
Chapter 4
... that the particles in the beam had a negative charge because they were attracted to the positive plate. He hypothesized that the particles came from inside atoms. He had two pieces of evidence to support his hypothesis. No matter what metal Thomson used for the disk, the particles produced were iden ...
... that the particles in the beam had a negative charge because they were attracted to the positive plate. He hypothesized that the particles came from inside atoms. He had two pieces of evidence to support his hypothesis. No matter what metal Thomson used for the disk, the particles produced were iden ...
Types of Chemical Reactions
... in the fume hoods. These chemicals are toxic and will harm the environment if not disposed of properly. • Do not eat, drink, or apply the chemicals to skin. Many of these chemicals are highly corrosive and in addition to being toxic, they will burn your skin and muscle tissue. Ouch! • If any of the ...
... in the fume hoods. These chemicals are toxic and will harm the environment if not disposed of properly. • Do not eat, drink, or apply the chemicals to skin. Many of these chemicals are highly corrosive and in addition to being toxic, they will burn your skin and muscle tissue. Ouch! • If any of the ...
Equilibrium Constant - Faculty Server Contact
... Activity coefficient (g): measure of how a specific real system deviates from some reference system that is taken to be ideal. In an ideal solution, activity would equal concentration. The departure from ideal behavior is caused mainly by: •Electrostatic interactions between charged ions. •The form ...
... Activity coefficient (g): measure of how a specific real system deviates from some reference system that is taken to be ideal. In an ideal solution, activity would equal concentration. The departure from ideal behavior is caused mainly by: •Electrostatic interactions between charged ions. •The form ...
Chapter 12 - Bruder Chemistry
... Atoms first absorb energy and then lose energy as they emit light Each line in the emission spectrum corresponds to one exact frequency of light being given off or emitted by an atom. The light emitted by an electron moving from a higher to lower energy level has a frequency directly proportional to ...
... Atoms first absorb energy and then lose energy as they emit light Each line in the emission spectrum corresponds to one exact frequency of light being given off or emitted by an atom. The light emitted by an electron moving from a higher to lower energy level has a frequency directly proportional to ...
Chapter 3 Mass Relations in Chemistry: Stoichiometry Outline
... 1. Calculate the amount of product that will form if the first reactant were completely consumed. 2. Repeat the calculation for the second reactant in the same way. 3. Choose the smaller amount of product and relate it to the reactant that produced it. This is the limiting reactant and the resulting ...
... 1. Calculate the amount of product that will form if the first reactant were completely consumed. 2. Repeat the calculation for the second reactant in the same way. 3. Choose the smaller amount of product and relate it to the reactant that produced it. This is the limiting reactant and the resulting ...
chapter3
... 1. Calculate the amount of product that will form if the first reactant were completely consumed. 2. Repeat the calculation for the second reactant in the same way. 3. Choose the smaller amount of product and relate it to the reactant that produced it. This is the limiting reactant and the resulting ...
... 1. Calculate the amount of product that will form if the first reactant were completely consumed. 2. Repeat the calculation for the second reactant in the same way. 3. Choose the smaller amount of product and relate it to the reactant that produced it. This is the limiting reactant and the resulting ...
Hybridization and St..
... Hybridization also occurs in compounds of beryllium. The electron configuration if Be is 1s22s2. It would appear to have no half-filled orbitals with which to form covalent bonds. ...
... Hybridization also occurs in compounds of beryllium. The electron configuration if Be is 1s22s2. It would appear to have no half-filled orbitals with which to form covalent bonds. ...
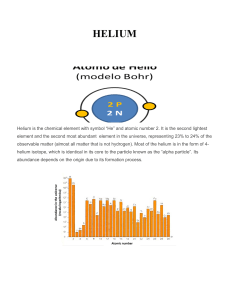
HELIUM - IDC
... Helium is believed to be formed during primordial nucleosynthesis, at 3 minutes and 45 seconds after the start of the universe when the universe expansion cooled enough to 1 billion of ° K and finally the 2hydrogen isotopes could be formed initiating a rapid sequence of nuclear reactions into 3-Heli ...
... Helium is believed to be formed during primordial nucleosynthesis, at 3 minutes and 45 seconds after the start of the universe when the universe expansion cooled enough to 1 billion of ° K and finally the 2hydrogen isotopes could be formed initiating a rapid sequence of nuclear reactions into 3-Heli ...
IE EA
... bond dissociation energies of the N-H and P-H bonds and the electron affinities of NH2 and PH2 are needed. However, if one assumes that the differences in these quantities are about the same as the differences in the average bond dissociation energies (386 kJ mol-1 for NH3 and 322 kJ mol-1 for PH3) ...
... bond dissociation energies of the N-H and P-H bonds and the electron affinities of NH2 and PH2 are needed. However, if one assumes that the differences in these quantities are about the same as the differences in the average bond dissociation energies (386 kJ mol-1 for NH3 and 322 kJ mol-1 for PH3) ...
North Carolina Test of Chemistry RELEASED
... In a flexible container, 15.9 L of gas is under 589 kPa of pressure at a temperature of 56.5°C. If the pressure and temperature change to STP, what is the new volume? ...
... In a flexible container, 15.9 L of gas is under 589 kPa of pressure at a temperature of 56.5°C. If the pressure and temperature change to STP, what is the new volume? ...
Part II - KFUPM Faculty List
... 4Fe (s) + 3O2(g) 2Fe2O3(s) The ΔHf for Fe2O3 (s) is ‒ 826 kJ/mol, and S (J/K∙mol) for Fe2O3(s), Fe(s) and O2(g) are 90, 27 and 205, respectively. Calculate K for this reaction at 25C. ...
... 4Fe (s) + 3O2(g) 2Fe2O3(s) The ΔHf for Fe2O3 (s) is ‒ 826 kJ/mol, and S (J/K∙mol) for Fe2O3(s), Fe(s) and O2(g) are 90, 27 and 205, respectively. Calculate K for this reaction at 25C. ...
Inorganic Chemistry/Chemical Bonding/Lewis Dot Structures
... covalently-bonded molecule, as well as coordination compounds. The Lewis structure was named after Gilbert N. Lewis, who introduced it in his 1916 article The Atom and the Molecule [3] . They are similar to electron dot diagrams in that the valence electrons in lone pairs are represented as dots, bu ...
... covalently-bonded molecule, as well as coordination compounds. The Lewis structure was named after Gilbert N. Lewis, who introduced it in his 1916 article The Atom and the Molecule [3] . They are similar to electron dot diagrams in that the valence electrons in lone pairs are represented as dots, bu ...
File
... b) Nucleus: the dense centre region of an atom. It contains the protons and neutrons (if there are any). c) Proton: a sub-atomic particle that is found it nucleus of an atom. Protons have a charge of 1+ and a mass of 1 amu. d) Neutron: a sub-atomic particle that is found in the nucleus of an atom. N ...
... b) Nucleus: the dense centre region of an atom. It contains the protons and neutrons (if there are any). c) Proton: a sub-atomic particle that is found it nucleus of an atom. Protons have a charge of 1+ and a mass of 1 amu. d) Neutron: a sub-atomic particle that is found in the nucleus of an atom. N ...
Unit - III - E
... Many bonding situations can be described with more than one valid Lewis Dot Structure (for example, ozone, O3). In an LDS diagram of O3, the center atom will have a single bond with one atom and a double bond with the other. The LDS diagram cannot tell us which atom has the double bond; the first an ...
... Many bonding situations can be described with more than one valid Lewis Dot Structure (for example, ozone, O3). In an LDS diagram of O3, the center atom will have a single bond with one atom and a double bond with the other. The LDS diagram cannot tell us which atom has the double bond; the first an ...
AP Chemistry Summer Assignment
... foundation in chemistry and insure all students are on a relatively even plane. It will be important for everyone to come to class the first day prepared. While I review, extensive remediation is not an option as we work towards our goal of being 100% prepared for the AP Exam in early May 2016. Ther ...
... foundation in chemistry and insure all students are on a relatively even plane. It will be important for everyone to come to class the first day prepared. While I review, extensive remediation is not an option as we work towards our goal of being 100% prepared for the AP Exam in early May 2016. Ther ...
examples of chemical and physical reactions.
... called _______________. The substances that are present at the end of the reaction are called the _____________. Example: If we take a paper, the reactant is the paper. If we burn the paper the reaction is burning. At the end of the reaction i.e. when the paper completely burns, the product is ash. ...
... called _______________. The substances that are present at the end of the reaction are called the _____________. Example: If we take a paper, the reactant is the paper. If we burn the paper the reaction is burning. At the end of the reaction i.e. when the paper completely burns, the product is ash. ...
Homework Booklet [4,S]
... Calculate the formula for magnesium oxide from Lucy’s results. Calculate the relative formula mass (RFM) of magnesium oxide with this formula. Calculate the % of magnesium in the magnesium oxide. Peter’s results do not give the correct answer for the formula. Suggest some possible experimental reaso ...
... Calculate the formula for magnesium oxide from Lucy’s results. Calculate the relative formula mass (RFM) of magnesium oxide with this formula. Calculate the % of magnesium in the magnesium oxide. Peter’s results do not give the correct answer for the formula. Suggest some possible experimental reaso ...
No Slide Title
... concentration is added gradually added to another solution of unknown concentration until the chemical reaction between the two solutions is complete. ________________ – the point at which the reaction is complete _______________ – substance that changes color at (or near) the equivalence point ...
... concentration is added gradually added to another solution of unknown concentration until the chemical reaction between the two solutions is complete. ________________ – the point at which the reaction is complete _______________ – substance that changes color at (or near) the equivalence point ...
File - Mc Guckin Science
... b) Nucleus: the dense centre region of an atom. It contains the protons and neutrons (if there are any). c) Proton: a sub-atomic particle that is found it nucleus of an atom. Protons have a charge of 1+ and a mass of 1 amu. d) Neutron: a sub-atomic particle that is found in the nucleus of an atom. N ...
... b) Nucleus: the dense centre region of an atom. It contains the protons and neutrons (if there are any). c) Proton: a sub-atomic particle that is found it nucleus of an atom. Protons have a charge of 1+ and a mass of 1 amu. d) Neutron: a sub-atomic particle that is found in the nucleus of an atom. N ...
Chapter Five
... { If I have a dozen atoms, I have 12 atoms by definition. The mole (mol) is a very important unit of quantity in chemistry. It is used to count large numbers of atoms, molecules, and other submicroscopic pieces of matter. If you have 1 mole of something, you have 6.02 × 1023 of it. ...
... { If I have a dozen atoms, I have 12 atoms by definition. The mole (mol) is a very important unit of quantity in chemistry. It is used to count large numbers of atoms, molecules, and other submicroscopic pieces of matter. If you have 1 mole of something, you have 6.02 × 1023 of it. ...
Atoms—Basic Units of Matter
... Would it surprise you to learn that the chair you are sitting on and the air you breathe are made up of the same thing? The world you live in is made of matter. Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. Things you can see, such as your chair, and things you can’t see, such as air, are mat ...
... Would it surprise you to learn that the chair you are sitting on and the air you breathe are made up of the same thing? The world you live in is made of matter. Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. Things you can see, such as your chair, and things you can’t see, such as air, are mat ...
TEST-Atomic Structure
... ____ 13. Which statement about subatomic particles is NOT true? a. Protons and neutrons have almost the same mass. b. Protons and electrons have opposite charges. c. Unlike protons and electrons, neutrons have no charge. d. Protons and neutrons have the same charge. ____ 14. Which statement about s ...
... ____ 13. Which statement about subatomic particles is NOT true? a. Protons and neutrons have almost the same mass. b. Protons and electrons have opposite charges. c. Unlike protons and electrons, neutrons have no charge. d. Protons and neutrons have the same charge. ____ 14. Which statement about s ...















![Homework Booklet [4,S]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/010355871_1-63c750e3d1b58eaaebbb3f5d45651c44-300x300.png)






