special - Carl Zeiss
... ZERODUR glass ceramics that had been specially developed by Schott for astronomy – a classic example of a successful transfer of technology from basic scientific research. The PMAS has been available to German and Spanish astronomers since the fall of 2002 as a generally accessible user instrument b ...
... ZERODUR glass ceramics that had been specially developed by Schott for astronomy – a classic example of a successful transfer of technology from basic scientific research. The PMAS has been available to German and Spanish astronomers since the fall of 2002 as a generally accessible user instrument b ...
Starry Night Companion - Starry Night Education
... is 5°. The sides of the Great Square of Pegasus average 15° in length. The distance from one end of the W of Cassiopeia to the other is 13°. The distance from Betelgeuse to Rigel in Orion is 19°, and the length of Orion’s belt is just under 3°. Your hand is a portable angle measurer. The width of yo ...
... is 5°. The sides of the Great Square of Pegasus average 15° in length. The distance from one end of the W of Cassiopeia to the other is 13°. The distance from Betelgeuse to Rigel in Orion is 19°, and the length of Orion’s belt is just under 3°. Your hand is a portable angle measurer. The width of yo ...
Estimation of the lunar reflectance by ground-based observation
... for our telescope. The extra-atmospheric intensity (DN ) of Vega was calculated using the optical depth of the atmosphere, τ , and Vega observations, and is shown in Fig. 4. The range of DN0 of Vega was defined by the range of τ (τmin ∼ τmax ) and the range of ±1σ of ln DNobs using the Lambert-Beer ...
... for our telescope. The extra-atmospheric intensity (DN ) of Vega was calculated using the optical depth of the atmosphere, τ , and Vega observations, and is shown in Fig. 4. The range of DN0 of Vega was defined by the range of τ (τmin ∼ τmax ) and the range of ±1σ of ln DNobs using the Lambert-Beer ...
1. The catalogue structure
... not correspond to zodiacal constellations, which is why the stars that pertain to a single zodiacal constellation can wind up in different zodiacal signs. The canonical version of the Almagest catalogue contained in the work of Peters and Knobel ([1339]) is presented as a table that consists of six ...
... not correspond to zodiacal constellations, which is why the stars that pertain to a single zodiacal constellation can wind up in different zodiacal signs. The canonical version of the Almagest catalogue contained in the work of Peters and Knobel ([1339]) is presented as a table that consists of six ...
Calculations of tithis
... to 10,000 AD. We then test this formulation against the predicted tithis (full Moon) of lunar eclipses and show that the formulation gives accurate tithis from at least 2,000 BC to 3,000 AD. 1. Introduction The ancient Indian calendar dates back several thousand years and the relevant literature has ...
... to 10,000 AD. We then test this formulation against the predicted tithis (full Moon) of lunar eclipses and show that the formulation gives accurate tithis from at least 2,000 BC to 3,000 AD. 1. Introduction The ancient Indian calendar dates back several thousand years and the relevant literature has ...
lecture03_2013_sky_phases_eclipses
... • What is the cause of the seasons on Earth? • As the Earth orbits the sun, the tilt of the axis causes different portions of the Earth to receive more or less direct sunlight at different times of year. The two hemispheres have opposite seasons. The summer solstice is the time when the northern hem ...
... • What is the cause of the seasons on Earth? • As the Earth orbits the sun, the tilt of the axis causes different portions of the Earth to receive more or less direct sunlight at different times of year. The two hemispheres have opposite seasons. The summer solstice is the time when the northern hem ...
The Next Great Exoplanet Hunt Please share
... probability for transits is equal to the stellar diameter divided by the orbital diameter, which is only 0.1% for an Earth-like orbit around a Sun-like star. For this reason, a meaningful transit survey must include tens of thousands of stars, or more. Because faint stars far outnumber bright ones i ...
... probability for transits is equal to the stellar diameter divided by the orbital diameter, which is only 0.1% for an Earth-like orbit around a Sun-like star. For this reason, a meaningful transit survey must include tens of thousands of stars, or more. Because faint stars far outnumber bright ones i ...
THE DAWN OF X-RAY ASTRONOMY
... termined that Sco X–1 could not have the thermal spectrum that would be expected from neutron stars (Giacconi et al., 1965),6 which implied that an optical counterpart should have magnitude 13. In a first rocket flight to measure the angular size of the source it was found to be less than 7 arc sec ...
... termined that Sco X–1 could not have the thermal spectrum that would be expected from neutron stars (Giacconi et al., 1965),6 which implied that an optical counterpart should have magnitude 13. In a first rocket flight to measure the angular size of the source it was found to be less than 7 arc sec ...
Astronomical signs of Korean tombs
... relics. For a long time, Korean saw heavens on the observatories and recorded amount astronomical phenomena in their history books such as Samguksagi (三國史記), Goryeosa (高麗史), Joseonwangjosillok (朝鮮王朝實錄) and so forth. These history books contain various astronomical records such as solar and lunar ecl ...
... relics. For a long time, Korean saw heavens on the observatories and recorded amount astronomical phenomena in their history books such as Samguksagi (三國史記), Goryeosa (高麗史), Joseonwangjosillok (朝鮮王朝實錄) and so forth. These history books contain various astronomical records such as solar and lunar ecl ...
Epsilon Aurigae: a rare stellar eclipse - Project VS
... the orbit crosses the F-star just above the star's middle. (Source used: http://www.citizensky.org/book/export/html/1033) To hold the disk together, astronomers believe there must be at least one star at its center, yet none is visible. Modern theory estimates disk's diameter of ~8 AU, made of dusty ...
... the orbit crosses the F-star just above the star's middle. (Source used: http://www.citizensky.org/book/export/html/1033) To hold the disk together, astronomers believe there must be at least one star at its center, yet none is visible. Modern theory estimates disk's diameter of ~8 AU, made of dusty ...
Set 2 Astronomy questions
... At the Sun’s distance of 8 kiloparsecs from the Galactic center, how many years would it take for material here to complete one rotational circuit? ANSWER: 225 MILLION Need a formula. TOSS-UP 4) ASTRONOMY Short Answer Containing roughly ten times more gas than Earth’s, why does Titan’s atmosphere ex ...
... At the Sun’s distance of 8 kiloparsecs from the Galactic center, how many years would it take for material here to complete one rotational circuit? ANSWER: 225 MILLION Need a formula. TOSS-UP 4) ASTRONOMY Short Answer Containing roughly ten times more gas than Earth’s, why does Titan’s atmosphere ex ...
Starwalk Manual En
... If you have an iPhone 3GS/4/4S/5/5s/5c, iPad or iPad mini, tilt your device and the Star Spotter function will be activated. Star Walk™ uses the digital compass to learn which way you are looking. A live representation of what you see in the sky will appear on your display and the sky will start fol ...
... If you have an iPhone 3GS/4/4S/5/5s/5c, iPad or iPad mini, tilt your device and the Star Spotter function will be activated. Star Walk™ uses the digital compass to learn which way you are looking. A live representation of what you see in the sky will appear on your display and the sky will start fol ...
Stellar Census
... The Lives of Stars Stars live for a very long time, up to 100 million years or more No humans can possibly observe a star this long! How can we learn about the stages in a star’s life? We can perform a celestial census, getting a snapshot of many stars at different stages of their life We can then ...
... The Lives of Stars Stars live for a very long time, up to 100 million years or more No humans can possibly observe a star this long! How can we learn about the stages in a star’s life? We can perform a celestial census, getting a snapshot of many stars at different stages of their life We can then ...
1 Distance: A History of Parallax and Brief Introduction to Standard
... four spheres for each the five planets, three spheres each for the sun and moon, and one sphere for the fixed stars [Hoskin 36]. The spheres were tilted at various angles and interlocked in their rotation. Eudoxus has taken a simple model and transformed it into a clocklike machine in order to more ...
... four spheres for each the five planets, three spheres each for the sun and moon, and one sphere for the fixed stars [Hoskin 36]. The spheres were tilted at various angles and interlocked in their rotation. Eudoxus has taken a simple model and transformed it into a clocklike machine in order to more ...
August 2014 Saguaro Skies
... why not take a few pictures and put yourself on the presentation list at an upcoming meeting. Even little things, such as the ingenious torque measurement device that Paul Lind showed us last year, are worth sharing. Or, perhaps you have images or results from a prior observing project which we have ...
... why not take a few pictures and put yourself on the presentation list at an upcoming meeting. Even little things, such as the ingenious torque measurement device that Paul Lind showed us last year, are worth sharing. Or, perhaps you have images or results from a prior observing project which we have ...
Media Center Jeopardy
... A stage in the life cycle of many stars when they increase in size and begin the conversion of helium to carbon. ...
... A stage in the life cycle of many stars when they increase in size and begin the conversion of helium to carbon. ...
A History of Star Catalogues - The Albuquerque Astronomical Society
... His book “Astronomiae instauratae progymnasmata” (Introduction to the New Astronomy) contains a catalogue of 777 stars. (Watbooks-Brahe 2003) They are measured with far greater accuracy than any previous measurements. The book was printed between 1588 and 1598 by Tycho’s private press on the Island ...
... His book “Astronomiae instauratae progymnasmata” (Introduction to the New Astronomy) contains a catalogue of 777 stars. (Watbooks-Brahe 2003) They are measured with far greater accuracy than any previous measurements. The book was printed between 1588 and 1598 by Tycho’s private press on the Island ...
FIELD ASTRONOMY
... observations and to solve the PZS triangle, the surveyor must have one other factor. He must know the precise time of the observation so that he can fix the position of the terrestrial or horizon system of coordinates in relation to the celestial coordinate system. In the field of practical astrono ...
... observations and to solve the PZS triangle, the surveyor must have one other factor. He must know the precise time of the observation so that he can fix the position of the terrestrial or horizon system of coordinates in relation to the celestial coordinate system. In the field of practical astrono ...
Project 1. CCD image analysis
... of which is sensitive to light. The light sensitive face is rectangular in shape and subdivided into a grid of discrete rectangular areas (picture elements or pixels) each about 10‐30 micron across. The CCD is placed in the focal plane of a telescope so the light‐sensitive surface ...
... of which is sensitive to light. The light sensitive face is rectangular in shape and subdivided into a grid of discrete rectangular areas (picture elements or pixels) each about 10‐30 micron across. The CCD is placed in the focal plane of a telescope so the light‐sensitive surface ...
moon phases and eclipses - Morehead Planetarium and Science
... “lunar” refer to? (The Moon.) [Note: Young children often do not know what “solar” and “lunar” mean.] 27. Tell everyone they’ll use their moon balls to find out why eclipses happen. 28. Ask everyone to make a lunar eclipse – when the Moon passes through Earth’s shadow. They should experiment with ...
... “lunar” refer to? (The Moon.) [Note: Young children often do not know what “solar” and “lunar” mean.] 27. Tell everyone they’ll use their moon balls to find out why eclipses happen. 28. Ask everyone to make a lunar eclipse – when the Moon passes through Earth’s shadow. They should experiment with ...
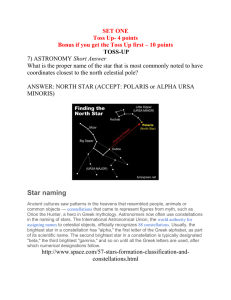
TOSS-UP 7) ASTRONOMY Short Answer
... Ancient cultures saw patterns in the heavens that resembled people, animals or common objects — constellations that came to represent figures from myth, such as Orion the Hunter, a hero in Greek mythology. Astronomers now often use constellations in the naming of stars. The International Astronomica ...
... Ancient cultures saw patterns in the heavens that resembled people, animals or common objects — constellations that came to represent figures from myth, such as Orion the Hunter, a hero in Greek mythology. Astronomers now often use constellations in the naming of stars. The International Astronomica ...
Chinese astronomy

Astronomy in China has a very long history, with historians indicating that the Chinese were the most persistent and accurate observers of celestial phenomena anywhere in the world before the Arabs. Star names later categorized in the twenty-eight mansions have been found on oracle bones unearthed at Anyang, dating back to the middle Shang Dynasty (Chinese Bronze Age), and the mansion (xiù:宿) system's nucleus seems to have taken shape by the time of the ruler Wu Ding (1339-1281 BC).Detailed records of astronomical observations began during the Warring States period (fourth century BC) and flourished from the Han period onward. Chinese astronomy was equatorial, centered as it was on close observation of circumpolar stars, and was based on different principles from those prevailing in traditional Western astronomy, where heliacal risings and settings of zodiac constellations formed the basic ecliptic framework.Some elements of Indian astronomy reached China with the expansion of Buddhism after the Eastern Han Dynasty (25–220 AD), but the most detailed incorporation of Indian astronomical thought occurred during the Tang Dynasty (618-907), when numerous Indian astronomers took up residence in the Chinese capital, and Chinese scholars, such as the great Tantric Buddhist monk and mathematician Yi Xing, mastered its system. Islamic astronomers collaborated closely with their Chinese colleagues during the Yuan Dynasty, and, after a period of relative decline during the Ming Dynasty, astronomy was revitalized under the stimulus of Western cosmology and technology after the Jesuits established their missions. The telescope was introduced in the seventeenth century. In 1669, the Peking observatory was completely redesigned and refitted under the direction of Ferdinand Verbiest. Today, China continues to be active in astronomy, with many observatories and its own space program.