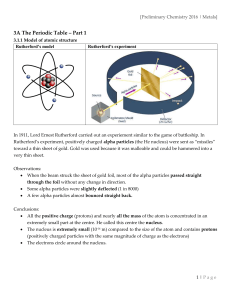
Unit 3 Periodic Table Vocabulary
... Alkaline Earth Metals - Any of a group of metallic elements that includes beryllium, magnesium, calcium, strontium, barium, and radium. Because the alkaline-earth metals have two electrons in their outer shell, they react easily with other elements and are found in nature only in compounds. Sentence ...
... Alkaline Earth Metals - Any of a group of metallic elements that includes beryllium, magnesium, calcium, strontium, barium, and radium. Because the alkaline-earth metals have two electrons in their outer shell, they react easily with other elements and are found in nature only in compounds. Sentence ...
groups - Orangefield ISD
... Mass of individual atoms ◦ Protons and neutrons have approx. same mass ◦ Electrons are MUCH smaller ◦ B/c the masses are so small (must use scientific notation, which is cumbersome), chemists developed a standard for ...
... Mass of individual atoms ◦ Protons and neutrons have approx. same mass ◦ Electrons are MUCH smaller ◦ B/c the masses are so small (must use scientific notation, which is cumbersome), chemists developed a standard for ...
CHAPTER 5, THE PERIODIC LAW Section 1, History of the Periodic
... AM – alkali metal AEM – alkaliearth metal TM – transition metal M/S – metalloid/semimetal H – halogen NG – noble gas L – lanthanide A – actinide ...
... AM – alkali metal AEM – alkaliearth metal TM – transition metal M/S – metalloid/semimetal H – halogen NG – noble gas L – lanthanide A – actinide ...
Atomic Theory - Aurora City Schools
... Do we have to know this? • But you’ll hear more about that in chemistry. For now realize that each energy level is made up of sublevels that hold specific amounts of electrons. • The sublevels are called orbitals and are named s, p, d, f • You can see these patterns in the periodic table. ...
... Do we have to know this? • But you’ll hear more about that in chemistry. For now realize that each energy level is made up of sublevels that hold specific amounts of electrons. • The sublevels are called orbitals and are named s, p, d, f • You can see these patterns in the periodic table. ...
Chemical Periodicity - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... The metallic elements at the far left of the periodic table have low electronegativities. By contrast, the nonmetallic elements at the far right (excluding the noble gases), have high electronegativities. The electronegativity of cesium, a metal, the least electronegative element, is 0.7; the elect ...
... The metallic elements at the far left of the periodic table have low electronegativities. By contrast, the nonmetallic elements at the far right (excluding the noble gases), have high electronegativities. The electronegativity of cesium, a metal, the least electronegative element, is 0.7; the elect ...
Chemical Periodicity - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... The metallic elements at the far left of the periodic table have low electronegativities. By contrast, the nonmetallic elements at the far right (excluding the noble gases), have high electronegativities. The electronegativity of cesium, a metal, the least electronegative element, is 0.7; the elect ...
... The metallic elements at the far left of the periodic table have low electronegativities. By contrast, the nonmetallic elements at the far right (excluding the noble gases), have high electronegativities. The electronegativity of cesium, a metal, the least electronegative element, is 0.7; the elect ...
Reactions of Main Group ...ith Nitrogen - Chemwiki
... General characteristics of the alkali metals include: relatively abundant high chemical reactivity (the most active metals) low melting and boiling points largest atomic and ionic radii highly metallic character low first ionization energy (they lose their valence electrons easily creating a strong ...
... General characteristics of the alkali metals include: relatively abundant high chemical reactivity (the most active metals) low melting and boiling points largest atomic and ionic radii highly metallic character low first ionization energy (they lose their valence electrons easily creating a strong ...
Notes
... Potassium. K+ is required for glucose metabolism, protein synthesis and activation of some enzymes (e.g. pyruvate kinase and dialkylglycine decarboxylase). The K+ binds to anionic sites on the enzyme, changing its conformation and activating it. Magnesium. Mg2+ has numerous roles but probably the mo ...
... Potassium. K+ is required for glucose metabolism, protein synthesis and activation of some enzymes (e.g. pyruvate kinase and dialkylglycine decarboxylase). The K+ binds to anionic sites on the enzyme, changing its conformation and activating it. Magnesium. Mg2+ has numerous roles but probably the mo ...
Unit 1 Review Sheet
... 1. Outline the development of the modern periodic table from Newlands to Glenn Seaborg? Include the theorists and explain what their contributions to the development of the periodic table were. ...
... 1. Outline the development of the modern periodic table from Newlands to Glenn Seaborg? Include the theorists and explain what their contributions to the development of the periodic table were. ...
AP Chemistry Chapter 7
... • Made some exceptions to place elements in rows with similar properties (Te and I) • Horizontal rows have similar chemical properties • Gaps for “yet to be discovered” elements • Left questions: why didn’t some elements fit in order of increasing mass? Why did some elements exhibit periodic behavio ...
... • Made some exceptions to place elements in rows with similar properties (Te and I) • Horizontal rows have similar chemical properties • Gaps for “yet to be discovered” elements • Left questions: why didn’t some elements fit in order of increasing mass? Why did some elements exhibit periodic behavio ...
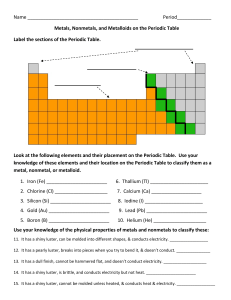
Name Period_____________ Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids on
... Use your knowledge of the physical properties of metals and nonmetals to classify these: 11. It has a shiny luster, can be molded into different shapes, & conducts electricity. _________________ 12. It has a pearly luster, breaks into pieces when you try to bend it, & doesn’t conduct. ______________ ...
... Use your knowledge of the physical properties of metals and nonmetals to classify these: 11. It has a shiny luster, can be molded into different shapes, & conducts electricity. _________________ 12. It has a pearly luster, breaks into pieces when you try to bend it, & doesn’t conduct. ______________ ...
The Periodic Table
... • Not found pure in nature, but combined with other elements (as compounds). • Soft – can be cut with a knife. • Usually lustrous but will dull in contact with air. ...
... • Not found pure in nature, but combined with other elements (as compounds). • Soft – can be cut with a knife. • Usually lustrous but will dull in contact with air. ...
The Periodic Table
... • Not found pure in nature, but combined with other elements (as compounds). • Soft – can be cut with a knife. • Usually lustrous but will dull in contact with air. ...
... • Not found pure in nature, but combined with other elements (as compounds). • Soft – can be cut with a knife. • Usually lustrous but will dull in contact with air. ...
Honors Chapter 6 Powerpoint
... metals and nonmetals, metal atoms tend to lose electrons, and nonmetal atoms tend to gain electrons. The transfer has a predictable effect on the size of the ions that form. ...
... metals and nonmetals, metal atoms tend to lose electrons, and nonmetal atoms tend to gain electrons. The transfer has a predictable effect on the size of the ions that form. ...
PT Trends WS
... 9. Compare the neutral atom to the ion of the same element for the following elements, Na, Ga, N, and F. Draw the atom (protons, neutrons, and electrons) and ion including electron configuration labeled in the energy levels. Provide the atomic symbol for all. During the formation of an ...
... 9. Compare the neutral atom to the ion of the same element for the following elements, Na, Ga, N, and F. Draw the atom (protons, neutrons, and electrons) and ion including electron configuration labeled in the energy levels. Provide the atomic symbol for all. During the formation of an ...
Chapter 3 Atoms and Elements Classification of Matter Matter Matter
... Examples of atomic number and number of protons: Carbon has atomic number 6; every C atom has six protons. Copper has atomic number 29; every Cu atom has 29 protons. ...
... Examples of atomic number and number of protons: Carbon has atomic number 6; every C atom has six protons. Copper has atomic number 29; every Cu atom has 29 protons. ...
The Periodic Table
... 27. Draw lewis dot structures to represent number of valence electrons in an atom or ion 28. Use octet rule to predict how reactive or inert an element may be 7.2 Ionic Bonds and Ionic Compounds 29. Explain the electrical charge of an ionic compound 30. First learn logic of ionic bond formation, the ...
... 27. Draw lewis dot structures to represent number of valence electrons in an atom or ion 28. Use octet rule to predict how reactive or inert an element may be 7.2 Ionic Bonds and Ionic Compounds 29. Explain the electrical charge of an ionic compound 30. First learn logic of ionic bond formation, the ...
The Periodic Law
... • More than 60 elements had been discovered. • There was no method to accurately determine an elements atomic mass or number of atoms of an element in a compound. • 1860, Germany, first international congress of chemists ...
... • More than 60 elements had been discovered. • There was no method to accurately determine an elements atomic mass or number of atoms of an element in a compound. • 1860, Germany, first international congress of chemists ...
Periodic Table
... While it was the first periodic table, Mendeleev had very different elements, such as the very reactive potassium and the very stable copper, in the same family. Forty years later Moseley rearranged the elements by their atomic number which gave the table better periodicity. Mendeleev ...
... While it was the first periodic table, Mendeleev had very different elements, such as the very reactive potassium and the very stable copper, in the same family. Forty years later Moseley rearranged the elements by their atomic number which gave the table better periodicity. Mendeleev ...
Chapter 9: The Atom
... Chapter 9.2 Objectives and Vocabulary Use the periodic table to obtain information about the elements. Explain the relationship between an element's placement on the periodic table and its chemical properties. Understand a simple model of electron arrangement. ...
... Chapter 9.2 Objectives and Vocabulary Use the periodic table to obtain information about the elements. Explain the relationship between an element's placement on the periodic table and its chemical properties. Understand a simple model of electron arrangement. ...
Chapter 6 Notes
... Based on their electron configurations. The noble gases all have a full outer shell so they rarely take part in a reaction ...
... Based on their electron configurations. The noble gases all have a full outer shell so they rarely take part in a reaction ...
PERIODIC TABLE OF THE ELEMENTS
... Are malleable and ductile · Are brittle (if solid) Lose electrons in a chemical · Gain or share electrons in a reaction chemical reaction Metals ...
... Are malleable and ductile · Are brittle (if solid) Lose electrons in a chemical · Gain or share electrons in a reaction chemical reaction Metals ...
Revision map for the Periodic Table
... 21. The rows of elements are called periods. 22. The higher the atomic number of an element, the higher the period. 23. The number of shells of electrons determines the period an element is in. 24. The Periodic Table is arranged in several blocks. 25. The elements are arranged in columns in the Peri ...
... 21. The rows of elements are called periods. 22. The higher the atomic number of an element, the higher the period. 23. The number of shells of electrons determines the period an element is in. 24. The Periodic Table is arranged in several blocks. 25. The elements are arranged in columns in the Peri ...
Period 2 element
The period 2 elements are the chemical elements in the second row (or period) of the periodic table. The periodic table is laid out in rows to illustrate recurring (periodic) trends in the chemical behavior of the elements as their atomic number increases; a new row is started when chemical behavior begins to repeat, creating columns of elements with similar properties.The second period contains the elements lithium, beryllium, boron, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, and neon. This situation can be explained by modern theories of atomic structure. In a quantum mechanical description of atomic structure, this period corresponds to the filling of the 2s and 2p orbitals. Period 2 elements obey the octet rule in that they need eight electrons to complete their valence shell. The maximum number of electrons that these elements can accommodate is ten, two in the 1s orbital, two in the 2s orbital and six in the 2p orbital. All of the elements in the period can form diatomic molecules except beryllium and neon.