A Cladistic Analysis of Phenotype Associations with
... Genes that code for products involved in the physiology of a phenotype are logical candidates for explaining interindividual variation in that phenotype. We present a methodology for discovering associations between genetic variation at such candidate loci (assayedthrough restriction endonuclease ma ...
... Genes that code for products involved in the physiology of a phenotype are logical candidates for explaining interindividual variation in that phenotype. We present a methodology for discovering associations between genetic variation at such candidate loci (assayedthrough restriction endonuclease ma ...
Course Outline
... be added algebraically to arrive at a prediction of a phenotype given a genotype. • Dominance refers to the observation that heterozygotes resemble one class of homozygotes more than the other. • Epistasis refers to a locus-by-locus Interaction, such as when alleles at two loci antagonize or synergi ...
... be added algebraically to arrive at a prediction of a phenotype given a genotype. • Dominance refers to the observation that heterozygotes resemble one class of homozygotes more than the other. • Epistasis refers to a locus-by-locus Interaction, such as when alleles at two loci antagonize or synergi ...
Chapter 8
... The total genetic variation for a population is the sum of these effects: VG = VA + VD + VI + VM • Genetic environment does not alter additive effects, so additive effects are the basis for a response to selection • Non-additive genetic variance is dependent on the alleles at the same loci and alle ...
... The total genetic variation for a population is the sum of these effects: VG = VA + VD + VI + VM • Genetic environment does not alter additive effects, so additive effects are the basis for a response to selection • Non-additive genetic variance is dependent on the alleles at the same loci and alle ...
The scope of Population Genetics Forces acting on allele
... • Consider a population with N diploid individuals. The total number of gene copies is then 2N. • Initial allele frequencies for A and a are p and q, and we randomly draw WITH REPLACEMENT enough gene copies to make the next generation. • The probability of drawing i copies of allele A is: ...
... • Consider a population with N diploid individuals. The total number of gene copies is then 2N. • Initial allele frequencies for A and a are p and q, and we randomly draw WITH REPLACEMENT enough gene copies to make the next generation. • The probability of drawing i copies of allele A is: ...
Association genetics in Pinus taeda L. II. Carbon isotope
... Department of Plant Sciences, University of California, CA, USA; 2Department of Forest Systems and Resources, Forest Research Institute, CIFOR-INIA, Madrid, Spain; 3School of Forest Resources and Conservation, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL, USA and 4Institute of Forest Genetics, Pacific Sou ...
... Department of Plant Sciences, University of California, CA, USA; 2Department of Forest Systems and Resources, Forest Research Institute, CIFOR-INIA, Madrid, Spain; 3School of Forest Resources and Conservation, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL, USA and 4Institute of Forest Genetics, Pacific Sou ...
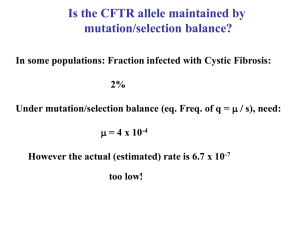
Is the CFTR allele maintained by mutation/selection balance?
... Polymorphism is simply a snapshot of a continuous process of mutational input and subsequent random extinction or fixation of alleles. ...
... Polymorphism is simply a snapshot of a continuous process of mutational input and subsequent random extinction or fixation of alleles. ...
Here - American Shetland Sheepdog Association
... (90% – 100%). The more commonly observed genotypes in healthy dogs were AabbCC and aabbCC. (Eight of the nine possible -‐-‐-‐-‐cc genotypes were too rare to assign risk; however, affected Shelties w ...
... (90% – 100%). The more commonly observed genotypes in healthy dogs were AabbCC and aabbCC. (Eight of the nine possible -‐-‐-‐-‐cc genotypes were too rare to assign risk; however, affected Shelties w ...
HARNETT COUNTY HIGH SCHOOLS Course: Biology Title of Unit
... • Develop a cause and effect model in order to describe how mutations: changing amino acid sequence, protein function, phenotype. Only mutations in sex cells (egg and sperm) or in the gamete produced from the primary sex cells can result in heritable changes. Bio.3.2.2 • Interpret Punnett squares (m ...
... • Develop a cause and effect model in order to describe how mutations: changing amino acid sequence, protein function, phenotype. Only mutations in sex cells (egg and sperm) or in the gamete produced from the primary sex cells can result in heritable changes. Bio.3.2.2 • Interpret Punnett squares (m ...
PDF file
... • QC filtering of SNPs and individuals (Mendel error, MAF, etc.) 111 K SNPs retained 29 sires, 61 dams, 534 offspring ...
... • QC filtering of SNPs and individuals (Mendel error, MAF, etc.) 111 K SNPs retained 29 sires, 61 dams, 534 offspring ...
Understand the Basics of Genetic Testing
... subdivision two or three of this section shall be guilty of a violation punishable by a civil fine of not more than one thousand dollars. (b) Any person who willfully violates the provisions of subdivision two or three of this section shall be guilty of a misdemeanor punishable by a fine of not more ...
... subdivision two or three of this section shall be guilty of a violation punishable by a civil fine of not more than one thousand dollars. (b) Any person who willfully violates the provisions of subdivision two or three of this section shall be guilty of a misdemeanor punishable by a fine of not more ...
Lecture Slides - McMaster University`s Faculty of Health Sciences
... relatives, most commonly sibs Sibs share 0,1 and 2 alleles at 25%, 50% and ...
... relatives, most commonly sibs Sibs share 0,1 and 2 alleles at 25%, 50% and ...
PowerPoint-Präsentation
... geographic adaptability, barley is particularly noted for its tolerance to cold, drought, alkali, and salinity. The barley genome - with 5.3 billion letters of genetic code - is one of the largest in cereal crops measuring about twice the size of the human genome. Barley is a true diploid, thus, it ...
... geographic adaptability, barley is particularly noted for its tolerance to cold, drought, alkali, and salinity. The barley genome - with 5.3 billion letters of genetic code - is one of the largest in cereal crops measuring about twice the size of the human genome. Barley is a true diploid, thus, it ...
Genome Biology and
... • Certain proteins evolve much more rapidly: positive selection – Proteins implicated in reproduction, host defence and immune response seem to be under, which drives Reprinted from: Mouse Genome Sequencing Consortium, Nature 420, 520 - 562 (2002) ...
... • Certain proteins evolve much more rapidly: positive selection – Proteins implicated in reproduction, host defence and immune response seem to be under, which drives Reprinted from: Mouse Genome Sequencing Consortium, Nature 420, 520 - 562 (2002) ...
Selection - Seattle Central College
... success* – “Bout” of selection: An event that alters allele frequencies ...
... success* – “Bout” of selection: An event that alters allele frequencies ...
Horizontal transfer generates genetic variation in an asexual
... VaMs102 assembly. The two files in the order of paired-end reads were screened to produce a subset of the file for the JR2 assembly. A pair of paired-end read from strain JR2 was kept in the subset file if and only if it was concordantly mapped to one genome assembly but discordantly mapped to the o ...
... VaMs102 assembly. The two files in the order of paired-end reads were screened to produce a subset of the file for the JR2 assembly. A pair of paired-end read from strain JR2 was kept in the subset file if and only if it was concordantly mapped to one genome assembly but discordantly mapped to the o ...
q 2 - University of Evansville Faculty Web sites
... – founding group contains sample of alleles not necessarily in same frequency as parent population ...
... – founding group contains sample of alleles not necessarily in same frequency as parent population ...
The Genetic Basis of Complex Inheritance
... • Most traits that vary in the population, including common human diseases with the genetic component, are complex traits ...
... • Most traits that vary in the population, including common human diseases with the genetic component, are complex traits ...
Outline of lectures 9-10
... 9. At the gene level, the individuals in the top end of the population are more likely to have the alleles that predispose to a large value of the character. Selecting, one changes the gene frequencies at all these loci. Random mating among the survivors, with recombination, then results in genotyp ...
... 9. At the gene level, the individuals in the top end of the population are more likely to have the alleles that predispose to a large value of the character. Selecting, one changes the gene frequencies at all these loci. Random mating among the survivors, with recombination, then results in genotyp ...
Bitter Taste Study in a Sardinian Genetic Isolate
... tasted score. All together, we tested 280 persons in Talana and calculated age- and sex-adjusted PTC scores using the corrections of Harris and Kalmus (1958), whose distribution showed a typical bimodal curve (Figure 1). From the minimum node in frequency between tasters and non-tasters in the distr ...
... tasted score. All together, we tested 280 persons in Talana and calculated age- and sex-adjusted PTC scores using the corrections of Harris and Kalmus (1958), whose distribution showed a typical bimodal curve (Figure 1). From the minimum node in frequency between tasters and non-tasters in the distr ...
Ancestral genotypes now susceptible to diease
... susceptibility genotypes can still have weakly deleterious effects on fitness [2,3]. This model predicts that multiple rare, new alleles increasing risk will be found at trait loci, as was recently observed at the ABCA1 gene responsible for low HDL cholesterol [4]. Indeed, a model of weak purifying ...
... susceptibility genotypes can still have weakly deleterious effects on fitness [2,3]. This model predicts that multiple rare, new alleles increasing risk will be found at trait loci, as was recently observed at the ABCA1 gene responsible for low HDL cholesterol [4]. Indeed, a model of weak purifying ...
The Promises and Pitfalls of Genoeconomics
... These advances in genetics are in turn transforming medical research. Some diseases have been linked to single genetic mutations in specific genes (e.g., Huntington’s disease and Fragile X syndrome), which can be assayed to diagnose the disease, predict the age of onset and/or severity, and better u ...
... These advances in genetics are in turn transforming medical research. Some diseases have been linked to single genetic mutations in specific genes (e.g., Huntington’s disease and Fragile X syndrome), which can be assayed to diagnose the disease, predict the age of onset and/or severity, and better u ...
Free Full Text ( Final Version , 673kb )
... (31), with several millions of such potential markers spread over the genome (32). Because functionally relevant polymorphisms are expected to be associated with the disease, anonymous flanking SNPs in strong LD with such functional polymorphisms are also expected to be disease associated. Our marke ...
... (31), with several millions of such potential markers spread over the genome (32). Because functionally relevant polymorphisms are expected to be associated with the disease, anonymous flanking SNPs in strong LD with such functional polymorphisms are also expected to be disease associated. Our marke ...
Tag SNP

A tag SNP is a representative single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) in a region of the genome with high linkage disequilibrium that represents a group of SNPs called a haplotype. It is possible to identify genetic variation and association to phenotypes without genotyping every SNP in a chromosomal region. This reduces the expense and time of mapping genome areas associated with disease, since it eliminates the need to study every individual SNP. Tag SNPs are useful in whole-genome SNP association studies in which hundreds of thousands of SNPs across the entire genome are genotyped.