Finding mutations that matter - Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer
... have found only modest associations between the current bioinformatic predictors and the risk of disease. Capanu is realistic but hopeful for the future of such research: “Future improvement of bioinformatic tools to predict functional relevance will enhance the ability of this hierarchical modellin ...
... have found only modest associations between the current bioinformatic predictors and the risk of disease. Capanu is realistic but hopeful for the future of such research: “Future improvement of bioinformatic tools to predict functional relevance will enhance the ability of this hierarchical modellin ...
BW 180-182
... Read pages 180-182 in your text book to help you answer these questions! Define the following vocabulary: Gene: _____________________________________________________________________________________________ Allele: ______________________________________________________________________________________ ...
... Read pages 180-182 in your text book to help you answer these questions! Define the following vocabulary: Gene: _____________________________________________________________________________________________ Allele: ______________________________________________________________________________________ ...
Clinical Next Generation Sequencing (From Bench to Clinitions)
... Target Exome Sequencing With targeted sequencing, a subset of genes or regions of the genome are isolated and sequenced. Targeted approaches using next-generation sequencing (NGS) allow researchers to focus time, expenses, and data analysis on specific areas of interest. Such targeted analysis can ...
... Target Exome Sequencing With targeted sequencing, a subset of genes or regions of the genome are isolated and sequenced. Targeted approaches using next-generation sequencing (NGS) allow researchers to focus time, expenses, and data analysis on specific areas of interest. Such targeted analysis can ...
ppt
... Tens of thousands of human genomes have now been sequenced at low depth Can detect most polymorphisms with frequency >0.01 True whole genome association studies now possible at a very large scale Direct to Consumer Genomics: 23 & Me and other genotyping services http://www.1000genomes.org/ ...
... Tens of thousands of human genomes have now been sequenced at low depth Can detect most polymorphisms with frequency >0.01 True whole genome association studies now possible at a very large scale Direct to Consumer Genomics: 23 & Me and other genotyping services http://www.1000genomes.org/ ...
Introduction to Genetics
... Probability • Probability: the likelihood that an event will occur • i.e.: coin flip = ½ or 50% • Determined by: • Probability = # times expected to occur ...
... Probability • Probability: the likelihood that an event will occur • i.e.: coin flip = ½ or 50% • Determined by: • Probability = # times expected to occur ...
Two-Stage Association Mapping in Dogs Identifies Coat Color Locus
... Large families, inbred, good genealogical records, relatively short generation times ...
... Large families, inbred, good genealogical records, relatively short generation times ...
The identification of human quantitative trait loci
... average parameters over models. Eliminates problem of multiple testing. Yields unbiased estimates of effect size. Allows prioritization of polymorphisms for further lab evaluation. Calculation of Posterior Probability of Effect. ...
... average parameters over models. Eliminates problem of multiple testing. Yields unbiased estimates of effect size. Allows prioritization of polymorphisms for further lab evaluation. Calculation of Posterior Probability of Effect. ...
Document
... What were the definitions of evolution? Population genetics – Tracks the fate of Mendelian genes across generations – Allele or genotype will become more or less common over time? ...
... What were the definitions of evolution? Population genetics – Tracks the fate of Mendelian genes across generations – Allele or genotype will become more or less common over time? ...
PCR Lecture - Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution
... SNP discovery can be based on expressed sequence tags (ESTs), genomic restriction fragments, aligned BAC sequences, random shot gun clone sequences, overlapping genomic clone sequences Parallel genotyping of SNPs using generic high-density oligonucleotide tag arrays • Fan et al. (2000) Genome Resear ...
... SNP discovery can be based on expressed sequence tags (ESTs), genomic restriction fragments, aligned BAC sequences, random shot gun clone sequences, overlapping genomic clone sequences Parallel genotyping of SNPs using generic high-density oligonucleotide tag arrays • Fan et al. (2000) Genome Resear ...
Problem Set 1 1. Name 4 important differences between mitosis and
... 3. The frequency of allele A is 0.6 and the frequency of the allele combination AB is 0.2. What is the probability that an individual with allele A also has allele B? ...
... 3. The frequency of allele A is 0.6 and the frequency of the allele combination AB is 0.2. What is the probability that an individual with allele A also has allele B? ...
manuka short course
... • Read peer-reviewed articles employing a variety of study designs in genetic obesity research. • Research basics on Twin studies, Knock out mouse, Linkage analysis, Candidate association and GWAS (Genome Wide Association Studies) • Detailed info on Genetic Risk Scoring – used in the development ...
... • Read peer-reviewed articles employing a variety of study designs in genetic obesity research. • Research basics on Twin studies, Knock out mouse, Linkage analysis, Candidate association and GWAS (Genome Wide Association Studies) • Detailed info on Genetic Risk Scoring – used in the development ...
Study Guide for College Genetics Test
... The symptoms of this disease usually begin to develop in middle age. It is caused by a dominant allele (H). A man heterozygous for the Huntington’s allele marries a woman who has the homozygous recessive genotype. They plan to have children. What is the probability that they will have a child who de ...
... The symptoms of this disease usually begin to develop in middle age. It is caused by a dominant allele (H). A man heterozygous for the Huntington’s allele marries a woman who has the homozygous recessive genotype. They plan to have children. What is the probability that they will have a child who de ...
Variation – Chapter 9
... • Allele – form of a gene, distinguished by effect on phenotype • Haplotype – form of a gene, distinguished by DNA sequence • Gene copy – number of copies of a given gene, used without distinguishing allele or sequence differences – Allele copies Variation in phenotype can be due to genes AND enviro ...
... • Allele – form of a gene, distinguished by effect on phenotype • Haplotype – form of a gene, distinguished by DNA sequence • Gene copy – number of copies of a given gene, used without distinguishing allele or sequence differences – Allele copies Variation in phenotype can be due to genes AND enviro ...
9/06 Pedigrees and Human Genetics
... • 6.2 Geneticists Often Use Pedigrees to Study the Inheritance of Characteristics in Humans, 136 • 6.3 Analysis of Pedigrees Requires Recognizing Patterns Associated with Different Modes of Inheritance, 136 • 6.4 The Study of Twins Can Be Used to Assess the Importance of Genes and Environment on Var ...
... • 6.2 Geneticists Often Use Pedigrees to Study the Inheritance of Characteristics in Humans, 136 • 6.3 Analysis of Pedigrees Requires Recognizing Patterns Associated with Different Modes of Inheritance, 136 • 6.4 The Study of Twins Can Be Used to Assess the Importance of Genes and Environment on Var ...
The Future of Genetic Testing is Now
... had reached 80 years of age without chronic or major illness.5 The first step will be to generate in GWA studies the single nucleotide polymorphisms that differentiate these healthy individuals from the group with chronic diseases. It is not only the absence of dysfunctional genes that determine hea ...
... had reached 80 years of age without chronic or major illness.5 The first step will be to generate in GWA studies the single nucleotide polymorphisms that differentiate these healthy individuals from the group with chronic diseases. It is not only the absence of dysfunctional genes that determine hea ...
Text S1.
... substitutions that have been found in patients with disease. We required the dbSNP status because OMIM variant entries only provide amino acid locations with respect to the protein. The protein locations are relative to the protein sequence, but the exact protein sequence which is used as a referenc ...
... substitutions that have been found in patients with disease. We required the dbSNP status because OMIM variant entries only provide amino acid locations with respect to the protein. The protein locations are relative to the protein sequence, but the exact protein sequence which is used as a referenc ...
DNA 1: Today`s story, logic & goals
... Take home: "High genomic deleterious mutation rates in hominids" accumulate over 5000 generations & confound linkage methods ...
... Take home: "High genomic deleterious mutation rates in hominids" accumulate over 5000 generations & confound linkage methods ...
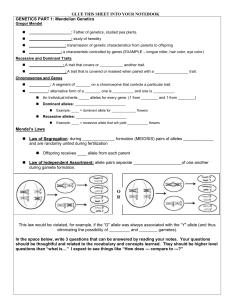
Fill-in Handout - Liberty Union High School District
... This law would be violated, for example, if the “G" allele was always associated with the “Y" allele (and thus eliminating the possibility of _________ and ________ gametes). In the space below, write 3 questions that can be answered by reading your notes. Your questions should be thoughtful and rel ...
... This law would be violated, for example, if the “G" allele was always associated with the “Y" allele (and thus eliminating the possibility of _________ and ________ gametes). In the space below, write 3 questions that can be answered by reading your notes. Your questions should be thoughtful and rel ...
Genome-wide_Association_2017
... • “Relatedness” between individuals (due to both population structure and cryptic relatedness) is captured in the modelling of the covariance between individuals • Can increase power by implicitly conditioning on associated loci other than the candidate locus (quantitative traits) • Variety of softw ...
... • “Relatedness” between individuals (due to both population structure and cryptic relatedness) is captured in the modelling of the covariance between individuals • Can increase power by implicitly conditioning on associated loci other than the candidate locus (quantitative traits) • Variety of softw ...
Text S2 Selection on GWAS SNPs and Traits As GWAS SNPs are
... selection (although empirically the human populations of different continents tend to produce elevated iHS scores in different regions of the genome [1]). This is because rather than comparing populations or groups of populations, iHS compares one allele of a SNP to the other. Thus, any selective pr ...
... selection (although empirically the human populations of different continents tend to produce elevated iHS scores in different regions of the genome [1]). This is because rather than comparing populations or groups of populations, iHS compares one allele of a SNP to the other. Thus, any selective pr ...
Who Is My Mommy?
... biological traits are passed on to successive generations. • S7L3a Students will explain the role of genes and chromosomes in the process of inheriting a specific trait. • S7L3c Students will recognize that selective breeding can produce plants and animals with desired traits. ...
... biological traits are passed on to successive generations. • S7L3a Students will explain the role of genes and chromosomes in the process of inheriting a specific trait. • S7L3c Students will recognize that selective breeding can produce plants and animals with desired traits. ...
Deriving Biological Inferences From Studies
... cases and controls. It may also arise from biased methods of recording or obtaining information by interview. Errors in conduction or design of the study also may introduce spurious association. ...
... cases and controls. It may also arise from biased methods of recording or obtaining information by interview. Errors in conduction or design of the study also may introduce spurious association. ...
HW 6
... frequencies for the next generation. There should be 8 individuals in generation two. In this generation, allow only individuals of the same genotype at the A locus mate. This simulates strong inbreeding. Calculate the third generation based on the punnett square predictions. There should be 16 offs ...
... frequencies for the next generation. There should be 8 individuals in generation two. In this generation, allow only individuals of the same genotype at the A locus mate. This simulates strong inbreeding. Calculate the third generation based on the punnett square predictions. There should be 16 offs ...
Genome-wide association study

In genetic epidemiology, a genome-wide association study (GWA study, or GWAS), also known as whole genome association study (WGA study, or WGAS) or common-variant association study (CVAS), is an examination of many common genetic variants in different individuals to see if any variant is associated with a trait. GWASs typically focus on associations between single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and traits like major diseases.These studies normally compare the DNA of two groups of participants: people with the disease (cases) and similar people without (controls). This approach is known as phenotype-first, in which the participants are classified first by their clinical manifestation(s), as opposed to genotype-first. Each person gives a sample of DNA, from which millions of genetic variants are read using SNP arrays. If one type of the variant (one allele) is more frequent in people with the disease, the SNP is said to be ""associated"" with the disease. The associated SNPs are then considered to mark a region of the human genome which influences the risk of disease. In contrast to methods which specifically test one or a few genetic regions, the GWA studies investigate the entire genome. The approach is therefore said to be non-candidate-driven in contrast to gene-specific candidate-driven studies. GWA studies identify SNPs and other variants in DNA which are associated with a disease, but cannot on their own specify which genes are causal.The first successful GWAS was published in 2005 and investigated patients with age-related macular degeneration. It found two SNPs which had significantly altered allele frequency when comparing with healthy controls. As of 2011, hundreds or thousands of individuals are tested, over 1,200 human GWA studies have examined over 200 diseases and traits, and almost 4,000 SNP associations have been found. Several GWA studies have received criticism for omitting important quality control steps, rendering the findings invalid, but modern publications address these issues. However, the methodology itself still has opponents.