Cause and Effect
... - the parts that make up a story - these parts of a story work together - changing one element in the story can affect all other elements Three Parts: - Who is in the story (characters)? - Where the story takes place (setting)? - -What happens as the events unfold (plot)? Plot often contains a pro ...
... - the parts that make up a story - these parts of a story work together - changing one element in the story can affect all other elements Three Parts: - Who is in the story (characters)? - Where the story takes place (setting)? - -What happens as the events unfold (plot)? Plot often contains a pro ...
Grade 10 Grammar Notes
... Ex. The girl and her cat stared and sighed through the evening and into the night, but they seemed quite happy nonetheless. 2) SUBORDINATE - only joins clauses, making one sentence out of two. The subordinate conj. (unlike the coord. conj.) makes the clause that it starts subordinate to the one it a ...
... Ex. The girl and her cat stared and sighed through the evening and into the night, but they seemed quite happy nonetheless. 2) SUBORDINATE - only joins clauses, making one sentence out of two. The subordinate conj. (unlike the coord. conj.) makes the clause that it starts subordinate to the one it a ...
For example - WordPress.com
... part of the predicate of a sentence, such as hear, become, happen. Often, prefixes and suffixes (affixes) will signify that a word is a verb. For exa mple, the suffixes -ify, -ize, -ate, or -en usually signify that a word is a verb, as in typify, characterize, irrigate, and sweeten. Prefixes such as ...
... part of the predicate of a sentence, such as hear, become, happen. Often, prefixes and suffixes (affixes) will signify that a word is a verb. For exa mple, the suffixes -ify, -ize, -ate, or -en usually signify that a word is a verb, as in typify, characterize, irrigate, and sweeten. Prefixes such as ...
Grammar and Punctuation Key Terms
... colour. They can be used to modify a 3. Superlative (-est or most). noun or complement a verb. big, bigger, biggest stupid, more stupid, most stupid An adverb is a word which modifies TIME – before, now, then, already, soon, seldom. or Example: We have met before. adds to the meaning of a verb, an P ...
... colour. They can be used to modify a 3. Superlative (-est or most). noun or complement a verb. big, bigger, biggest stupid, more stupid, most stupid An adverb is a word which modifies TIME – before, now, then, already, soon, seldom. or Example: We have met before. adds to the meaning of a verb, an P ...
Unit 3: Phrases
... WHAT IS A PREPOSITIONAL PHRASE? A GROUP of words beginning with a preposition and ending with a noun or pronoun It RELATES to some other word in the sentence. Includes a preposition, the object of the preposition, and any modifiers of that object ...
... WHAT IS A PREPOSITIONAL PHRASE? A GROUP of words beginning with a preposition and ending with a noun or pronoun It RELATES to some other word in the sentence. Includes a preposition, the object of the preposition, and any modifiers of that object ...
1B_DGP_Notes_Sentence_8
... Modifies adjectives, verbs, and other adverbs Tells How? When? Where? To what extent? not and never are always adverbs yet can be an adverb or a coordinating conjunction depending on how it’s being used Verb that acts like an adjective Ends in –ing or –ed or –en (or other past tense ending) Examples ...
... Modifies adjectives, verbs, and other adverbs Tells How? When? Where? To what extent? not and never are always adverbs yet can be an adverb or a coordinating conjunction depending on how it’s being used Verb that acts like an adjective Ends in –ing or –ed or –en (or other past tense ending) Examples ...
SYLLABUS ELPSS CLASS I I. An unseen Passage and questions
... c. Describing words 6. Choose the correct spelling d. Words instead of nouns (Pronouns) III. ...
... c. Describing words 6. Choose the correct spelling d. Words instead of nouns (Pronouns) III. ...
The Eight Parts of Speech
... II. State of being verbs fall into two categories: 1. Forms of be: am, is, are, was, were, being, been They were happy. 2. A linking verb links an adjective, noun, or pronoun (the predicate adjective or predicate nominative) to the subject. ...
... II. State of being verbs fall into two categories: 1. Forms of be: am, is, are, was, were, being, been They were happy. 2. A linking verb links an adjective, noun, or pronoun (the predicate adjective or predicate nominative) to the subject. ...
The Word Class Book
... A group of words built round a noun is called a noun phrase. It acts like a noun in a sentence. Index ...
... A group of words built round a noun is called a noun phrase. It acts like a noun in a sentence. Index ...
The Word Class Book
... A group of words built round a noun is called a noun phrase. It acts like a noun in a sentence. Index ...
... A group of words built round a noun is called a noun phrase. It acts like a noun in a sentence. Index ...
Different words do different jobs in a sentence. The word class book
... A group of words built round a noun is called a noun phrase. It acts like a noun in a sentence. Index ...
... A group of words built round a noun is called a noun phrase. It acts like a noun in a sentence. Index ...
Parts of Speech - Ohio County Schools
... Words as Different Parts of Speech • The way a word is used in a sentence determines what part of speech it is. DIFFERENT USES OF A WORD As a noun: I purchased a FM radio. As a verb: In an emergency, radio for help. As an adjective: I will use a radio transmission. ...
... Words as Different Parts of Speech • The way a word is used in a sentence determines what part of speech it is. DIFFERENT USES OF A WORD As a noun: I purchased a FM radio. As a verb: In an emergency, radio for help. As an adjective: I will use a radio transmission. ...
VERBALS participles = verb acting like an adjective The swimming
... • Adverb infinitives are used to modify predicate adjectives. • The new soldiers were ready to listen and obey. • This puzzle is difficult to complete. ...
... • Adverb infinitives are used to modify predicate adjectives. • The new soldiers were ready to listen and obey. • This puzzle is difficult to complete. ...
PRONOUN USAGE
... The quality that distinguishes the entities as masculine or feminine. Some students have a tendency to use masculine pronouns––he, him, his––for nouns which may include female and male subjects. Problematic: Each of the doctors ate his lunch outside. The above use of pronouns should be avoided, unle ...
... The quality that distinguishes the entities as masculine or feminine. Some students have a tendency to use masculine pronouns––he, him, his––for nouns which may include female and male subjects. Problematic: Each of the doctors ate his lunch outside. The above use of pronouns should be avoided, unle ...
Pronoun Notes
... The quality that distinguishes the entities as masculine or feminine. Some students have a tendency to use masculine pronouns––he, him, his––for nouns which may include female and male subjects. Problematic: Each of the doctors ate his lunch outside. The above use of pronouns should be avoided, unle ...
... The quality that distinguishes the entities as masculine or feminine. Some students have a tendency to use masculine pronouns––he, him, his––for nouns which may include female and male subjects. Problematic: Each of the doctors ate his lunch outside. The above use of pronouns should be avoided, unle ...
Checklist of Grammatical Terms and Categories 1
... The following checklist may be helpful to those who have finished the book and are reviewing. Students who are comfortable with theses are terms and categories will find this knowledge to be a major asset in understanding explanations of passages in commentaries or in oral teaching, as well as in th ...
... The following checklist may be helpful to those who have finished the book and are reviewing. Students who are comfortable with theses are terms and categories will find this knowledge to be a major asset in understanding explanations of passages in commentaries or in oral teaching, as well as in th ...
act-nouns and their functions
... Indirect object An indirect object precedes the direct object and tells to whom or for whom the action of the verb is done and who is receiving the direct object. There must be a direct object to have an indirect object. Indirect objects are usually found with verbs of giving or communicating like g ...
... Indirect object An indirect object precedes the direct object and tells to whom or for whom the action of the verb is done and who is receiving the direct object. There must be a direct object to have an indirect object. Indirect objects are usually found with verbs of giving or communicating like g ...
Grammar and Usage_1
... Examples: The jet engine passed inspection. Passed is the verb. Who or what passed? The engine, so engine is the subject. If you included the word jet as the subject, lightning will not strike you. Technically, jet is an adjective here and is part of what is known as the complete subject. From the c ...
... Examples: The jet engine passed inspection. Passed is the verb. Who or what passed? The engine, so engine is the subject. If you included the word jet as the subject, lightning will not strike you. Technically, jet is an adjective here and is part of what is known as the complete subject. From the c ...
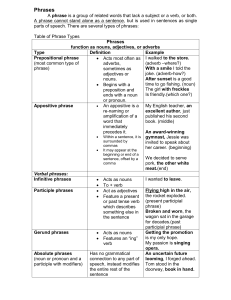
Phrases - KoplikEnglish10
... verb. If it is an independent clause, it may stand alone as a sentence: Ex: White dogs are pretty. If it is a dependent (subordinate) clause, it may not stand alone: Ex: Although white dogs are pretty. As shown in the preceding example, a subordinating word is used in dependent clauses. This word re ...
... verb. If it is an independent clause, it may stand alone as a sentence: Ex: White dogs are pretty. If it is a dependent (subordinate) clause, it may not stand alone: Ex: Although white dogs are pretty. As shown in the preceding example, a subordinating word is used in dependent clauses. This word re ...
What comes after verbs? - RIT
... - An adverb phrase may come after an intransitive verb -- v(I). - An adverb phrase may be a prepositional phrase or a simple adverb. - An adverb phrase answers WHEN, WHERE, WHY, HOW questions. 3. Period (.) - A period (.) may come after an intransitive verb -- v(I). 4. Noun or Adjective - A noun or ...
... - An adverb phrase may come after an intransitive verb -- v(I). - An adverb phrase may be a prepositional phrase or a simple adverb. - An adverb phrase answers WHEN, WHERE, WHY, HOW questions. 3. Period (.) - A period (.) may come after an intransitive verb -- v(I). 4. Noun or Adjective - A noun or ...
Parts of Speech lesson 1
... pronouns that they modify. Proper adjectives modify proper form and begin with a capital letter. Predicate adjectives follow linking verbs and describe. Examples of Adjectives: Proper adjectives: Persian rug, Mexican rice, European tourists Common adjectives: yellow, dirty, more, ten, next. Predicat ...
... pronouns that they modify. Proper adjectives modify proper form and begin with a capital letter. Predicate adjectives follow linking verbs and describe. Examples of Adjectives: Proper adjectives: Persian rug, Mexican rice, European tourists Common adjectives: yellow, dirty, more, ten, next. Predicat ...
Year Groups - Information S.P.A.G. Booklet
... Active voice: many verbs can be active or passive, e.g. The cat scratched Anna (active voice), Anna was scratched by the cat (passive voice). In the active sentence, the subject (the cat) performs the action. In the passive sentence, the subject (Anna) is on the receiving end of the action. The two ...
... Active voice: many verbs can be active or passive, e.g. The cat scratched Anna (active voice), Anna was scratched by the cat (passive voice). In the active sentence, the subject (the cat) performs the action. In the passive sentence, the subject (Anna) is on the receiving end of the action. The two ...