1.0 Knowledge of Algebra, Patterns, and Functions – Students will
... parentheses would change the value of the expression. Use what you know about numeric expressions to justify why your answer is correct. Use words, numbers, and/or symbols in your justification. ...
... parentheses would change the value of the expression. Use what you know about numeric expressions to justify why your answer is correct. Use words, numbers, and/or symbols in your justification. ...
PowerPoint Presentation - GCF and LCM Problem Solving
... will drip every 4 seconds and the other faucet drips every 9 seconds. If a drop of water falls from both faucets at the same, how many seconds will it be before you see the faucets drip at the same time again? ...
... will drip every 4 seconds and the other faucet drips every 9 seconds. If a drop of water falls from both faucets at the same, how many seconds will it be before you see the faucets drip at the same time again? ...
a 2
... When multiplying exponential forms that have the same base, we can add the exponents and keep the same base n a nb = na +b Simplify monomials raised to a power To simplify an exponential form raised to a power, we can multiply the exponents and keep the same base ( n a ) b = nab Multiply polynomials ...
... When multiplying exponential forms that have the same base, we can add the exponents and keep the same base n a nb = na +b Simplify monomials raised to a power To simplify an exponential form raised to a power, we can multiply the exponents and keep the same base ( n a ) b = nab Multiply polynomials ...
Number Representation ()
... doing arithmetic • Hex: if human looking at long strings of binary numbers, its much easier to convert to hex and look 4 bits/symbol • Terrible for arithmetic on paper ...
... doing arithmetic • Hex: if human looking at long strings of binary numbers, its much easier to convert to hex and look 4 bits/symbol • Terrible for arithmetic on paper ...
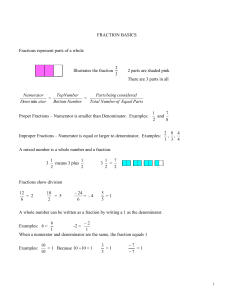
FRACTION BASICS
... It is easy to tell that 24 of them are going to be chocolate chip. Let’s write a math problem to represent how we get 24 as an answer. Ask yourself? Did we divide 48 in half? Did we divide 48 by one half? 48 Did we divide 48 by two? 48 2 ...
... It is easy to tell that 24 of them are going to be chocolate chip. Let’s write a math problem to represent how we get 24 as an answer. Ask yourself? Did we divide 48 in half? Did we divide 48 by one half? 48 Did we divide 48 by two? 48 2 ...
Complex Numbers, Convolution, Fourier Transform
... When you add z to z*, the imaginary parts cancel and you get a real number: (a + bi) + (a - bi) = 2a When you multiply z to z*, you get the real number equal to |z|2: (a + bi)(a - bi) = a2 – (bi)2 = a2 + b2 ...
... When you add z to z*, the imaginary parts cancel and you get a real number: (a + bi) + (a - bi) = 2a When you multiply z to z*, you get the real number equal to |z|2: (a + bi)(a - bi) = a2 – (bi)2 = a2 + b2 ...
2.2 Maths Frameworking 3ed. 3-year and 2-year
... language into mathematics. This activity gives them the opportunity to practise this in a range of contexts. Pupils often do not realise that you can test for congruence by placing one shape on top of the other. Encourage the use of tracing paper to do this. Also reinforce the fact that shapes can h ...
... language into mathematics. This activity gives them the opportunity to practise this in a range of contexts. Pupils often do not realise that you can test for congruence by placing one shape on top of the other. Encourage the use of tracing paper to do this. Also reinforce the fact that shapes can h ...
Leap Frog Solutions 2013
... Problem 4. If a and b are distinct numbers picked at random from the set ...
... Problem 4. If a and b are distinct numbers picked at random from the set ...
Chapter 2.7 Inequalitities
... Properties of Inequalities. Essentially, all of the properties that you learned to solve linear equations apply to solving linear inequalities with the exception that if you multiply or divide by a negative you must reverse the inequality sign. So to solve an inequality just do the same steps as wi ...
... Properties of Inequalities. Essentially, all of the properties that you learned to solve linear equations apply to solving linear inequalities with the exception that if you multiply or divide by a negative you must reverse the inequality sign. So to solve an inequality just do the same steps as wi ...
Full text
... beyond 3 which is not yet crossed out, we next put a slash through each fifth number beyond 5, and continue in a similar manner. Those numbers remaining (not crossed out) are p r i m e s . In o r d e r to place this p r o c e s s in a setting which is more suitable for generalization, we will now mo ...
... beyond 3 which is not yet crossed out, we next put a slash through each fifth number beyond 5, and continue in a similar manner. Those numbers remaining (not crossed out) are p r i m e s . In o r d e r to place this p r o c e s s in a setting which is more suitable for generalization, we will now mo ...
Topics in Logic and Proofs
... We have seen that a logic operator, such as p → q, is defined by its truth table. In other words, a different table gives a different logic operator. Question. How many different logic operators involving p and q are possible? There is no doubt, however, that some of these operators are actually int ...
... We have seen that a logic operator, such as p → q, is defined by its truth table. In other words, a different table gives a different logic operator. Question. How many different logic operators involving p and q are possible? There is no doubt, however, that some of these operators are actually int ...
Addition
Addition (often signified by the plus symbol ""+"") is one of the four elementary, mathematical operations of arithmetic, with the others being subtraction, multiplication and division.The addition of two whole numbers is the total amount of those quantities combined. For example, in the picture on the right, there is a combination of three apples and two apples together; making a total of 5 apples. This observation is equivalent to the mathematical expression ""3 + 2 = 5"" i.e., ""3 add 2 is equal to 5"".Besides counting fruits, addition can also represent combining other physical objects. Using systematic generalizations, addition can also be defined on more abstract quantities, such as integers, rational numbers, real numbers and complex numbers and other abstract objects such as vectors and matrices.In arithmetic, rules for addition involving fractions and negative numbers have been devised amongst others. In algebra, addition is studied more abstractly.Addition has several important properties. It is commutative, meaning that order does not matter, and it is associative, meaning that when one adds more than two numbers, the order in which addition is performed does not matter (see Summation). Repeated addition of 1 is the same as counting; addition of 0 does not change a number. Addition also obeys predictable rules concerning related operations such as subtraction and multiplication.Performing addition is one of the simplest numerical tasks. Addition of very small numbers is accessible to toddlers; the most basic task, 1 + 1, can be performed by infants as young as five months and even some non-human animals. In primary education, students are taught to add numbers in the decimal system, starting with single digits and progressively tackling more difficult problems. Mechanical aids range from the ancient abacus to the modern computer, where research on the most efficient implementations of addition continues to this day.