Algebra II
... 39. A cryptographer devises the following method for encoding positive integers. First, the integer is expressed in base 5. Second, a 1-1 correspondence is established between the digits that appear in the expressions in base 5 and the elements in the set V, W, X, Y, Z. Using this correspondence, th ...
... 39. A cryptographer devises the following method for encoding positive integers. First, the integer is expressed in base 5. Second, a 1-1 correspondence is established between the digits that appear in the expressions in base 5 and the elements in the set V, W, X, Y, Z. Using this correspondence, th ...
Algebra 1 – 2.5
... 1. The order in which you add numbers in a sum doesn’t matter. 2. If you add more than 2 numbers, the order in which you group them doesn’t matter. 3. When you add 0 to any number, the result is the number itself. 4. When you add any number to its opposite, the result is 0. When the sum of two numb ...
... 1. The order in which you add numbers in a sum doesn’t matter. 2. If you add more than 2 numbers, the order in which you group them doesn’t matter. 3. When you add 0 to any number, the result is the number itself. 4. When you add any number to its opposite, the result is 0. When the sum of two numb ...
Mathayom 1
... Directions: You will have 40 minutes to complete this test. Remember to SHOW ALL WORK and LABEL ALL UNITS!! Ask me if you need more paper to show your work. No credit without showing ...
... Directions: You will have 40 minutes to complete this test. Remember to SHOW ALL WORK and LABEL ALL UNITS!! Ask me if you need more paper to show your work. No credit without showing ...
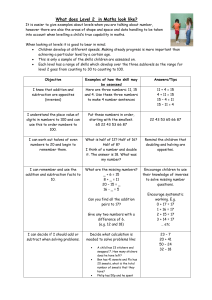
What does level 2 look like
... however there are also the areas of shape and space and data handling to be taken into account when levelling a child’s true capability in maths. When looking at levels it is good to bear in mind; Children develop at different speeds. Making steady progress is more important than achieving a parti ...
... however there are also the areas of shape and space and data handling to be taken into account when levelling a child’s true capability in maths. When looking at levels it is good to bear in mind; Children develop at different speeds. Making steady progress is more important than achieving a parti ...
3rd Grade Math Checklist
... Number Sense & Computation 1.1b) Identify the fractional part of a drawing or a set (restricted to halves, thirds, fourths). * 1.1c) Using concrete materials or pictures, identify different combinations of coins up to $1.00. * 1.2c) Identify place value through ten-thousands (for example, in 86,243, ...
... Number Sense & Computation 1.1b) Identify the fractional part of a drawing or a set (restricted to halves, thirds, fourths). * 1.1c) Using concrete materials or pictures, identify different combinations of coins up to $1.00. * 1.2c) Identify place value through ten-thousands (for example, in 86,243, ...
Document
... • Calculators are VERY, VERY SMART and they are VERY, VERY OBEDIENT … they will do exactly what we ask them to do. It is important to enter the information correctly. • The calculator may only give you an approximate answer and not and exact answer • Most calculators obey the order of operations ...
... • Calculators are VERY, VERY SMART and they are VERY, VERY OBEDIENT … they will do exactly what we ask them to do. It is important to enter the information correctly. • The calculator may only give you an approximate answer and not and exact answer • Most calculators obey the order of operations ...
Aim: What are imaginary and complex numbers?
... form a + bi, where a and b are real numbers and i is the imaginary unit. ...
... form a + bi, where a and b are real numbers and i is the imaginary unit. ...
Solving Two- Step Equations
... How to solve two-step equations • “Undo” the operations in the reverse order of the order of operations. • You are using the work back-words strategy • In order of operations we do multiplication or division first, then addition and subtraction. When solving an equation we do the opposite! ...
... How to solve two-step equations • “Undo” the operations in the reverse order of the order of operations. • You are using the work back-words strategy • In order of operations we do multiplication or division first, then addition and subtraction. When solving an equation we do the opposite! ...
Addition
Addition (often signified by the plus symbol ""+"") is one of the four elementary, mathematical operations of arithmetic, with the others being subtraction, multiplication and division.The addition of two whole numbers is the total amount of those quantities combined. For example, in the picture on the right, there is a combination of three apples and two apples together; making a total of 5 apples. This observation is equivalent to the mathematical expression ""3 + 2 = 5"" i.e., ""3 add 2 is equal to 5"".Besides counting fruits, addition can also represent combining other physical objects. Using systematic generalizations, addition can also be defined on more abstract quantities, such as integers, rational numbers, real numbers and complex numbers and other abstract objects such as vectors and matrices.In arithmetic, rules for addition involving fractions and negative numbers have been devised amongst others. In algebra, addition is studied more abstractly.Addition has several important properties. It is commutative, meaning that order does not matter, and it is associative, meaning that when one adds more than two numbers, the order in which addition is performed does not matter (see Summation). Repeated addition of 1 is the same as counting; addition of 0 does not change a number. Addition also obeys predictable rules concerning related operations such as subtraction and multiplication.Performing addition is one of the simplest numerical tasks. Addition of very small numbers is accessible to toddlers; the most basic task, 1 + 1, can be performed by infants as young as five months and even some non-human animals. In primary education, students are taught to add numbers in the decimal system, starting with single digits and progressively tackling more difficult problems. Mechanical aids range from the ancient abacus to the modern computer, where research on the most efficient implementations of addition continues to this day.