structure of atoms
... Thomson’s model of the atom – plum pudding or blueberry muffin, static Explored by Rutherford using scattering experiments Shot alpha particles through gold foil, get info on inner structure of atoms from the pattern of scattered alpha particles (know the basic ideas here) Surprising thing was t ...
... Thomson’s model of the atom – plum pudding or blueberry muffin, static Explored by Rutherford using scattering experiments Shot alpha particles through gold foil, get info on inner structure of atoms from the pattern of scattered alpha particles (know the basic ideas here) Surprising thing was t ...
Periodic Table of Elements
... entering an orbital farther away from the nucleus. As such this electron would be less attracted to the nucleus and would release less energy when added. 6. Metallic character : The metallic character tends to decrease going across left to right along a period. Metallic properties increases as we mo ...
... entering an orbital farther away from the nucleus. As such this electron would be less attracted to the nucleus and would release less energy when added. 6. Metallic character : The metallic character tends to decrease going across left to right along a period. Metallic properties increases as we mo ...
HS standard 4 2017
... Sr behaves MOST like magnesium because it is in the same family, the alkaline earth metals. Members of the same family have the same number of valence electrons; this is an important reason why they behave alike. 17) A researcher is trying to create a new super conductive wire. Which category on the ...
... Sr behaves MOST like magnesium because it is in the same family, the alkaline earth metals. Members of the same family have the same number of valence electrons; this is an important reason why they behave alike. 17) A researcher is trying to create a new super conductive wire. Which category on the ...
Click Here
... The size of an anion will be larger than that of the parent atom because the addition of one or more electrons would result in increased repulsion among the electrons and a decrease in effective nuclear charge When we find some atoms and ions which contain the same number of electrons, we call them ...
... The size of an anion will be larger than that of the parent atom because the addition of one or more electrons would result in increased repulsion among the electrons and a decrease in effective nuclear charge When we find some atoms and ions which contain the same number of electrons, we call them ...
Periodic Relationships Among the Elements
... • The ability of an atom to attract electrons in a molecule Energy is usually evolved in these processes (negative signs) •EN across a period increases from left to right •EN within the group increases from down to up •EN for metals is low while it is high for non-metals * The fluorine is the highes ...
... • The ability of an atom to attract electrons in a molecule Energy is usually evolved in these processes (negative signs) •EN across a period increases from left to right •EN within the group increases from down to up •EN for metals is low while it is high for non-metals * The fluorine is the highes ...
The periodic table shows trends in atomic structure.
... Seaborg went on to predict the properties of elements with even higher atomic numbers. It wasn’t long before all these elements had been produced. Some were first made in labs at Berkeley. Seaborg’s predictions turned out to be true. Much as Mendeleev had done almost a century before, Seaborg had ma ...
... Seaborg went on to predict the properties of elements with even higher atomic numbers. It wasn’t long before all these elements had been produced. Some were first made in labs at Berkeley. Seaborg’s predictions turned out to be true. Much as Mendeleev had done almost a century before, Seaborg had ma ...
File
... upon their similar properties. He left blank spaces where he thought undiscovered elements would go, based on their properties ...
... upon their similar properties. He left blank spaces where he thought undiscovered elements would go, based on their properties ...
Unit 3 Review - RHSChemistry
... states of matter (s, l, g) f. React readily with ________, metals especially alkali, to produce salts. (halogen = salt former) ...
... states of matter (s, l, g) f. React readily with ________, metals especially alkali, to produce salts. (halogen = salt former) ...
Parts of the Periodic Table
... than alkali metals. They also have higher melting points. (Remember: Melting Point is an intensive property. It stays the same, no matter how much of a substance you have.) • Although less reactive than alkali metals, they are still too reactive to be found in nature as free elements. • EX: Calcium ...
... than alkali metals. They also have higher melting points. (Remember: Melting Point is an intensive property. It stays the same, no matter how much of a substance you have.) • Although less reactive than alkali metals, they are still too reactive to be found in nature as free elements. • EX: Calcium ...
Addrienne`s Element Lesson Plan
... Definition: A column or group of columns in the periodic table; elements in one group have the same number of electrons in the outermost shell Context: Elements in each group share similar chemical properties. period Definition: A row of the periodic table; each row corresponds to the number of elec ...
... Definition: A column or group of columns in the periodic table; elements in one group have the same number of electrons in the outermost shell Context: Elements in each group share similar chemical properties. period Definition: A row of the periodic table; each row corresponds to the number of elec ...
Slide 1
... Groups are divided into blocks based on sublevels. There is an s-block, p-block, d-block, and f-block. S-block is group 1 and 2. Group 1 electron configurations end with ns1, group 2 end with ns2. P-block is group 13 through 18. Electron configurations proceed as np1, np2, np3, np4, np5, and np6. Th ...
... Groups are divided into blocks based on sublevels. There is an s-block, p-block, d-block, and f-block. S-block is group 1 and 2. Group 1 electron configurations end with ns1, group 2 end with ns2. P-block is group 13 through 18. Electron configurations proceed as np1, np2, np3, np4, np5, and np6. Th ...
02 The structure of the periodic table II
... increased, scientists began to think about organizing them in some way Between 1829 to 1869, many different classification systems were proposed, each organizing the elements in a different way ...
... increased, scientists began to think about organizing them in some way Between 1829 to 1869, many different classification systems were proposed, each organizing the elements in a different way ...
Chapter 4
... • Nobody noticed it before because it is completely unreactive. • In 1868, helium had been discovered as part of the sun and in 1895, Ramsay showed its existence on earth. • In 1898, Ramsay discovered krypton and xenon. Friedrich Ernst Dorn discovered radon in 1900. ...
... • Nobody noticed it before because it is completely unreactive. • In 1868, helium had been discovered as part of the sun and in 1895, Ramsay showed its existence on earth. • In 1898, Ramsay discovered krypton and xenon. Friedrich Ernst Dorn discovered radon in 1900. ...
The placement of an element on the periodic table gives clues about
... The periodic table was developed by Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869. It provides a powerful tool for studying the elements and how they combine. There are over 100 known elements, so it is necessary to use a systematic method to organize them. The periodic table indicates each element's atomic symbol, atom ...
... The periodic table was developed by Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869. It provides a powerful tool for studying the elements and how they combine. There are over 100 known elements, so it is necessary to use a systematic method to organize them. The periodic table indicates each element's atomic symbol, atom ...
Periodic Table HW Unit
... Elements can be differentiated by chemical properties. Chemical properties describe how an element behaves during a chemical reaction. Some elements exist in two or more forms in the same phase. These ...
... Elements can be differentiated by chemical properties. Chemical properties describe how an element behaves during a chemical reaction. Some elements exist in two or more forms in the same phase. These ...
Chapter 6 Review
... Use this completion exercise to check your understanding of the concepts and terms that are introduced in this section. Each blank can be completed with a term, short phrase, or number. The periodic table displays the symbols and ...
... Use this completion exercise to check your understanding of the concepts and terms that are introduced in this section. Each blank can be completed with a term, short phrase, or number. The periodic table displays the symbols and ...
Recording Measurements
... a. Which two of the given elements have the most similar chemical properties? sulfur and oxygen b. Explain your answer in terms of atomic structure. They have the same number of valence electrons 8. Based on the Periodic Table, explain why Na and K have similar chemical properties. [1] They have the ...
... a. Which two of the given elements have the most similar chemical properties? sulfur and oxygen b. Explain your answer in terms of atomic structure. They have the same number of valence electrons 8. Based on the Periodic Table, explain why Na and K have similar chemical properties. [1] They have the ...
Concepts
... they are also arranged according to their ability to bond with other atoms (their chemical properties). Arranging the table by mass creates discrepancies within the pattern of the elements. The periodicity of the elements is not entirely lost if the elements are arranged by atomic mass. Since the pe ...
... they are also arranged according to their ability to bond with other atoms (their chemical properties). Arranging the table by mass creates discrepancies within the pattern of the elements. The periodicity of the elements is not entirely lost if the elements are arranged by atomic mass. Since the pe ...
Chapter 5 Organizing The Elements
... _____(the number of isotopes and their mass in nature) • Atoms of 2 isotopes have different _________masses(isotopes have different # of neutrons than protons) they are usually equal ...
... _____(the number of isotopes and their mass in nature) • Atoms of 2 isotopes have different _________masses(isotopes have different # of neutrons than protons) they are usually equal ...
Chapter 6 Review
... Elements that are characterized by the filling of p orbitals are classified as _____. As you move from left to right across the second period of the periodic table, ionization energy __. Atomic size generally decreases as you ____. ...
... Elements that are characterized by the filling of p orbitals are classified as _____. As you move from left to right across the second period of the periodic table, ionization energy __. Atomic size generally decreases as you ____. ...
Test Review Guide
... Use the periodic table to describe atom types in terms of #’s of protons and e-s Ar has __________________ protons and _____________________electrons Understand the Bohr model of the atom and what the symbols represent The Bohr circles represent ______________________________________________________ ...
... Use the periodic table to describe atom types in terms of #’s of protons and e-s Ar has __________________ protons and _____________________electrons Understand the Bohr model of the atom and what the symbols represent The Bohr circles represent ______________________________________________________ ...
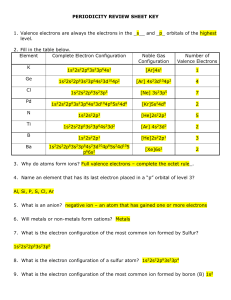
periodicity review sheet key
... Using the graphs from your notes, period table or text book, answer the following with: increases(I), decreases (D), or remains the same (R). __R___ 14. As the number of neutrons in an atom of a given element increases, its atomic number generally ________________ . __I___ 15. Going down a group of ...
... Using the graphs from your notes, period table or text book, answer the following with: increases(I), decreases (D), or remains the same (R). __R___ 14. As the number of neutrons in an atom of a given element increases, its atomic number generally ________________ . __I___ 15. Going down a group of ...
Section 2: Exploring the Periodic Table
... – metal: an element that is shiny and that conducts heat and electricity well – nonmetal: an element that conducts heat and electricity poorly – semiconductor (or metalloid): an element or compound that conducts electric current better than an insulator does but not as well as a conductor does ...
... – metal: an element that is shiny and that conducts heat and electricity well – nonmetal: an element that conducts heat and electricity poorly – semiconductor (or metalloid): an element or compound that conducts electric current better than an insulator does but not as well as a conductor does ...
Chemical Periodicity - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... The metallic elements at the far left of the periodic table have low electronegativities. By contrast, the nonmetallic elements at the far right (excluding the noble gases), have high electronegativities. The electronegativity of cesium, a metal, the least electronegative element, is 0.7; the elect ...
... The metallic elements at the far left of the periodic table have low electronegativities. By contrast, the nonmetallic elements at the far right (excluding the noble gases), have high electronegativities. The electronegativity of cesium, a metal, the least electronegative element, is 0.7; the elect ...