H - Deans Community High School
... changes that take place. • Trends in the periodic table • The relationship between the arrangement of elements in the periodic table and their bonding, structure and properties. • Polar covalent bonds in the context of the bonding continuum, followed before studying intermolecular forces. ...
... changes that take place. • Trends in the periodic table • The relationship between the arrangement of elements in the periodic table and their bonding, structure and properties. • Polar covalent bonds in the context of the bonding continuum, followed before studying intermolecular forces. ...
CHAPTER 2 ATOMS, MOLECULES, AND IONS Questions
... a. Dinitrogen monoxide is correct. N and O are both nonmetals, resulting in a covalent compound. We need to use the covalent rules of nomenclature. The other two names are for ionic compounds. b. Copper(I) oxide is correct. With a metal in a compound, we have an ionic compound. Because copper, like ...
... a. Dinitrogen monoxide is correct. N and O are both nonmetals, resulting in a covalent compound. We need to use the covalent rules of nomenclature. The other two names are for ionic compounds. b. Copper(I) oxide is correct. With a metal in a compound, we have an ionic compound. Because copper, like ...
Chemistry Revision Checklist F4 2017 (inc F3)
... Define proton number (atomic number) as the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom Define nucleon number (mass number) as the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom Use proton number and the simple structure of atoms to explain the basis of the Periodic Table (see sectio ...
... Define proton number (atomic number) as the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom Define nucleon number (mass number) as the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom Use proton number and the simple structure of atoms to explain the basis of the Periodic Table (see sectio ...
Chapter 7 - Foothill College
... Remember that Rutherford discovered the nuclear nature of the atom by bombarding thin sheets of metal foil with relatively massive α particles. From his experiment, he concluded that the electrons in an atom are located in a region surrounding a very tiny, dense nucleus that contains most of the ato ...
... Remember that Rutherford discovered the nuclear nature of the atom by bombarding thin sheets of metal foil with relatively massive α particles. From his experiment, he concluded that the electrons in an atom are located in a region surrounding a very tiny, dense nucleus that contains most of the ato ...
Introduction to the Atom
... 1. atoms positive charge is concentrated in the nucleus 2. proton (p) has opposite (+) charge of electron (-) 3. mass of p is 1840 x mass of e- (1.67 x 10-24 g) ...
... 1. atoms positive charge is concentrated in the nucleus 2. proton (p) has opposite (+) charge of electron (-) 3. mass of p is 1840 x mass of e- (1.67 x 10-24 g) ...
High School Chemistry Essential Questions
... matter to represent, analyze, and communicate structure and relationships in chemical systems and chemical interactions? B. What is the atomic model of molecules, what evidence do we have for the atomic model of molecules, and how do we use the atomic model of molecules to represent, analyze, and co ...
... matter to represent, analyze, and communicate structure and relationships in chemical systems and chemical interactions? B. What is the atomic model of molecules, what evidence do we have for the atomic model of molecules, and how do we use the atomic model of molecules to represent, analyze, and co ...
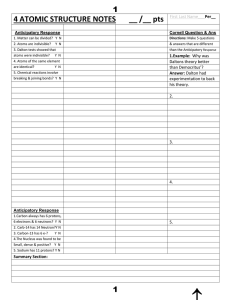
4 ATOMIC STRUCTURE NOTES __ /__ pts
... Part B True-False Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT. ________ 11. The atomic number of an element is the sum of the protons and electrons in an atom of that element. ________ 12. The atomic number of an atom is the total number of protons in ...
... Part B True-False Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT. ________ 11. The atomic number of an element is the sum of the protons and electrons in an atom of that element. ________ 12. The atomic number of an atom is the total number of protons in ...
Chemistry - Textbooks Online
... that students should have a continuous access to these topics. Hence, the knowledge gained in higher secondary first year will help the students to have a continuous access to these topics. The knowledge gained in +1 will help the students to achieve excellence in the path of quest for chemical know ...
... that students should have a continuous access to these topics. Hence, the knowledge gained in higher secondary first year will help the students to have a continuous access to these topics. The knowledge gained in +1 will help the students to achieve excellence in the path of quest for chemical know ...
File - Varsity Field
... Arrhenius – proposed that acids, bases and salts can dissolve in water and forms ions → i.e. electrolytes. – focuses on the formation of hydrogen ions (H+) and hydroxide ions (OH-) in aqueous solutions. • An acid is a substance that, when added to water, increases the concentration of H+ - ions (in ...
... Arrhenius – proposed that acids, bases and salts can dissolve in water and forms ions → i.e. electrolytes. – focuses on the formation of hydrogen ions (H+) and hydroxide ions (OH-) in aqueous solutions. • An acid is a substance that, when added to water, increases the concentration of H+ - ions (in ...
Are you ready for S279?
... those of the noble gases (e.g. helium, neon and argon), which take part in few chemical reactions. Atoms chemically bond with other atoms in order to achieve the stable electronic configuration of a noble gas. This can be achieved by either: (i) transferring electrons (ionic bonding) to form positi ...
... those of the noble gases (e.g. helium, neon and argon), which take part in few chemical reactions. Atoms chemically bond with other atoms in order to achieve the stable electronic configuration of a noble gas. This can be achieved by either: (i) transferring electrons (ionic bonding) to form positi ...
University of Groningen In-situ element analysis from gamma
... Since neutrons are uncharged, their interaction with electrons in matter proceeds via the magnetic moments of the two particles rather than the Coulomb force. The neutrons interact with the nuclei of atoms through the strong nuclear interaction. This hadronic interaction has a very short ranged, whi ...
... Since neutrons are uncharged, their interaction with electrons in matter proceeds via the magnetic moments of the two particles rather than the Coulomb force. The neutrons interact with the nuclei of atoms through the strong nuclear interaction. This hadronic interaction has a very short ranged, whi ...
Atoms – Building Blocks of Matter Notes
... nearest whole number, therefore it is the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus. ...
... nearest whole number, therefore it is the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus. ...
Synthesis of Alum Lab
... NH3 is added to Cu2+: Cu(NH3)42+ cupric tetraamine NH3 is added to Ag+: Ag(NH3)2+ silver diamine Conc. OH- is added to Zn(OH)2: Zn(OH)42+ Fe3+ in thiocyanate (SCN-): Fe(SCN)63- complex Co2+ with chlorine: CoCl42Al oxidized in base: Al(OH)4- ...
... NH3 is added to Cu2+: Cu(NH3)42+ cupric tetraamine NH3 is added to Ag+: Ag(NH3)2+ silver diamine Conc. OH- is added to Zn(OH)2: Zn(OH)42+ Fe3+ in thiocyanate (SCN-): Fe(SCN)63- complex Co2+ with chlorine: CoCl42Al oxidized in base: Al(OH)4- ...
A) 0% B) 20% C) 50% D) 80% E) 100% 1. Naturally occurring boron
... from 50 oC to 90 oC. Which of the following statements is true about the average kinetic energy of the atoms? A) The average kinetic energy does not change. B) The average kinetic energy of the sample increased by a factor of 363/323. C) The average kinetic energy of the sample increased by a facto ...
... from 50 oC to 90 oC. Which of the following statements is true about the average kinetic energy of the atoms? A) The average kinetic energy does not change. B) The average kinetic energy of the sample increased by a factor of 363/323. C) The average kinetic energy of the sample increased by a facto ...
Key - GCC
... 1) Describe the difference between potential energy and kinetic energy. PE: stored energy; KE: energy of motion/vibration/reaction 2) What is the difference between heat and temperature? Temperature is a measure of the kinetic energy of molecules in a substance. Heat is a measurement of the total en ...
... 1) Describe the difference between potential energy and kinetic energy. PE: stored energy; KE: energy of motion/vibration/reaction 2) What is the difference between heat and temperature? Temperature is a measure of the kinetic energy of molecules in a substance. Heat is a measurement of the total en ...
Review History of the Atomic Model
... Dalton devised the first modern atomic model. Which one of the following characteristics is NOT part of Dalton's atomic model? a. Atoms of different elements are different. b. All atoms of the same element are identical. c. Atoms combine to form compounds. d. Atoms consist of positive particles and ...
... Dalton devised the first modern atomic model. Which one of the following characteristics is NOT part of Dalton's atomic model? a. Atoms of different elements are different. b. All atoms of the same element are identical. c. Atoms combine to form compounds. d. Atoms consist of positive particles and ...
School of Chemistry and Physics Westville Campus, Durban
... electrons would there be in an atom of iron? A ...
... electrons would there be in an atom of iron? A ...
practice final examination
... 10. Answer true or false for each of the following questions below (circle your choice): a) ...
... 10. Answer true or false for each of the following questions below (circle your choice): a) ...
chapter 4_Bonding and structure
... – Sulfur and oxygen are both in group VIA, and so each atom has 6 valence electrons. The total number of electrons is 24 (6 from the one S atom and 18 from the three O atoms). ...
... – Sulfur and oxygen are both in group VIA, and so each atom has 6 valence electrons. The total number of electrons is 24 (6 from the one S atom and 18 from the three O atoms). ...
Hein and Arena - faculty at Chemeketa
... Surrounding the atomic nucleus are electrons. The name electron comes from the Greek word for amber, a brownish-yellow fossil resin studied by the early Greeks. They found that when amber was rubbed by a piece of cloth, it attracted such things as bits of straw. This phenomenon, known as the amber ...
... Surrounding the atomic nucleus are electrons. The name electron comes from the Greek word for amber, a brownish-yellow fossil resin studied by the early Greeks. They found that when amber was rubbed by a piece of cloth, it attracted such things as bits of straw. This phenomenon, known as the amber ...
PHYSICAL SETTING CHEMISTRY
... Directions (51–65): Record your answers in the spaces provided in your answer booklet. Some questions may require the use of the 2011 Edition Reference Tables for Physical Setting/Chemistry. 51 Draw a Lewis electron-dot diagram for a chloride ion, Cl⫺. [1] Base your answers to questions 52 and 53 on ...
... Directions (51–65): Record your answers in the spaces provided in your answer booklet. Some questions may require the use of the 2011 Edition Reference Tables for Physical Setting/Chemistry. 51 Draw a Lewis electron-dot diagram for a chloride ion, Cl⫺. [1] Base your answers to questions 52 and 53 on ...
Year Review Booklet (optional)
... Bohr came up with an atomic model to explain the spectrum of ______________________. He said that the atom has certain _______________ levels which are allowed. These levels corresponded to ____________________ in which electrons move. If an electron absorbs a certain photon of energy, it will jump ...
... Bohr came up with an atomic model to explain the spectrum of ______________________. He said that the atom has certain _______________ levels which are allowed. These levels corresponded to ____________________ in which electrons move. If an electron absorbs a certain photon of energy, it will jump ...