Numbers: Fun and Challenge
... • Dirichlet’s famous theorem that there are infinitely many prime numbers in any arithmetic progression amounts to L(1, χ) 6= 0. • Similarly the Prime number theorem, which asserts that the number of prime numbers up to a real number x is asymptotic to logx x amounts to the non-vanishing of ζ(s) at ...
... • Dirichlet’s famous theorem that there are infinitely many prime numbers in any arithmetic progression amounts to L(1, χ) 6= 0. • Similarly the Prime number theorem, which asserts that the number of prime numbers up to a real number x is asymptotic to logx x amounts to the non-vanishing of ζ(s) at ...
Problem Set 2 Solutions: Number Theory
... 1. There are 4 one-digit reversibly prime numbers, namely all the primes less than 10. The other reversibly prime numbers are 11, 13, 17, 31, 37, 71, 73, 79, and 97. Therefore, there are 13 reversibly prime numbers. 2. Since τ (n) is odd, n must be a perfect square. Furthermore, it must be the fourt ...
... 1. There are 4 one-digit reversibly prime numbers, namely all the primes less than 10. The other reversibly prime numbers are 11, 13, 17, 31, 37, 71, 73, 79, and 97. Therefore, there are 13 reversibly prime numbers. 2. Since τ (n) is odd, n must be a perfect square. Furthermore, it must be the fourt ...
Math 9 2.2 Problem Solving With Rational Numbers in Decimal Form
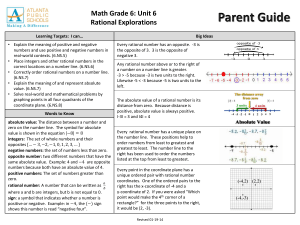
... Circle the correct response to complete each statement. 1. One way to model the subtraction of rational numbers is by (adding/subtracting) the opposite on a number line. 2. The product or quotient of two rational numbers with different signs is (positive/negative). 3. The product or quotient of two ...
... Circle the correct response to complete each statement. 1. One way to model the subtraction of rational numbers is by (adding/subtracting) the opposite on a number line. 2. The product or quotient of two rational numbers with different signs is (positive/negative). 3. The product or quotient of two ...