On Syntactic Functions
... The PHRASE. Identifying phrases He paid the bill for us. (direct +indirect object) He spared for her the trouble of going there. (direct +indirect object) She passed the salt to me/She passed me the salt. (direct +indirect object) I gave a bunch of flowers to my friend./I gave my friend a bunch of ...
... The PHRASE. Identifying phrases He paid the bill for us. (direct +indirect object) He spared for her the trouble of going there. (direct +indirect object) She passed the salt to me/She passed me the salt. (direct +indirect object) I gave a bunch of flowers to my friend./I gave my friend a bunch of ...
EXERCISES
... Exercise 2.11 Pronoun classes (section 2.24) Circle the antecedents of the underlined pronouns. **[Correct answers are bracketed] 1. Scientists have discovered that [pets] have a therapeutic effect on their owners. 2. [A dog], for instance, can improve the health of the people it comes in contact wi ...
... Exercise 2.11 Pronoun classes (section 2.24) Circle the antecedents of the underlined pronouns. **[Correct answers are bracketed] 1. Scientists have discovered that [pets] have a therapeutic effect on their owners. 2. [A dog], for instance, can improve the health of the people it comes in contact wi ...
Nomen? - Dover High School
... 6. What is she doing? 7. Who else is in the picture? 8. Who is Flavia? 9. What are the two girls doing? 10. Why is Flavia happy? ...
... 6. What is she doing? 7. Who else is in the picture? 8. Who is Flavia? 9. What are the two girls doing? 10. Why is Flavia happy? ...
Fragments - ttosspon
... I sat down. In the school bus. Howard, the school bully, came and sat down beside me. Could be a dependent clause As I sat down. Howard, the school bully, came and sat ...
... I sat down. In the school bus. Howard, the school bully, came and sat down beside me. Could be a dependent clause As I sat down. Howard, the school bully, came and sat ...
Creating Sentences with Participial Phrases
... To emphasize the quick, successive actions described in these three sentences, we can combine them by turning the verbs guided and bounced into present participles: Guiding the ball through the upper chutes, down a runover lane, off the slingshot bumpers to the flippers, I cradled it there, bouncing ...
... To emphasize the quick, successive actions described in these three sentences, we can combine them by turning the verbs guided and bounced into present participles: Guiding the ball through the upper chutes, down a runover lane, off the slingshot bumpers to the flippers, I cradled it there, bouncing ...
The Clause:
... – Concession: although, even though, though – Condition: if, than, unless • After completing our homework, we watched a long movie. ...
... – Concession: although, even though, though – Condition: if, than, unless • After completing our homework, we watched a long movie. ...
PSSA English Language Arts Glossary
... A group of words that contains a subject and predicate. An independent clause can stand as a sentence. A dependent, or subordinate, clause must be attached to an independent clause to form a sentence. ...
... A group of words that contains a subject and predicate. An independent clause can stand as a sentence. A dependent, or subordinate, clause must be attached to an independent clause to form a sentence. ...
ENGLISH ELLIPTICAL CONSTRUCTION
... Based on the description above, the writer can give a short explanation of elliptical construction as follows. Ellipsis can be seen from the structure, the place, and the kind. Viewed from the structure, when the sentences are positive we can use the structure of elliptical construction: Subject + v ...
... Based on the description above, the writer can give a short explanation of elliptical construction as follows. Ellipsis can be seen from the structure, the place, and the kind. Viewed from the structure, when the sentences are positive we can use the structure of elliptical construction: Subject + v ...
Grammar Essentials
... In this course, students will review the rules of grammar, identify common grammar errors, and refine their business writing style. ...
... In this course, students will review the rules of grammar, identify common grammar errors, and refine their business writing style. ...
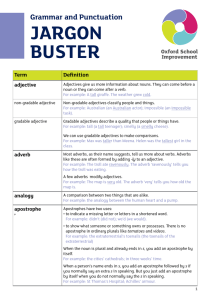
jargon buster - Gorsey Bank Primary School
... A relative clause explains or describes something that has just been mentioned, and is introduced by that, which, who, whom, whose, when, or where. A relative clause can either restrict meaning: For example: Of all Tolkien’s books, the one which I prefer is The Hobbit. Or it can simply add further i ...
... A relative clause explains or describes something that has just been mentioned, and is introduced by that, which, who, whom, whose, when, or where. A relative clause can either restrict meaning: For example: Of all Tolkien’s books, the one which I prefer is The Hobbit. Or it can simply add further i ...
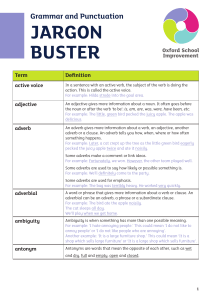
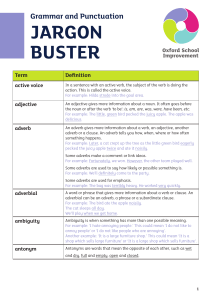
Active voice: The main focus of the sentence (the person, place, or
... The 5Ws and the H: The six basic question words: what, where, who, when, why and how. The red herring: A type of logical fallacy that is used to redirect the reader's attention from the real issue at hand. The straw man: A type of logical fallacy where an argument is not well-supported and can be ne ...
... The 5Ws and the H: The six basic question words: what, where, who, when, why and how. The red herring: A type of logical fallacy that is used to redirect the reader's attention from the real issue at hand. The straw man: A type of logical fallacy where an argument is not well-supported and can be ne ...
Participant Guide
... Another angle to take with this activity is to ask the students to describe the object in writing. This can be done after the students have observed several different objects. The descriptions could then be placed with the objects. 2. Is More Always Better? Sometimes when students are first introduc ...
... Another angle to take with this activity is to ask the students to describe the object in writing. This can be done after the students have observed several different objects. The descriptions could then be placed with the objects. 2. Is More Always Better? Sometimes when students are first introduc ...
NLP
... • The considered classes can be closed or open ▫ Closed classes are those containing a fixed set of items (es. prepositions) The usually contain function words (of, and, that, from, in, by,…) that are short, frequent and have a specific role in the grammar ...
... • The considered classes can be closed or open ▫ Closed classes are those containing a fixed set of items (es. prepositions) The usually contain function words (of, and, that, from, in, by,…) that are short, frequent and have a specific role in the grammar ...
Gerunds - jennifermlouis
... And she steals love’s sweet bait from fearful hooks.’ Discuss the effectiveness of this metaphor. Juliet is compared to a fish and Romeo to the ‘sweet bait’ on a hook. Just as a fish risks being caught and killed, so is the relationship that she is forming with Romeo a dangerous one. She wants him ...
... And she steals love’s sweet bait from fearful hooks.’ Discuss the effectiveness of this metaphor. Juliet is compared to a fish and Romeo to the ‘sweet bait’ on a hook. Just as a fish risks being caught and killed, so is the relationship that she is forming with Romeo a dangerous one. She wants him ...
Parallelism
... 1. An actor knows how to memorize his lines and getting into character. 2. Tell me where you were, what you were doing, and your reasons for doing it. 3. Clark's daily exercises include running, swimming, and to lift weights. ...
... 1. An actor knows how to memorize his lines and getting into character. 2. Tell me where you were, what you were doing, and your reasons for doing it. 3. Clark's daily exercises include running, swimming, and to lift weights. ...
morpheme
... عادة قبل الحروف الساكنة األنفية، نطق الصوت مع انسياب الهواء من خالل األنف: التأنف there is a subtle difference in the pronunciation of /i/ in the words seed and seen. In the second word, the effect of the nasal consonant [n] makes the [i] sound nasalized. We can represent this nasalization wi ...
... عادة قبل الحروف الساكنة األنفية، نطق الصوت مع انسياب الهواء من خالل األنف: التأنف there is a subtle difference in the pronunciation of /i/ in the words seed and seen. In the second word, the effect of the nasal consonant [n] makes the [i] sound nasalized. We can represent this nasalization wi ...
the appositive phrase - Mrs. Waters` English
... An appositive is a word placed after another word to explain or identify it. The appositive always appears after the word it explains or identifies. It is always a noun or a pronoun, and the word it explains is also a noun or pronoun. ex. My uncle, a lawyer, is visiting us. My teacher, Miss Marshall ...
... An appositive is a word placed after another word to explain or identify it. The appositive always appears after the word it explains or identifies. It is always a noun or a pronoun, and the word it explains is also a noun or pronoun. ex. My uncle, a lawyer, is visiting us. My teacher, Miss Marshall ...
2º bachillerato: grammar review
... 1. Wish, wanting change for the present or future with the simple past. If only I knew how to use a computer. Use: To express a wish in the present or in the future. The simple past here is an unreal past. When you use the verb to be the form is “were”. Example: I wish I were a millionaire! 2. Regre ...
... 1. Wish, wanting change for the present or future with the simple past. If only I knew how to use a computer. Use: To express a wish in the present or in the future. The simple past here is an unreal past. When you use the verb to be the form is “were”. Example: I wish I were a millionaire! 2. Regre ...
JarGon Buster
... The verb ‘will’ followed by the infinitive of the verb. For example: I will leave next week. The verb ‘will’ followed by ‘be’ and the present participle. For example: I will be leaving next week. The present progressive of the verb ‘go’ followed by ‘to’ and the verb. For example: I am going to leave ...
... The verb ‘will’ followed by the infinitive of the verb. For example: I will leave next week. The verb ‘will’ followed by ‘be’ and the present participle. For example: I will be leaving next week. The present progressive of the verb ‘go’ followed by ‘to’ and the verb. For example: I am going to leave ...
jargon buster - Cuddington and Dinton School
... The verb ‘will’ followed by the infinitive of the verb. For example: I will leave next week. The verb ‘will’ followed by ‘be’ and the present participle. For example: I will be leaving next week. The present progressive of the verb ‘go’ followed by ‘to’ and the verb. For example: I am going to leave ...
... The verb ‘will’ followed by the infinitive of the verb. For example: I will leave next week. The verb ‘will’ followed by ‘be’ and the present participle. For example: I will be leaving next week. The present progressive of the verb ‘go’ followed by ‘to’ and the verb. For example: I am going to leave ...
Basic IR Processes
... Resembles a preposition, but combined with a verb (“phrasal verbs”) Examples: find out, turn over, go on ...
... Resembles a preposition, but combined with a verb (“phrasal verbs”) Examples: find out, turn over, go on ...
english handbook
... So every word has got a function. You can’t mix them up without confusion being the result. And as literate people, we need to know those various functions. It is all very logical.4 ...
... So every word has got a function. You can’t mix them up without confusion being the result. And as literate people, we need to know those various functions. It is all very logical.4 ...
10 The Autobiography of Admiral Ahmose Part I
... In stative the transitive verb iwa “reward” has passive meaning. The compound preposition xft Hr can be translated as “in the presence/sight of,” lit. “before the face of.” The prepositional phrase r Dr lit. “to the limit” is best translated as an (apparent) adjective “whole, entire.” The next two n ...
... In stative the transitive verb iwa “reward” has passive meaning. The compound preposition xft Hr can be translated as “in the presence/sight of,” lit. “before the face of.” The prepositional phrase r Dr lit. “to the limit” is best translated as an (apparent) adjective “whole, entire.” The next two n ...
My friend Alex plays tennis.
... – noun or a pronoun that follows and renames another noun or pronoun. ...
... – noun or a pronoun that follows and renames another noun or pronoun. ...