Arrays
... Also note that i starts at 0 and goes up to but does not go to 10 which would be out of bounds ...
... Also note that i starts at 0 and goes up to but does not go to 10 which would be out of bounds ...
Significant Figure Rules
... 1. Non-zero digits are always significant. 2. Any zeros between two significant digits are significant. 3. A final zero or trailing zeros in the decimal portion ONLY are significant. Focus on these rules and learn them well. They will be used extensively throughout the remainder of this course. You ...
... 1. Non-zero digits are always significant. 2. Any zeros between two significant digits are significant. 3. A final zero or trailing zeros in the decimal portion ONLY are significant. Focus on these rules and learn them well. They will be used extensively throughout the remainder of this course. You ...
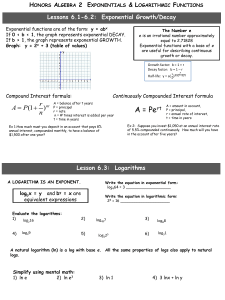
Lesson 15: Piecewise Functions
... PIECEWISE-LINEAR FUNCTION. Given a number of non-overlapping intervals on the real number line, a (real) piecewiselinear function is a function from the union of the intervals to the set of real numbers such that the function is defined by (possibly different) linear functions on each interval. ABSO ...
... PIECEWISE-LINEAR FUNCTION. Given a number of non-overlapping intervals on the real number line, a (real) piecewiselinear function is a function from the union of the intervals to the set of real numbers such that the function is defined by (possibly different) linear functions on each interval. ABSO ...
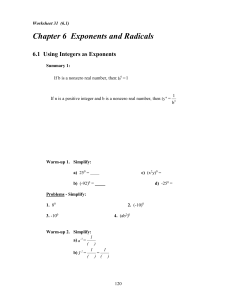
Worksheet 31 (6
... 2. The exponent of the 10 corresponds to the number of places the decimal point moves when changing the number to a number between 1 and 10. 3. The exponent is: - negative if the original number is less than 1: 0.0036 = (3.6) (10)-3 (Decimal moved to the right.) - positive if the original number is ...
... 2. The exponent of the 10 corresponds to the number of places the decimal point moves when changing the number to a number between 1 and 10. 3. The exponent is: - negative if the original number is less than 1: 0.0036 = (3.6) (10)-3 (Decimal moved to the right.) - positive if the original number is ...
CHAPTER 3: POLYNOMIAL AND RATIONAL FUNCTIONS
... 2. Change the inequality symbol to an equals sign and solve the related equation. 3. Find the values of the variable for which the related rational function is not defined. 4. The numbers found in steps (2) and (3) are called critical values. Use the critical values to divide the x-axis into interva ...
... 2. Change the inequality symbol to an equals sign and solve the related equation. 3. Find the values of the variable for which the related rational function is not defined. 4. The numbers found in steps (2) and (3) are called critical values. Use the critical values to divide the x-axis into interva ...
Elementary mathematics
Elementary mathematics consists of mathematics topics frequently taught at the primary or secondary school levels. The most basic topics in elementary mathematics are arithmetic and geometry. Beginning in the last decades of the 20th century, there has been an increased emphasis on problem solving. Elementary mathematics is used in everyday life in such activities as making change, cooking, buying and selling stock, and gambling. It is also an essential first step on the path to understanding science.In secondary school, the main topics in elementary mathematics are algebra and trigonometry. Calculus, even though it is often taught to advanced secondary school students, is usually considered college level mathematics.