf
... The Atomic Number is equal to the # of protons (P+) in an element. *** Notice Atomic Mass is never a whole number….the extra little bit is ...
... The Atomic Number is equal to the # of protons (P+) in an element. *** Notice Atomic Mass is never a whole number….the extra little bit is ...
UNIT VIII - St John Brebeuf
... The Atomic Number is equal to the # of protons (P+) in an element. *** Notice Atomic Mass is never a whole number….the extra little bit is ...
... The Atomic Number is equal to the # of protons (P+) in an element. *** Notice Atomic Mass is never a whole number….the extra little bit is ...
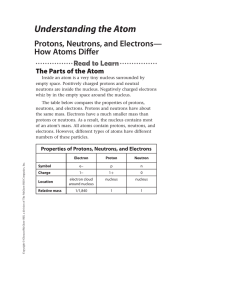
Understanding the Atom
... In 1896, a scientist named Henri Becquerel (1852–1908) studied minerals containing the element uranium. When these minerals were exposed to sunlight, they gave off a type of energy that could pass through paper. If Becquerel covered a photographic plate with black paper, this energy would pass throu ...
... In 1896, a scientist named Henri Becquerel (1852–1908) studied minerals containing the element uranium. When these minerals were exposed to sunlight, they gave off a type of energy that could pass through paper. If Becquerel covered a photographic plate with black paper, this energy would pass throu ...
Atomic Structure
... The atomic number (Z) is simply equal to the number of protons in the nucleus of the atom. As atoms are electrically neutral this will also be equal to the number of electrons in the atom. Atoms of different elements will have different atomic numbers The mass number (A) is equal to the number if pr ...
... The atomic number (Z) is simply equal to the number of protons in the nucleus of the atom. As atoms are electrically neutral this will also be equal to the number of electrons in the atom. Atoms of different elements will have different atomic numbers The mass number (A) is equal to the number if pr ...
File
... • Atoms that are chemically linked together are called molecules. The atoms in molecules can be the same or different. • Atoms link together after chemical reactions, when the electrons of the two atoms react together. • Molecules make up most of the matter that we know. It is relatively rare for at ...
... • Atoms that are chemically linked together are called molecules. The atoms in molecules can be the same or different. • Atoms link together after chemical reactions, when the electrons of the two atoms react together. • Molecules make up most of the matter that we know. It is relatively rare for at ...
Atomic Mass Units
... How to calculate the average atomic mass of an element: List all isotopes, mass numbers, and percent relative abundance of an element Multiply the mass number of each isotope by its relative abundance Add all the products together = atomic mass ...
... How to calculate the average atomic mass of an element: List all isotopes, mass numbers, and percent relative abundance of an element Multiply the mass number of each isotope by its relative abundance Add all the products together = atomic mass ...
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes
... E) are generally 100 or more times sweeter than sucrose. ...
... E) are generally 100 or more times sweeter than sucrose. ...
Slide 1
... 1,800 times smaller than a proton/neutron Atoms have neutral charges because positive protons and negative electrons cancel out. - When an atom is charged because of a proton/electron imbalance – it’s called an ion ...
... 1,800 times smaller than a proton/neutron Atoms have neutral charges because positive protons and negative electrons cancel out. - When an atom is charged because of a proton/electron imbalance – it’s called an ion ...
Key To T2 Review For Final Study Guide File - District 196 e
... The limiting reactant is the reactant that runs out first in a chemical reaction, therefore determining the amount of product produced. 9. What is an excess reactant? The reactant that there is more than enough of to complete the limiting reactant. Some of this reactant will be left over when the re ...
... The limiting reactant is the reactant that runs out first in a chemical reaction, therefore determining the amount of product produced. 9. What is an excess reactant? The reactant that there is more than enough of to complete the limiting reactant. Some of this reactant will be left over when the re ...
Chem 220 In Class Socrative Qs: atomic orbitals 28/09/2016 1
... energy released upon ionization decreases. c) The valence electrons experience greater screening, so Zeff is lower and the electrons are held less strongly. d) Down a column, n increases, so orbital energy increases. Down a column, n ↑ = orbital E ↑ = IE ↓ (easier to remove a higher‐E electron). ...
... energy released upon ionization decreases. c) The valence electrons experience greater screening, so Zeff is lower and the electrons are held less strongly. d) Down a column, n increases, so orbital energy increases. Down a column, n ↑ = orbital E ↑ = IE ↓ (easier to remove a higher‐E electron). ...
Chapter 2_Atoms and Periodic Table
... Valence Shell : Outermost, highest energy shell of an atom. Valence electrons: An electron in an outermost shell of an atom. These electrons are loosely held, they are most important in determining an element’s properties. ...
... Valence Shell : Outermost, highest energy shell of an atom. Valence electrons: An electron in an outermost shell of an atom. These electrons are loosely held, they are most important in determining an element’s properties. ...
Intro to the Periodic Table
... 7. Find the element with the atomic number of 8. a. What is the element name? _________________________ b. What is the element symbol? _________________________ c. How many protons are in one atom of this element? __________________ d. How many electrons are in one atom of this element? ____________ ...
... 7. Find the element with the atomic number of 8. a. What is the element name? _________________________ b. What is the element symbol? _________________________ c. How many protons are in one atom of this element? __________________ d. How many electrons are in one atom of this element? ____________ ...
Atomic Structure Timeline Song
... Its positive charge and tiny size Showed that he was rather wise Electrons moving ‘round the nucleus Describes the “Nuclear Model” for us ...
... Its positive charge and tiny size Showed that he was rather wise Electrons moving ‘round the nucleus Describes the “Nuclear Model” for us ...
About 440 B.C. Empedocles stated that all matter was composed of
... 2. All atoms of a given element are chemically identical to each other; Atoms of one element are different from the atoms of all other elements Page 1 Atomic Theory ...
... 2. All atoms of a given element are chemically identical to each other; Atoms of one element are different from the atoms of all other elements Page 1 Atomic Theory ...
File - Home 15-16
... John Dalton Although the concept of the atom was revived in the 18th century, it took the passing of another hundred years before significant progress was made. The work done in the 19th century by John Dalton (1766-1844), a schoolteacher in England, marks the beginning of the development of modern ...
... John Dalton Although the concept of the atom was revived in the 18th century, it took the passing of another hundred years before significant progress was made. The work done in the 19th century by John Dalton (1766-1844), a schoolteacher in England, marks the beginning of the development of modern ...