Conjunctions - Google Sites
... Some words can act as both conjunctions and adverbs at the same time!!! A conjunctive adverb is an adverb that acts as a conjunction to connect complete ideas. Conjunctive adverbs are often used as transitions. Transitions serve as bridges between different ideas. Frequently Used Conjunctive Adverbs ...
... Some words can act as both conjunctions and adverbs at the same time!!! A conjunctive adverb is an adverb that acts as a conjunction to connect complete ideas. Conjunctive adverbs are often used as transitions. Transitions serve as bridges between different ideas. Frequently Used Conjunctive Adverbs ...
Chapter 20: Fourth Declension Chapter 20 covers the following: the
... the original use of the ablative was to indicate where something came from. Other uses like means and objects of prepositions developed later. In other words, the ablative of separation shows the oldest, the original, use of the ablative. The ablative of separation naturally occurs with verbs that ...
... the original use of the ablative was to indicate where something came from. Other uses like means and objects of prepositions developed later. In other words, the ablative of separation shows the oldest, the original, use of the ablative. The ablative of separation naturally occurs with verbs that ...
3 Principles of English Phrase Structure
... It should be clear that this reinterpretation of the relative clause has dramatic consequences. It simply turns the true statement in (23) into the false statement in (24). The difference between the semantics of restrictive and non-restrictive relative clauses can be explained in terms of sets. Ass ...
... It should be clear that this reinterpretation of the relative clause has dramatic consequences. It simply turns the true statement in (23) into the false statement in (24). The difference between the semantics of restrictive and non-restrictive relative clauses can be explained in terms of sets. Ass ...
Nominal Complements: Subjective and Objective Complements
... (3) Verbs of discovery or perception of a relationship between an object and its complement bolu ‘find, come across’ deyu ‘leave’ ìnnā ‘see’ Most verbs of types (1) and (2) can (at least optionally) use a phrase headed by b˘ ‘in the capacity of, in the guise of’ as the objective complement. For verb ...
... (3) Verbs of discovery or perception of a relationship between an object and its complement bolu ‘find, come across’ deyu ‘leave’ ìnnā ‘see’ Most verbs of types (1) and (2) can (at least optionally) use a phrase headed by b˘ ‘in the capacity of, in the guise of’ as the objective complement. For verb ...
COMPLEMENTS
... Remember that a direct object receives some action from the subject. Direct object complements expand on this relationship when appropriate. Sometimes you might want to write, “The dog ate the cake” and leave it at that. Other times you need more information, like “The dog ate the cake at the weddin ...
... Remember that a direct object receives some action from the subject. Direct object complements expand on this relationship when appropriate. Sometimes you might want to write, “The dog ate the cake” and leave it at that. Other times you need more information, like “The dog ate the cake at the weddin ...
Gerunds - Images
... proved a major mistake. – Proved is the main verb. Mistake is the direct object. – What? + Proved a mistake=Giving Jerry the money – The gerund phrase is the subject of the main sentence. ...
... proved a major mistake. – Proved is the main verb. Mistake is the direct object. – What? + Proved a mistake=Giving Jerry the money – The gerund phrase is the subject of the main sentence. ...
DGP 6th Five-Day Plan Sent. 7
... A transitive verb takes a direct object. The object of the preposition follows the preposition and tells “what” or “whom.” A direct object is a noun or pronoun and is never in a prepositional phrase; it follows an action verb; you can ask yourself, “subject, verb, what?” OR “subject, verb, who ...
... A transitive verb takes a direct object. The object of the preposition follows the preposition and tells “what” or “whom.” A direct object is a noun or pronoun and is never in a prepositional phrase; it follows an action verb; you can ask yourself, “subject, verb, what?” OR “subject, verb, who ...
Grammar and Sentence Types
... independent clause and one or more dependent clauses connected to it. A dependent clause is similar to an independent clause, or complete sentence, but it lacks one of the elements that would make it a complete sentence. A complex sentence joins an independent clause with one or more dependent c ...
... independent clause and one or more dependent clauses connected to it. A dependent clause is similar to an independent clause, or complete sentence, but it lacks one of the elements that would make it a complete sentence. A complex sentence joins an independent clause with one or more dependent c ...
PARTS OF SPEECH Parts of speech can be divided into two distinct
... A preposition usually indicates the temporal, spatial or logical relationship of its object to the rest of the sentence as in the following examples: The book is on the table. The book is beneath the table. The book is leaning against the table. The book is beside the table. She held the book over t ...
... A preposition usually indicates the temporal, spatial or logical relationship of its object to the rest of the sentence as in the following examples: The book is on the table. The book is beneath the table. The book is leaning against the table. The book is beside the table. She held the book over t ...
DGP 6th Five-Day Plan Sent. 5
... 2. Label the parts of speech in the sentence above by using the abbreviations in the word bank below. Day 1 Word Bank: n - noun (2) N – proper noun (1) adj-adjective(1) av – action verb (1) – pres (present), past (past), f (future) art-article(1) prep - preposition (1) Day 1 Notes: A n ...
... 2. Label the parts of speech in the sentence above by using the abbreviations in the word bank below. Day 1 Word Bank: n - noun (2) N – proper noun (1) adj-adjective(1) av – action verb (1) – pres (present), past (past), f (future) art-article(1) prep - preposition (1) Day 1 Notes: A n ...
Participial Phrases
... 7. I want him to be my bodyguard. 8. Jim is expected to program computers at his new job. 9. They will try to build a new stadium in ten years. 10. To distill a quart of moonshine takes two hours. 11. The president wants to use nuclear energy for peaceful ...
... 7. I want him to be my bodyguard. 8. Jim is expected to program computers at his new job. 9. They will try to build a new stadium in ten years. 10. To distill a quart of moonshine takes two hours. 11. The president wants to use nuclear energy for peaceful ...
Lecture 11: Parts of speech
... formance degradations in a wide variety of languages (including Czech, Slovene, Estonian, and Romanian) (Hajič, 2000). Highly inflectional languages also have much more information than English coded in word morphology, like case (nominative, accusative, genitive) or gender (masculine, feminine). ...
... formance degradations in a wide variety of languages (including Czech, Slovene, Estonian, and Romanian) (Hajič, 2000). Highly inflectional languages also have much more information than English coded in word morphology, like case (nominative, accusative, genitive) or gender (masculine, feminine). ...
Tentative Unit 1 Schedule
... ‘I’ is the subject form and ‘me’ is the object form ‘You’ is both subject form and object form When combing first person (I), second person (you), and third person (he/she, James/Jill) into one noun phrase, they must go in the order: second person, third person, first person Ex: You, Jason, and I sh ...
... ‘I’ is the subject form and ‘me’ is the object form ‘You’ is both subject form and object form When combing first person (I), second person (you), and third person (he/she, James/Jill) into one noun phrase, they must go in the order: second person, third person, first person Ex: You, Jason, and I sh ...
Polysemy of verbal prefixes in Russian
... (2004), Babko-Malaya (1999)) is crucial, where the lexical prefixes are located in the res (result) projection, while the superlexical prefixes are above aspect. The intermediate prefixes (Tatevosov (2008)) are in proc. I suggest that the prexes are neither heads nor specifiers, but rather range ass ...
... (2004), Babko-Malaya (1999)) is crucial, where the lexical prefixes are located in the res (result) projection, while the superlexical prefixes are above aspect. The intermediate prefixes (Tatevosov (2008)) are in proc. I suggest that the prexes are neither heads nor specifiers, but rather range ass ...
Grammar Reference Book
... only isolated sentences but whole texts – but for the purposes of this course, we’ll start at the more basic level of sentences.) So far, we’ve been looking at parts of sentences, such as the noun or noun phrase and the verb or verb group, because they have their own internal structures and it’s imp ...
... only isolated sentences but whole texts – but for the purposes of this course, we’ll start at the more basic level of sentences.) So far, we’ve been looking at parts of sentences, such as the noun or noun phrase and the verb or verb group, because they have their own internal structures and it’s imp ...
Unit 7: Simple Sentences
... only isolated sentences but whole texts – but for the purposes of this course, we’ll start at the more basic level of sentences.) So far, we’ve been looking at parts of sentences, such as the noun or noun phrase and the verb or verb group, because they have their own internal structures and it’s imp ...
... only isolated sentences but whole texts – but for the purposes of this course, we’ll start at the more basic level of sentences.) So far, we’ve been looking at parts of sentences, such as the noun or noun phrase and the verb or verb group, because they have their own internal structures and it’s imp ...
A Controlled Language for Knowledge Formulation on the Semantic
... CT is still highly applicable in the latter. Here one could first prepare knowledge in CT and then translate it into a KR formalism, which is not designed for human friendliness, with little human intervention. The situation we are most interested in is large document collections such as the web, wh ...
... CT is still highly applicable in the latter. Here one could first prepare knowledge in CT and then translate it into a KR formalism, which is not designed for human friendliness, with little human intervention. The situation we are most interested in is large document collections such as the web, wh ...
Gerunds - gpssummerenglish
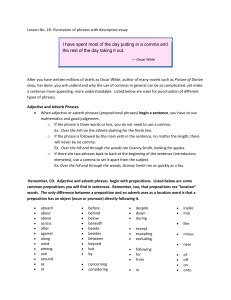
... Remember, CD. Adjective and adverb phrases begin with prepositions. Listed below are some common prepositions you will find in sentences. Remember, too, that prepositions rea “location” words. The only difference between a preposition and an adverb uses as a location word is that a preposition has a ...
... Remember, CD. Adjective and adverb phrases begin with prepositions. Listed below are some common prepositions you will find in sentences. Remember, too, that prepositions rea “location” words. The only difference between a preposition and an adverb uses as a location word is that a preposition has a ...
possession
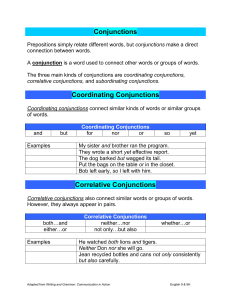
... and although) join clauses within a sentence. Connecting adverbs (like however) connect ideas but the clauses remain separate sentences: I was angry but I didn’t say anything. (but is a conjunction - one sentence) Although I was angry, I didn’t say anything. (although is a conjunction - one sentence ...
... and although) join clauses within a sentence. Connecting adverbs (like however) connect ideas but the clauses remain separate sentences: I was angry but I didn’t say anything. (but is a conjunction - one sentence) Although I was angry, I didn’t say anything. (although is a conjunction - one sentence ...
Gerunds Infinitives Participles
... An infinitive is a verb form--often preceded by the particle to--that can function as a noun, an adjective, or an adverb. Compare the verbals in these two sentences: I don't like crying in public unless I'm getting paid for it. I don't like to cry in public unless I'm getting paid for it. In the fir ...
... An infinitive is a verb form--often preceded by the particle to--that can function as a noun, an adjective, or an adverb. Compare the verbals in these two sentences: I don't like crying in public unless I'm getting paid for it. I don't like to cry in public unless I'm getting paid for it. In the fir ...
Brushstrokes – Notes
... Ex: My brother, Bill, is an astronaut. Bill, my older brother by two years, is an astronaut. The dog, a mixed Lab and Collie, limped across the lawn with her puppies. ...
... Ex: My brother, Bill, is an astronaut. Bill, my older brother by two years, is an astronaut. The dog, a mixed Lab and Collie, limped across the lawn with her puppies. ...
Brushstrokes Core sentence: The dog walked across
... Ex: My brother, Bill, is an astronaut. Bill, my older brother by two years, is an astronaut. The dog, a mixed Lab and Collie, limped across the lawn with her puppies. ...
... Ex: My brother, Bill, is an astronaut. Bill, my older brother by two years, is an astronaut. The dog, a mixed Lab and Collie, limped across the lawn with her puppies. ...
ObjectsPronouns
... • Definition: a noun or pronoun that receives the action of a verb or shows the result of the action • Answers the questions – "What?" or "Whom?" after an action verb. ...
... • Definition: a noun or pronoun that receives the action of a verb or shows the result of the action • Answers the questions – "What?" or "Whom?" after an action verb. ...
Syntax Terminology
... • Rhetorical: a question which you do not actually expect the reader to answer • i.e. Why did the War of 1812 take place? Some scholars argue that it was simply a land-grab by the Americans… ...
... • Rhetorical: a question which you do not actually expect the reader to answer • i.e. Why did the War of 1812 take place? Some scholars argue that it was simply a land-grab by the Americans… ...