File - CToThe3Chemistry
... Ability to attract electrons decreases as you move down groups, since the nucleus (and positive charge for attracting) is further and further away. Ability to attract electrons increases as you move across periods, since the nucleus (and positive charge for attracting) is becoming more and more posi ...
... Ability to attract electrons decreases as you move down groups, since the nucleus (and positive charge for attracting) is further and further away. Ability to attract electrons increases as you move across periods, since the nucleus (and positive charge for attracting) is becoming more and more posi ...
periodicity - Knockhardy
... Decreases down a group Despite the increase in nuclear charge, the increased shielding and the increased distance from the nucleus means the electrons are held less strongly and need less energy for their removal. ...
... Decreases down a group Despite the increase in nuclear charge, the increased shielding and the increased distance from the nucleus means the electrons are held less strongly and need less energy for their removal. ...
Cations (positive ions) are smaller than their respective atoms.
... single atom of this element. It is also # of electrons. The symbol for this element. This is the average atomic mass, it is the number of protons + neutrons, or the mass of the nucleus of an atom. ...
... single atom of this element. It is also # of electrons. The symbol for this element. This is the average atomic mass, it is the number of protons + neutrons, or the mass of the nucleus of an atom. ...
Periodicity
... elements with the most similar properties were side by side. He left empty spaces for elements that had not yet been discovered. Later those elements were found to fit right in the spaces of Mendeleev’s table. In 1913, Henry Moseley (1887-1915), a British physicist, determined the nuclear charge (at ...
... elements with the most similar properties were side by side. He left empty spaces for elements that had not yet been discovered. Later those elements were found to fit right in the spaces of Mendeleev’s table. In 1913, Henry Moseley (1887-1915), a British physicist, determined the nuclear charge (at ...
14-15-Periodic Trends
... Enthalpy of Electronic Attraction (Electron Affinity) •An element’s enthalpy of electronic attraction (ΔEAH) is the enthalpy change when a neutral atom in the gas phase acquires an extra electron in the lowest energy orbital available: •These values are negative for most elements, so an ‘increase’ ...
... Enthalpy of Electronic Attraction (Electron Affinity) •An element’s enthalpy of electronic attraction (ΔEAH) is the enthalpy change when a neutral atom in the gas phase acquires an extra electron in the lowest energy orbital available: •These values are negative for most elements, so an ‘increase’ ...
Name: Date: Period: 1. Read the following and make annotations
... A positive ion is known as a cation. The formation of a cation by the loss of one or more electrons always leads to a decrease in atomic radius because the removal of the highest-energy-level electrons results in a smaller electron cloud. Also, the remaining electrons are drawn closer to the nucleus ...
... A positive ion is known as a cation. The formation of a cation by the loss of one or more electrons always leads to a decrease in atomic radius because the removal of the highest-energy-level electrons results in a smaller electron cloud. Also, the remaining electrons are drawn closer to the nucleus ...
Alkaline Earth Metals
... electricity • in solid form, they are dull and brittle • usually have lower densities than metals • most of the crust, atmosphere and oceans are made up of nonmetals. • Bulk tissues of living organisms are composed almost entirely of nonmetals. • Many nonmetals (hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, ...
... electricity • in solid form, they are dull and brittle • usually have lower densities than metals • most of the crust, atmosphere and oceans are made up of nonmetals. • Bulk tissues of living organisms are composed almost entirely of nonmetals. • Many nonmetals (hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, ...
File
... The ionization energies for element X are listed in the table above. On the basis of the data, element X is most likely to ...
... The ionization energies for element X are listed in the table above. On the basis of the data, element X is most likely to ...
Honors Chemistry Periodic Table Notes Antoine Lavoisier (1700`s
... Cations have ______ electrons to become __________ charged– they become smaller than their ___________ atom. Electrons lost are __________ electrons. This can leave an empty outer orbital resulting in a smaller ________. Electrostatic repulsion between remaining electrons decreases, so remaining ele ...
... Cations have ______ electrons to become __________ charged– they become smaller than their ___________ atom. Electrons lost are __________ electrons. This can leave an empty outer orbital resulting in a smaller ________. Electrostatic repulsion between remaining electrons decreases, so remaining ele ...
Chemistry Periodic Table and Trends Periodic Table The periodic
... shell of the atom. It increases going down groups of the periodic table because energy shells are added to accommodate more electrons. For instance, Hydrogen (H), Lithium (Li) and Sodium (Na) are in the same group (column). For each atom, a new shell is added as you go down the group because each ha ...
... shell of the atom. It increases going down groups of the periodic table because energy shells are added to accommodate more electrons. For instance, Hydrogen (H), Lithium (Li) and Sodium (Na) are in the same group (column). For each atom, a new shell is added as you go down the group because each ha ...
Week 1 (wk1) - Riverside Local Schools
... 1. An electron can be removed from an atom if enough... 2. Using A as a symbol for an atom of any element, the process can be expressed as follows... A + energy 3. An ION is an atom or group of bonded atoms that has a... 4. A process that results in the formation of an ion is referred to as 5. T ...
... 1. An electron can be removed from an atom if enough... 2. Using A as a symbol for an atom of any element, the process can be expressed as follows... A + energy 3. An ION is an atom or group of bonded atoms that has a... 4. A process that results in the formation of an ion is referred to as 5. T ...
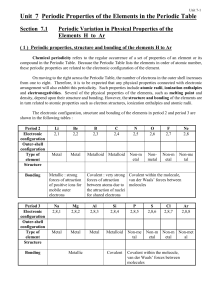
Unit 7 Periodic Properties of the Elements in the Periodic Table
... to the ‘cloud’ of negative electrons. Since the mobile valence electrons are responsible for the bonding in metals, it is not surprising that moving from sodium (one outer shell electron) through magnesium (two outer shell electrons) to aluminium (three outer shell electrons) the bonding gets gradua ...
... to the ‘cloud’ of negative electrons. Since the mobile valence electrons are responsible for the bonding in metals, it is not surprising that moving from sodium (one outer shell electron) through magnesium (two outer shell electrons) to aluminium (three outer shell electrons) the bonding gets gradua ...
The Periodic Table and Chemical Properties
... The designer of this table wanted to emphasize the periods, so it has two periods of 8 elements, then two of 18 elements, then two of 32, and so on. The “arms” that stick out from the spiral are the lanthanides and actinides. These are the elements that you will find in those two rows down below the ...
... The designer of this table wanted to emphasize the periods, so it has two periods of 8 elements, then two of 18 elements, then two of 32, and so on. The “arms” that stick out from the spiral are the lanthanides and actinides. These are the elements that you will find in those two rows down below the ...
Unit 10 Lecture Notes
... 1. The periodic table is probably the most important tool in chemistry 2. The name “periodic” is associated with the periodic law which states that the properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic number (simply, properties of elements repeat according to the periodic table arrange ...
... 1. The periodic table is probably the most important tool in chemistry 2. The name “periodic” is associated with the periodic law which states that the properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic number (simply, properties of elements repeat according to the periodic table arrange ...
Chapter 5: The Periodic Law
... Electronegativity: the tendency for an atom to attract electrons to itself when it is chemically combined with another element Expressed on the Pauling Electronegativity Scale Noble gases do not have electronegativities because they do not participate in many reactions ...
... Electronegativity: the tendency for an atom to attract electrons to itself when it is chemically combined with another element Expressed on the Pauling Electronegativity Scale Noble gases do not have electronegativities because they do not participate in many reactions ...
Chapter 6
... The behavior and properties of transition metals is not very predictable. Inner Transition Elements (beneath the main body of Periodic Table) Lanthanide series: Ce-Lu, also called rare earth metals Actinide series: Th-Lr, radioactive elements that exist for only very short periods of time before dec ...
... The behavior and properties of transition metals is not very predictable. Inner Transition Elements (beneath the main body of Periodic Table) Lanthanide series: Ce-Lu, also called rare earth metals Actinide series: Th-Lr, radioactive elements that exist for only very short periods of time before dec ...
Chapter 6 Periodic trends
... carbon), brittle, mostly gases - Metalloids- have properties of both metals and nonmetals Ex. Silicon- alone it is an insulator (nonmetal) o Combined with boron it is a conductor (metal) ...
... carbon), brittle, mostly gases - Metalloids- have properties of both metals and nonmetals Ex. Silicon- alone it is an insulator (nonmetal) o Combined with boron it is a conductor (metal) ...
Periodic Trends Homework 1) Why does atomic radius decrease as
... 2. Given any two elements within a group, is the element with the larger atomic number likely to have a larger or smaller radius? larger, more protons means more electrons and a larger atomic radius 3. Explain why is it harder to remove an inner shell electron than a valence electron from an atom. A ...
... 2. Given any two elements within a group, is the element with the larger atomic number likely to have a larger or smaller radius? larger, more protons means more electrons and a larger atomic radius 3. Explain why is it harder to remove an inner shell electron than a valence electron from an atom. A ...
groups - Northside Middle School
... Easily lose valence electron 1 valence electron Chemically reactive – do not occur as free elements in nature Soft, silvery Good conductor of electricity React violently with water React with halogens to form salts ...
... Easily lose valence electron 1 valence electron Chemically reactive – do not occur as free elements in nature Soft, silvery Good conductor of electricity React violently with water React with halogens to form salts ...
atomic - Sammons Sci
... Placed most elements in order of atomic mass and noticed repeating (periodic) trends in this arrangement. Did not exactly work arranging according to atomic mass 1. Why could most elements be arranged according to mass, but a few could not? 2. What was the reason for chemical periodicity? ...
... Placed most elements in order of atomic mass and noticed repeating (periodic) trends in this arrangement. Did not exactly work arranging according to atomic mass 1. Why could most elements be arranged according to mass, but a few could not? 2. What was the reason for chemical periodicity? ...
chem 1411 – chapter 8
... Increase in effective nuclear charge Decrease in atomic radius Both conditions require more energy to remove the electron from the valence shell Ionization energy of elements decreases down the group because, Decrease in effective nuclear charge Increase in atomic radius 4. Electron Affinity ...
... Increase in effective nuclear charge Decrease in atomic radius Both conditions require more energy to remove the electron from the valence shell Ionization energy of elements decreases down the group because, Decrease in effective nuclear charge Increase in atomic radius 4. Electron Affinity ...
chemistry chapter 11 & 12
... – React readily with halogens to form common salts • Example: NaCl (table salt) – React readily with water to form basic solutions (alkali), hydrogen and Energy. ...
... – React readily with halogens to form common salts • Example: NaCl (table salt) – React readily with water to form basic solutions (alkali), hydrogen and Energy. ...
III. Periodic Trends
... a. By what two metrics did he arrange the elements in his table? Increasing atomic mass & similar chemical and physical properties b. He predicted the discovery of several elements, and even described some of their physical and chemical properties. Gallium was one of those elements. The predictions ...
... a. By what two metrics did he arrange the elements in his table? Increasing atomic mass & similar chemical and physical properties b. He predicted the discovery of several elements, and even described some of their physical and chemical properties. Gallium was one of those elements. The predictions ...
Period 3 element
A period 3 element is one of the chemical elements in the third row (or period) of the periodic table of the chemical elements. The periodic table is laid out in rows to illustrate recurring (periodic) trends in the chemical behaviour of the elements as their atomic number increases: a new row is begun when the periodic table skips a row and a chemical behaviour begins to repeat, meaning that elements with similar behavior fall into the same vertical columns. The third period contains eight elements: sodium, magnesium, aluminium, silicon, phosphorus, sulfur, chlorine, and argon. The first two, sodium and magnesium, are members of the s-block of the periodic table, while the others are members of the p-block. Note that there is a 3d orbital, but it is not filled until Period 4, such giving the period table its characteristic shape of ""two rows at a time"". All of the period 3 elements occur in nature and have at least one stable isotope.