Lecture 19: Female External Genitalia and Breast Intro to
... The round greater vestibular (Bartholin) glands lie on either side of the vaginal orifice, posterior to the bulbs of the vestibule (also within the superficial perineal pouch) ~0.5 cm in diameter Along with cervical glands, the greater vestibular glands secrete much of the mucus necessary for ...
... The round greater vestibular (Bartholin) glands lie on either side of the vaginal orifice, posterior to the bulbs of the vestibule (also within the superficial perineal pouch) ~0.5 cm in diameter Along with cervical glands, the greater vestibular glands secrete much of the mucus necessary for ...
Pelvic Floor Muscle Training In Males: Practical
... The Massachusetts Male Aging Study23 demonstrated that ED is present in about 40% of men by age 40 with an increase in prevalence by approximately 10% for each decade thereafter. Although there are many potential causes of ED, the common denominator is insufficient blood flow to fill the corpora, o ...
... The Massachusetts Male Aging Study23 demonstrated that ED is present in about 40% of men by age 40 with an increase in prevalence by approximately 10% for each decade thereafter. Although there are many potential causes of ED, the common denominator is insufficient blood flow to fill the corpora, o ...
ch_16_lecture_presentation
... Divided sac of skin outside the abdomen that houses the testes Maintains testes at 3°C lower than normal body temperature to protect sperm viability ...
... Divided sac of skin outside the abdomen that houses the testes Maintains testes at 3°C lower than normal body temperature to protect sperm viability ...
Chapter 7 Male Reproductive System
... vas deferens, ductus deferens, or seminal duct: duct carrying the sperm from the epididymis to the urethra. (The urethra also connects with the urinary bladder and carries urine outside the body. A circular muscle constricts during intercourse to prevent urination.) seminal vesicles: two main glands ...
... vas deferens, ductus deferens, or seminal duct: duct carrying the sperm from the epididymis to the urethra. (The urethra also connects with the urinary bladder and carries urine outside the body. A circular muscle constricts during intercourse to prevent urination.) seminal vesicles: two main glands ...
File
... vas deferens, ductus deferens, or seminal duct: duct carrying the sperm from the epididymis to the urethra. (The urethra also connects with the urinary bladder and carries urine outside the body. A circular muscle constricts during intercourse to prevent urination.) seminal vesicles: two main glands ...
... vas deferens, ductus deferens, or seminal duct: duct carrying the sperm from the epididymis to the urethra. (The urethra also connects with the urinary bladder and carries urine outside the body. A circular muscle constricts during intercourse to prevent urination.) seminal vesicles: two main glands ...
Urogenital System
... The medullary sex cord cells form the testis cords that contain Sertoli cells Regions of the testis cords that contain germ cells will canalize and form the seminiferous tubules of the mature testis. The inner portion of the testis cords form the Rete testis The Rete testis connects with the efferen ...
... The medullary sex cord cells form the testis cords that contain Sertoli cells Regions of the testis cords that contain germ cells will canalize and form the seminiferous tubules of the mature testis. The inner portion of the testis cords form the Rete testis The Rete testis connects with the efferen ...
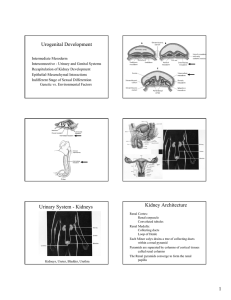
Urogenital Development Urinary System
... Germ cells are required for invasion of supporting cells Supporting cells are required for survival of germ cells Genital ridge enlarges and forms a cortex and medullathese regions have different fates in males and females After 6 weeks- males and females diverge- prior to this is called the Indiffe ...
... Germ cells are required for invasion of supporting cells Supporting cells are required for survival of germ cells Genital ridge enlarges and forms a cortex and medullathese regions have different fates in males and females After 6 weeks- males and females diverge- prior to this is called the Indiffe ...
Lecture 7: Urogenital System
... Slide 27: Illustrations showing differentiation of the ducts in females Main points: 1. In females, there is no testosterone, so the mesonephric duct and tubules degenerate. Remnants of the tubules form the epoophoron and paroophoron, and a small remnant of the duct near the vagina forms Gartner’s c ...
... Slide 27: Illustrations showing differentiation of the ducts in females Main points: 1. In females, there is no testosterone, so the mesonephric duct and tubules degenerate. Remnants of the tubules form the epoophoron and paroophoron, and a small remnant of the duct near the vagina forms Gartner’s c ...
SURGICAL EMERGENCIES OF THE URINARY TRACT Gary W
... The wound is debrided and reapposed with simple interrupted of 4-0 absorbable suture. Following the reanastomosis a urinary catheter is placed for five to seven days to serve as a stent. If prostatic or pelvic urethra damage are irreparable, antipubic urethrostomy may be performed as a salvage proce ...
... The wound is debrided and reapposed with simple interrupted of 4-0 absorbable suture. Following the reanastomosis a urinary catheter is placed for five to seven days to serve as a stent. If prostatic or pelvic urethra damage are irreparable, antipubic urethrostomy may be performed as a salvage proce ...
Urolithiasis - Pennsylvania Veterinary Medical Association
... Percutaneous tube cystostomy is primarily used as a cost-saving procedure, because it usually eliminates the need for general anesthesia, or it can be performed in situations where general anesthesia is not available, or as a time-saving procedure compared with other surgical interventions.11,16–19 ...
... Percutaneous tube cystostomy is primarily used as a cost-saving procedure, because it usually eliminates the need for general anesthesia, or it can be performed in situations where general anesthesia is not available, or as a time-saving procedure compared with other surgical interventions.11,16–19 ...
Pelvis + Perineum
... Consists of three parts – the pubococcygeus, the puborectalis and the iliococcygeus. Collectively they run from the body of the pubis, the tendinous arch of the obturator fascia and the ischial spine TO the perineal body, the coccyx, the anococcygeal ligament, the walls of the prostate or vagina, th ...
... Consists of three parts – the pubococcygeus, the puborectalis and the iliococcygeus. Collectively they run from the body of the pubis, the tendinous arch of the obturator fascia and the ischial spine TO the perineal body, the coccyx, the anococcygeal ligament, the walls of the prostate or vagina, th ...
PDF File (agradoc474 156 Kb)
... exclude other important diseases that may cause similar symptoms such as prostate or bladder cancer (Nickel et al., ...
... exclude other important diseases that may cause similar symptoms such as prostate or bladder cancer (Nickel et al., ...
Fundamentals of Anatomy and Physiology, Second Edition
... Mixture of sperm cells and secretions Provides energy to the sperm via fructose Neutralizes acidity of vagina Acts as a transport medium Contains enzymes that activate sperm Average volume is 2.5 to 6 mL Seminalplasmin: destroys certain bacteria © 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning ...
... Mixture of sperm cells and secretions Provides energy to the sperm via fructose Neutralizes acidity of vagina Acts as a transport medium Contains enzymes that activate sperm Average volume is 2.5 to 6 mL Seminalplasmin: destroys certain bacteria © 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning ...
1. The part of the uterine wall which is not shed during menstruation
... mesovarium. The mesovarium, along with the mesometrium and the mesosalpinx, creates the broad ligament. Because the ovary is completly encased in peritoneum, it would be outlined on a CT with intraperitoneal contrast material. The prostate, seminal vesicles and vagina are located below the rectovesi ...
... mesovarium. The mesovarium, along with the mesometrium and the mesosalpinx, creates the broad ligament. Because the ovary is completly encased in peritoneum, it would be outlined on a CT with intraperitoneal contrast material. The prostate, seminal vesicles and vagina are located below the rectovesi ...
Guide for Use - Hollister Incorporated
... brain to tell the urethral sphincter muscle to relax and the bladder to contract. 4 Urine flows down the urethra – the natural tube through which urine exits the bladder, and out of the body. ...
... brain to tell the urethral sphincter muscle to relax and the bladder to contract. 4 Urine flows down the urethra – the natural tube through which urine exits the bladder, and out of the body. ...
prostrate enlargement and homeopathy
... Is your sleep perturbed due to frequent bathroom trips at night? Do you feel that your bladder does not empty fully, or you have to exert while urinating due to a weak urine flow? These are the warning signs of an ongoing Prostate enlargement. Prostate is a small gland in the male reproductive syste ...
... Is your sleep perturbed due to frequent bathroom trips at night? Do you feel that your bladder does not empty fully, or you have to exert while urinating due to a weak urine flow? These are the warning signs of an ongoing Prostate enlargement. Prostate is a small gland in the male reproductive syste ...
eprint_4_2366_991
... epithelium is closely adherent and which extends as a sheath around the lower ureters and into the proximal urethra. • Around the male bladder neck is the smooth muscle internal sphincter innervated by adrenergic fibres, which prevents retrograde ejaculation. • The distal urethral sphincter is a hor ...
... epithelium is closely adherent and which extends as a sheath around the lower ureters and into the proximal urethra. • Around the male bladder neck is the smooth muscle internal sphincter innervated by adrenergic fibres, which prevents retrograde ejaculation. • The distal urethral sphincter is a hor ...
Embryology Relevant to Ultrasound Imaging of the Male Genitalia
... indifferent external genitalia occurs under the influence of testosterone produced by the interstitial cells of the fetal testis [14−16]. The tubercle becomes the future phallus and glans. The terminal part of the phallus destined to be the glans becomes solid. The grove between the urogenital folds ...
... indifferent external genitalia occurs under the influence of testosterone produced by the interstitial cells of the fetal testis [14−16]. The tubercle becomes the future phallus and glans. The terminal part of the phallus destined to be the glans becomes solid. The grove between the urogenital folds ...
Urinary system
... cm) on the left, 3.07 cm (SD 1.17 cm) on the right. Perforation of the fascia of obturator internus muscle occurred in 46.4%. In fresh frozen bodies, results were fundamentally similar. Injury of variable vessels can occur. CONCLUSION: There is a minimal risk of injury to the obturator bundle during ...
... cm) on the left, 3.07 cm (SD 1.17 cm) on the right. Perforation of the fascia of obturator internus muscle occurred in 46.4%. In fresh frozen bodies, results were fundamentally similar. Injury of variable vessels can occur. CONCLUSION: There is a minimal risk of injury to the obturator bundle during ...
Human Disease Ch 11
... Vas deferens – store sperm for up to several weeks – enters the abdominal cavity, then into prostate for ejaculation through urethra Scrotum- sac containing testis, epididymis Testis – store the hormones, and future sperm which when ready to mature will enter seminiferous tubules ...
... Vas deferens – store sperm for up to several weeks – enters the abdominal cavity, then into prostate for ejaculation through urethra Scrotum- sac containing testis, epididymis Testis – store the hormones, and future sperm which when ready to mature will enter seminiferous tubules ...
The Urinary Ureters, Bladder and Urethra
... the kidneys to the bladder. Beginning at the level of the second lumbar vertebra, the location of the ureters is retroperitoneal. Each ureter runs inferiorly and enters the posterolateral wall of the urinary bladder. This angle of entry is important, because it helps prevent urine from flowing back ...
... the kidneys to the bladder. Beginning at the level of the second lumbar vertebra, the location of the ureters is retroperitoneal. Each ureter runs inferiorly and enters the posterolateral wall of the urinary bladder. This angle of entry is important, because it helps prevent urine from flowing back ...
Sample
... sperm cells cannot travel from the epididymis up either vas deferens, they will never be ejaculated and will never be able to fertilize an ovum. 25. _______ is primarily produced by the seminal vesicles and prostate gland. a. Testosterone b. Estrogen ...
... sperm cells cannot travel from the epididymis up either vas deferens, they will never be ejaculated and will never be able to fertilize an ovum. 25. _______ is primarily produced by the seminal vesicles and prostate gland. a. Testosterone b. Estrogen ...
Human penis

The human penis is an external male intromittent organ that additionally serves as the urinal duct. The main parts are the root (radix); the body (corpus); and the epithelium of the penis including the shaft skin and the foreskin covering the glans penis. The body of the penis is made up of three columns of tissue: two corpora cavernosa on the dorsal side and corpus spongiosum between them on the ventral side. The human male urethra passes through the prostate gland, where it is joined by the ejaculatory duct, and then through the penis. The urethra traverses the corpus spongiosum, and its opening, the meatus (/miːˈeɪtəs/), lies on the tip of the glans penis. It is a passage both for urination and ejaculation of semen.The penis is homologous to the clitoris. An erection is the stiffening and rising of the penis, which occurs during sexual arousal, though it can also happen in non-sexual situations. The most common form of genital alteration is circumcision, removal of part or all of the foreskin for various cultural, religious and, more rarely, medical reasons. There is controversy surrounding circumcision.While results vary across studies, the consensus is that the average erect human penis is approximately 12.9–15 cm (5.1–5.9 in) in length with 95% of adult males falling within the interval 10.7–19.1 cm (4.2–7.5 in). Neither age nor size of the flaccid penis accurately predicts erectile length.