The Periodic Table and Periodic Law
... configuration of iron (a transition element) is [Ar]4s 23d 6, which has its valence electrons in orbits of both the third and fourth energy levels. ...
... configuration of iron (a transition element) is [Ar]4s 23d 6, which has its valence electrons in orbits of both the third and fourth energy levels. ...
Chp4Sec1and2
... the pattern that led to the periodic table? Mendeleev noticed that a pattern of properties appeared when he arranged the elements in order of increasing atomic mass. ...
... the pattern that led to the periodic table? Mendeleev noticed that a pattern of properties appeared when he arranged the elements in order of increasing atomic mass. ...
Catalyst – September, 7(1+1) 2009 - stroh
... electronegativity related? Key Point #5: Atomic radius and electronegativity are indirectly/inversely related. ...
... electronegativity related? Key Point #5: Atomic radius and electronegativity are indirectly/inversely related. ...
Atoms and the Periodic Table Mini quiz
... 1. The order of elements in the periodic table is based on a. the number of protons in the nucleus. c. the number of neutrons in the nucleus. b. the electric charge of the nucleus. d. atomic mass. 2. Atoms of elements that are in the same group have the same number of a. protons. c. valence electron ...
... 1. The order of elements in the periodic table is based on a. the number of protons in the nucleus. c. the number of neutrons in the nucleus. b. the electric charge of the nucleus. d. atomic mass. 2. Atoms of elements that are in the same group have the same number of a. protons. c. valence electron ...
H Unit 4: Periodic Table
... The table is also arranged in vertical columns called “groups” or “families” and horizontal rows called “periods.” Each arrangement is significant. The elements in each vertical column or group have similar properties. There are a number of major groups with similar properties. They are as follows: ...
... The table is also arranged in vertical columns called “groups” or “families” and horizontal rows called “periods.” Each arrangement is significant. The elements in each vertical column or group have similar properties. There are a number of major groups with similar properties. They are as follows: ...
10TH CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS CHEMISRY As a large
... b) Newland placed two elements in the same slot in a particular group. He could not offer any explanation for such an arrangement. c) Newland thought that only 50 elements existed in nature and no more elements were likely to be discovered. But he was proved wrong. d) When noble gas elements were di ...
... b) Newland placed two elements in the same slot in a particular group. He could not offer any explanation for such an arrangement. c) Newland thought that only 50 elements existed in nature and no more elements were likely to be discovered. But he was proved wrong. d) When noble gas elements were di ...
File
... The table is also arranged in vertical columns called “groups” or “families” and horizontal rows called “periods.” Each arrangement is significant. The elements in each vertical column or group have similar properties. There are a number of major groups with similar properties. They are as follows: ...
... The table is also arranged in vertical columns called “groups” or “families” and horizontal rows called “periods.” Each arrangement is significant. The elements in each vertical column or group have similar properties. There are a number of major groups with similar properties. They are as follows: ...
File
... Matter is anything that has a mass and takes up space. An element is the simplest form of matter, which cannot be broken down any further. Elements are listed on Table S and the periodic table. Their symbols start with an uppercase letter. a. Which of the following is not matter? ___________________ ...
... Matter is anything that has a mass and takes up space. An element is the simplest form of matter, which cannot be broken down any further. Elements are listed on Table S and the periodic table. Their symbols start with an uppercase letter. a. Which of the following is not matter? ___________________ ...
Elements are the building blocks of matter.
... 1. Which elements have outer shells that are full of electrons? Where are they located on the periodic table? 2. Which elements have only 1 electron in their outer shell? Where are they located on the periodic table? 3. What do you notice about the number of valence electrons (electrons in the outer ...
... 1. Which elements have outer shells that are full of electrons? Where are they located on the periodic table? 2. Which elements have only 1 electron in their outer shell? Where are they located on the periodic table? 3. What do you notice about the number of valence electrons (electrons in the outer ...
Periodic Table Ch4 Honors
... – With oxygen to make water – With carbon to make organic compounds – With nitrogen to make ammonia ...
... – With oxygen to make water – With carbon to make organic compounds – With nitrogen to make ammonia ...
unit iv – the periodic table
... The periodic table is the arrangement of the elements in order of their atomic numbers so that elements with similar properties fall in the same column or group. Noble Gases were added to the periodic table later - early 1900's Lanthanides - f-Block was added in the early 1900's after the identity ...
... The periodic table is the arrangement of the elements in order of their atomic numbers so that elements with similar properties fall in the same column or group. Noble Gases were added to the periodic table later - early 1900's Lanthanides - f-Block was added in the early 1900's after the identity ...
Ch 5: Periodiciy 2
... their atomic masses and their chemical properties. He found that some elements could not be put into groups with similar properties and at the same time stay in order. Mullis ...
... their atomic masses and their chemical properties. He found that some elements could not be put into groups with similar properties and at the same time stay in order. Mullis ...
File - Lenora Henderson`s Flipped Chemistry Classroom
... same time as Lothar Meyer (German chemist); these periodic tables were identical, but because Mendeleev published his table first and was able to explain its periodic trends better his was given the credit. ...
... same time as Lothar Meyer (German chemist); these periodic tables were identical, but because Mendeleev published his table first and was able to explain its periodic trends better his was given the credit. ...
Chemical Periodicity
... a) How does the size of the atom vary as you move left to right across the periodic table? Why? The atomic radius of atoms typically decreases from left to right across a period. This is because the force of attraction between nuclei and electrons lessens as you move down the table due to the electr ...
... a) How does the size of the atom vary as you move left to right across the periodic table? Why? The atomic radius of atoms typically decreases from left to right across a period. This is because the force of attraction between nuclei and electrons lessens as you move down the table due to the electr ...
Periodic Trends
... increasing the attraction between the nucleus and the outer energy level resulting in a greater ability for atoms to attract electrons to it. ...
... increasing the attraction between the nucleus and the outer energy level resulting in a greater ability for atoms to attract electrons to it. ...
Period
... • One-half the distance between the nuclei of identical atoms that are bonded together ...
... • One-half the distance between the nuclei of identical atoms that are bonded together ...
Periodic Trends - CK
... The concept of effective nuclear charge (Ze f f ) can be used in concert with electron shielding. In simplified form the effective nuclear charge is equal to the atomic number (Z) minus the number of inner or non-valence electrons. For example, lithium has 3 protons, 2 inner electrons, and 1 valence ...
... The concept of effective nuclear charge (Ze f f ) can be used in concert with electron shielding. In simplified form the effective nuclear charge is equal to the atomic number (Z) minus the number of inner or non-valence electrons. For example, lithium has 3 protons, 2 inner electrons, and 1 valence ...
periods - Madeira City Schools
... ¥ Elements at the bottom of the periodic table have electrons that are more “unhappy” than the elements at the top of the periodic table. ¥ Elements at the bottom of the periodic table are larger (greater atomic radius, remember the trend!) because they have more energy levels. Those electrons in ...
... ¥ Elements at the bottom of the periodic table have electrons that are more “unhappy” than the elements at the top of the periodic table. ¥ Elements at the bottom of the periodic table are larger (greater atomic radius, remember the trend!) because they have more energy levels. Those electrons in ...
Slide 1
... 2. In 1913 Henry Moseley determined the atomic number of each element based on the protons in the atom. 3. The modern periodic table is arranged in order of increasing atomic number. 4. There are seven rows or periods on the periodic table. 5. Each period corresponds to a principle energy level. 6. ...
... 2. In 1913 Henry Moseley determined the atomic number of each element based on the protons in the atom. 3. The modern periodic table is arranged in order of increasing atomic number. 4. There are seven rows or periods on the periodic table. 5. Each period corresponds to a principle energy level. 6. ...
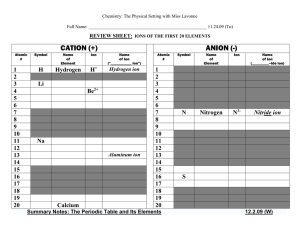
IONS OF THE FIRST 20 ELEMENTS
... The alkaline earth elements are metallic elements found in the second group of the periodic table. All alkaline earth elements have an oxidation number of +2, making them very reactive. Because of their reactivity, the alkaline metals are not found free in nature. The Alkaline Earth Metals are: Bery ...
... The alkaline earth elements are metallic elements found in the second group of the periodic table. All alkaline earth elements have an oxidation number of +2, making them very reactive. Because of their reactivity, the alkaline metals are not found free in nature. The Alkaline Earth Metals are: Bery ...
Unit 2 - Periodic Behavior and Ionic Bonding
... A. The physical and chemical properties of the elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers B. Elements on the table are arranged in order of increasing atomic number (number of protons) II. ...
... A. The physical and chemical properties of the elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers B. Elements on the table are arranged in order of increasing atomic number (number of protons) II. ...
Activity 2 Elements and Their Properties
... bodies different in form.” The first modern definition of element, which is not much different, is from Robert Boyle: “Bodies, which not being made of any other bodies, or of one another, are the ingredients of which all those . . . mixed bodies are . . . compounded.” Scientists now state that an el ...
... bodies different in form.” The first modern definition of element, which is not much different, is from Robert Boyle: “Bodies, which not being made of any other bodies, or of one another, are the ingredients of which all those . . . mixed bodies are . . . compounded.” Scientists now state that an el ...
Chemical Periodicity
... 3 How is the modern periodic table different from the first periodic table? The first periodic table was in columns, not rows, only shows their atomic number. 4 What is the modern periodic law? Characteristics of the elements occur periodically when organized by atomic number. 5 Organization of ...
... 3 How is the modern periodic table different from the first periodic table? The first periodic table was in columns, not rows, only shows their atomic number. 4 What is the modern periodic law? Characteristics of the elements occur periodically when organized by atomic number. 5 Organization of ...
Appendices: Cluster 2 Atoms and Elements
... • systematically placed the elements into an organized table. • stated that the properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic masses and that the relationship among the elements is called periodic law. • arranged the 63 elements known at that time in order of their atomic mass so th ...
... • systematically placed the elements into an organized table. • stated that the properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic masses and that the relationship among the elements is called periodic law. • arranged the 63 elements known at that time in order of their atomic mass so th ...
Period 3 element
A period 3 element is one of the chemical elements in the third row (or period) of the periodic table of the chemical elements. The periodic table is laid out in rows to illustrate recurring (periodic) trends in the chemical behaviour of the elements as their atomic number increases: a new row is begun when the periodic table skips a row and a chemical behaviour begins to repeat, meaning that elements with similar behavior fall into the same vertical columns. The third period contains eight elements: sodium, magnesium, aluminium, silicon, phosphorus, sulfur, chlorine, and argon. The first two, sodium and magnesium, are members of the s-block of the periodic table, while the others are members of the p-block. Note that there is a 3d orbital, but it is not filled until Period 4, such giving the period table its characteristic shape of ""two rows at a time"". All of the period 3 elements occur in nature and have at least one stable isotope.