CHAPTER 3: POLYNOMIAL AND RATIONAL FUNCTIONS
... 2. Change the inequality symbol to an equals sign and solve the related equation. 3. Find the values of the variable for which the related rational function is not defined. 4. The numbers found in steps (2) and (3) are called critical values. Use the critical values to divide the x-axis into interva ...
... 2. Change the inequality symbol to an equals sign and solve the related equation. 3. Find the values of the variable for which the related rational function is not defined. 4. The numbers found in steps (2) and (3) are called critical values. Use the critical values to divide the x-axis into interva ...
1. If the pattern continues, which term will consist of 21 squares?
... adding four each time. So to continue the pattern would be ...
... adding four each time. So to continue the pattern would be ...
Algebra 2, with Trig
... If P (x ) is a polynomial function of degree n 1 with leading coefficient an 0 , then P (x ) has exactly n linear factors. P( x) an x c1 x c2 x c3 x cn where c1, c2, … , cn are complex numbers. (real and/or imaginary) The Number of Zeros of a Polynomial Function Theorem: If P ...
... If P (x ) is a polynomial function of degree n 1 with leading coefficient an 0 , then P (x ) has exactly n linear factors. P( x) an x c1 x c2 x c3 x cn where c1, c2, … , cn are complex numbers. (real and/or imaginary) The Number of Zeros of a Polynomial Function Theorem: If P ...
We are given a set of n lectures (in no particular order) that are
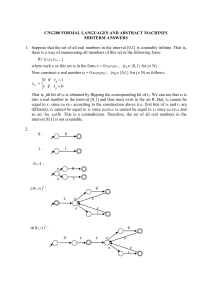
... When the initial automaton is reduced to a two-state automaton, the transition on the arc gives us the desired regular expression. Thus, L(M) = a*b(aUba*b)* 4. Suppose that L={an : n is prime} is regular. Then, according to pumping lemma, there must be an integer n≥1 such that any string w L with ...
... When the initial automaton is reduced to a two-state automaton, the transition on the arc gives us the desired regular expression. Thus, L(M) = a*b(aUba*b)* 4. Suppose that L={an : n is prime} is regular. Then, according to pumping lemma, there must be an integer n≥1 such that any string w L with ...
Problems
... Then Dave lays cards in K rows and three columns on a table starting with card numbered by 1 filling the first row from left to right, then second row, and so on till he finishes with the last row. Hal then says in which column Dave put the card with a number he thought of. Dave then picks up the ca ...
... Then Dave lays cards in K rows and three columns on a table starting with card numbered by 1 filling the first row from left to right, then second row, and so on till he finishes with the last row. Hal then says in which column Dave put the card with a number he thought of. Dave then picks up the ca ...
Exam 1.2 - Mrs. Matthews Class
... 20. A story is often told about how the great mathematician Carl Friedrich Gauss (17771855) at a very young age was told by his teacher to find the sum of the first 100 counting numbers. While his classmates toiled at the problem, Carl simply wrote down a single number and handed it in to his teache ...
... 20. A story is often told about how the great mathematician Carl Friedrich Gauss (17771855) at a very young age was told by his teacher to find the sum of the first 100 counting numbers. While his classmates toiled at the problem, Carl simply wrote down a single number and handed it in to his teache ...
Elementary mathematics
Elementary mathematics consists of mathematics topics frequently taught at the primary or secondary school levels. The most basic topics in elementary mathematics are arithmetic and geometry. Beginning in the last decades of the 20th century, there has been an increased emphasis on problem solving. Elementary mathematics is used in everyday life in such activities as making change, cooking, buying and selling stock, and gambling. It is also an essential first step on the path to understanding science.In secondary school, the main topics in elementary mathematics are algebra and trigonometry. Calculus, even though it is often taught to advanced secondary school students, is usually considered college level mathematics.