Chapter 5 - The Periodic Law
... (1) Tellurium and iodine's places were switched 2. Horizontal rows have similar chemical properties B. Missing Elements 1. Gaps existed in Mendeleev’s table a. Mendeleev predicted the properties of the “yet to be discovered” elements (1) Scandium, germanium and gallium agreed with predictions C. Una ...
... (1) Tellurium and iodine's places were switched 2. Horizontal rows have similar chemical properties B. Missing Elements 1. Gaps existed in Mendeleev’s table a. Mendeleev predicted the properties of the “yet to be discovered” elements (1) Scandium, germanium and gallium agreed with predictions C. Una ...
Ch 5 power point
... History of the Periodic Table - Mosley • In 1911, English scientists Mosley and Rutherford recognized that elements fit into patterns better when they were arranged according to increasing number of protons, rather than increasing atomic mass. • Mosley’s work led to the modern definition of atomic ...
... History of the Periodic Table - Mosley • In 1911, English scientists Mosley and Rutherford recognized that elements fit into patterns better when they were arranged according to increasing number of protons, rather than increasing atomic mass. • Mosley’s work led to the modern definition of atomic ...
Chemistry test Review
... – Describes how many protons are in the nucleus of an atom – Also describes the number of electrons in a neutral atom ...
... – Describes how many protons are in the nucleus of an atom – Also describes the number of electrons in a neutral atom ...
Atoms, Bonding, and the Periodic Table Understanding Main Ideas
... If the statement is true, write true. If the statement is false, change the underlined word or words to make the statement true. 1. _____________ An atom’s valence electrons are those electrons that have the highest energy. 2. _____________ Atoms tend to be stable and nonreactive if they have six va ...
... If the statement is true, write true. If the statement is false, change the underlined word or words to make the statement true. 1. _____________ An atom’s valence electrons are those electrons that have the highest energy. 2. _____________ Atoms tend to be stable and nonreactive if they have six va ...
Periodic Table of Elements
... 1. There was a regular gradation in the physical and chemical properties of element. 2. Mendeléev left some gaps in his Periodic Table. Mendeléev predicted the existence of some elements that had not been discovered at that time. And named them Eka–boron, Eka–aluminium and Eka–silicon which were lat ...
... 1. There was a regular gradation in the physical and chemical properties of element. 2. Mendeléev left some gaps in his Periodic Table. Mendeléev predicted the existence of some elements that had not been discovered at that time. And named them Eka–boron, Eka–aluminium and Eka–silicon which were lat ...
CH 6: The Periodic Table
... • The Roman numeral in the American convention indicates the number of valence electrons. – Group IA elements have 1 valence electron. – Group VA elements have 5 valence electrons. • When using the IUPAC designations for group numbers, the last digit indicates the number of valence electrons. – Grou ...
... • The Roman numeral in the American convention indicates the number of valence electrons. – Group IA elements have 1 valence electron. – Group VA elements have 5 valence electrons. • When using the IUPAC designations for group numbers, the last digit indicates the number of valence electrons. – Grou ...
Periodic table trends
... • Reactivity is how likely and violently the atom will react with other substances • Metals- reactivity decreases across a period and increases down a family • Non-metals- reactivity increases across a period and decreases down a family ...
... • Reactivity is how likely and violently the atom will react with other substances • Metals- reactivity decreases across a period and increases down a family • Non-metals- reactivity increases across a period and decreases down a family ...
Develo ment of the Atomic Theo John Dalton - (English 1766
... elements appeared to be misplaced in terms of their properties. He assumed that their atomic mass was just calculated incorrectly. 50 yrs. later a British scientist - Henry Moseley discovered the atomic numbers of the elements. He noticed that when the elements were rearranged in order of increasing ...
... elements appeared to be misplaced in terms of their properties. He assumed that their atomic mass was just calculated incorrectly. 50 yrs. later a British scientist - Henry Moseley discovered the atomic numbers of the elements. He noticed that when the elements were rearranged in order of increasing ...
1 CHAPTER 5 – THE PERIODIC LAW What types of useful
... A. Before the Periodic Table was invented, about 63 elements were known. However, they were not organized and only random properties were known about each of the elements. Scientist (who are always looking for patterns) wanted to organize these. B. Dmitri Mendeleev – he made cards for all 63 known e ...
... A. Before the Periodic Table was invented, about 63 elements were known. However, they were not organized and only random properties were known about each of the elements. Scientist (who are always looking for patterns) wanted to organize these. B. Dmitri Mendeleev – he made cards for all 63 known e ...
Periodic Table Metals, Non
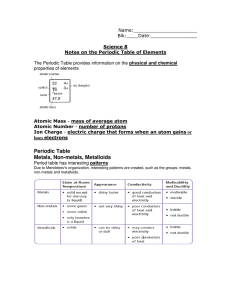
... Notes on the Periodic Table of Elements The Periodic Table provides information on the physical and chemical properties of elements ...
... Notes on the Periodic Table of Elements The Periodic Table provides information on the physical and chemical properties of elements ...
1 CHAPTER 5 – THE PERIODIC LAW What types of useful
... A. Before the Periodic Table was invented, about 63 elements were known. However, they were not organized and only random properties were known about each of the elements. Scientist (who are always looking for patterns) wanted to organize these. B. Dmitri Mendeleev – he made cards for all 63 known e ...
... A. Before the Periodic Table was invented, about 63 elements were known. However, they were not organized and only random properties were known about each of the elements. Scientist (who are always looking for patterns) wanted to organize these. B. Dmitri Mendeleev – he made cards for all 63 known e ...
"Part 1" Resource
... unbroken order of increasing weight of their atoms - the periodicity concept - which was then used by Mark Leach's model of the telluric screw Newlands and Meyer. The vis Tellurique, published a decade prior to the table of Dimitri Mendeleev, was little noticed by chemists. His paper describing his ...
... unbroken order of increasing weight of their atoms - the periodicity concept - which was then used by Mark Leach's model of the telluric screw Newlands and Meyer. The vis Tellurique, published a decade prior to the table of Dimitri Mendeleev, was little noticed by chemists. His paper describing his ...
CHAPTER 5, THE PERIODIC LAW Section 1, History of the Periodic
... Atomic radius is defined as ! the distance between the nuclei of identical atoms that are bonded together. An ion is an atom or group of bonded atoms that has a positive or negative charge. Ionization is any process that results in the formation of an ion. The atom’s electron affinity is the energy ...
... Atomic radius is defined as ! the distance between the nuclei of identical atoms that are bonded together. An ion is an atom or group of bonded atoms that has a positive or negative charge. Ionization is any process that results in the formation of an ion. The atom’s electron affinity is the energy ...
Periodic Properties of the Elements
... element’s physical properties. After selecting the element, you will analyze the patterns of these properties as they occur across a period as well as trends that exist down a group. You will identify several mystery elements by investigating and interpreting periodic trends. Remember that valence e ...
... element’s physical properties. After selecting the element, you will analyze the patterns of these properties as they occur across a period as well as trends that exist down a group. You will identify several mystery elements by investigating and interpreting periodic trends. Remember that valence e ...
Matching - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... ____ 32. What is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom in the gaseous state called? a. nuclear energy c. shielding energy b. ionization energy d. electronegative energy ____ 33. For Group 2 (2A) metals, which electron is the most difficult to remove? a. the first b. the second c. th ...
... ____ 32. What is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom in the gaseous state called? a. nuclear energy c. shielding energy b. ionization energy d. electronegative energy ____ 33. For Group 2 (2A) metals, which electron is the most difficult to remove? a. the first b. the second c. th ...
Regions of the Periodic Table
... noble gases: elements in group VIIIA of the periodic table. 8 valence electrons (except for He which has 2)—full valence shells do not form ions do not react with other compounds ...
... noble gases: elements in group VIIIA of the periodic table. 8 valence electrons (except for He which has 2)—full valence shells do not form ions do not react with other compounds ...
Periodicity
... atomic theory, many elements were discovered. To be able to understand and predict their properties it was necessary to organize them. In 1869, Dimitri Mendeleev published his periodic table. In his table the elements were arranged in order of increasing atomic mass. The properties of the elements a ...
... atomic theory, many elements were discovered. To be able to understand and predict their properties it was necessary to organize them. In 1869, Dimitri Mendeleev published his periodic table. In his table the elements were arranged in order of increasing atomic mass. The properties of the elements a ...
orbital form the s block (groups 1 and 2). Elements in
... increasing atomic number. The vertical columns in the periodic table are referred to as groups and the horizontal rows are known as periods. The elements in groups 1 and 2 and those in groups 13 to 18 are called main-group elements. Elements in groups 3 to 12 are known as transition elements and the ...
... increasing atomic number. The vertical columns in the periodic table are referred to as groups and the horizontal rows are known as periods. The elements in groups 1 and 2 and those in groups 13 to 18 are called main-group elements. Elements in groups 3 to 12 are known as transition elements and the ...
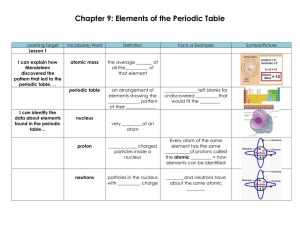
Chapter 9: Elements of the Periodic Table
... do not ordinarily form _____________ because atoms of noble gases do not usually ______, lose or _________ electrons ...
... do not ordinarily form _____________ because atoms of noble gases do not usually ______, lose or _________ electrons ...
Week 9 (wk9) - Riverside Local Schools
... 3. Group 1 elements contain a single s electron. The ease with which the single electron is lost helps make the Group 1 metal 4. The elements of Group 1 of the periodic table are known as… 5. In their pure state, all of the alkali metals have a silvery appearance and are… 6. The elements of Group 2 ...
... 3. Group 1 elements contain a single s electron. The ease with which the single electron is lost helps make the Group 1 metal 4. The elements of Group 1 of the periodic table are known as… 5. In their pure state, all of the alkali metals have a silvery appearance and are… 6. The elements of Group 2 ...
Elements of the Periodic Table
... One very useful noble gas is neon. Although neon is colorless, when one runs an electric charge through a tube of the substance it glows a reddish orange color. These true neon lights are mainly used for advertising signs when a business wants to catch the eye of potential customers. Neon can also b ...
... One very useful noble gas is neon. Although neon is colorless, when one runs an electric charge through a tube of the substance it glows a reddish orange color. These true neon lights are mainly used for advertising signs when a business wants to catch the eye of potential customers. Neon can also b ...
Week 1 (wk1) - Riverside Local Schools
... 3. For main-group elements, the valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost... ELECTRONEGATIVITY (pg. 151-152) 1. Valence electrons hold atoms together in... 2. LINUS PAULING, one of America’s most famous chemists, devised a scale of numerical values reflecting the tendency of an atom to... ...
... 3. For main-group elements, the valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost... ELECTRONEGATIVITY (pg. 151-152) 1. Valence electrons hold atoms together in... 2. LINUS PAULING, one of America’s most famous chemists, devised a scale of numerical values reflecting the tendency of an atom to... ...
MATTER AND PERIODIC TABLE
... positively charged protons and neutral neutrons. A cloud of negatively charged electrons surrounds the nucleus of an atom. ...
... positively charged protons and neutral neutrons. A cloud of negatively charged electrons surrounds the nucleus of an atom. ...
Chapter 5.1 History of PT - Effingham County Schools
... Dmitri Mendeleev noticed that when the elements were arranged in order of increasing atomic mass, certain similarities in their chemical properties appeared at regular ...
... Dmitri Mendeleev noticed that when the elements were arranged in order of increasing atomic mass, certain similarities in their chemical properties appeared at regular ...
Group 3 element

Group 3 is a group of elements in the periodic table. This group, like other d-block groups, should contain four elements, but it is not agreed what elements belong in the group. Scandium (Sc) and yttrium (Y) are always included, but the other two spaces are usually occupied by lanthanum (La) and actinium (Ac), or by lutetium (Lu) and lawrencium (Lr); less frequently, it is considered the group should be expanded to 32 elements (with all the lanthanides and actinides included) or contracted to contain only scandium and yttrium. The group itself has not acquired a trivial name; however, scandium, yttrium and the lanthanides are sometimes called rare earth metals.Three group 3 elements occur naturally, scandium, yttrium, and either lanthanum or lutetium. Lanthanum continues the trend started by two lighter members in general chemical behavior, while lutetium behaves more similarly to yttrium. This is in accordance with the trend for period 6 transition metals to behave more similarly to their upper periodic table neighbors. This trend is seen from hafnium, which is almost identical chemically to zirconium, to mercury, which is quite distant chemically from cadmium, but still shares with it almost equal atomic size and other similar properties. They all are silvery-white metals under standard conditions. The fourth element, either actinium or lawrencium, has only radioactive isotopes. Actinium, which occurs only in trace amounts, continues the trend in chemical behavior for metals that form tripositive ions with a noble gas configuration; synthetic lawrencium is calculated and partially shown to be more similar to lutetium and yttrium. So far, no experiments have been conducted to synthesize any element that could be the next group 3 element. Unbiunium (Ubu), which could be considered a group 3 element if preceded by lanthanum and actinium, might be synthesized in the near future, it being only three spaces away from the current heaviest element known, ununoctium.