File
... Periodic Table Atomic Mass - mass of average atom Atomic Number - number of protons & electrons of a neutral atom Ion Charge - electric charge that forms when an atom gains or loses electrons ...
... Periodic Table Atomic Mass - mass of average atom Atomic Number - number of protons & electrons of a neutral atom Ion Charge - electric charge that forms when an atom gains or loses electrons ...
Chapter 6
... • Law of Octaves – same properties repeat every 8th element • (but it didn’t account for Noble gases and transition metals) ...
... • Law of Octaves – same properties repeat every 8th element • (but it didn’t account for Noble gases and transition metals) ...
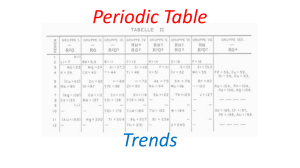
2- Periodic Trends
... Mendeleev (correctly) predicted the mass of elements yet to be discovered and left spaces open for them ...
... Mendeleev (correctly) predicted the mass of elements yet to be discovered and left spaces open for them ...
Chemical-Periodicity
... • Dmitri Mendeleev (1834 – 1907) – Russian chemist – Noticed regular (periodic) recurrence of chemical and physical properties after arranging by increasing atomic mass. • Eventually led to grouping by similar properties side by side ...
... • Dmitri Mendeleev (1834 – 1907) – Russian chemist – Noticed regular (periodic) recurrence of chemical and physical properties after arranging by increasing atomic mass. • Eventually led to grouping by similar properties side by side ...
The Periodic Table
... • Columns are also grouped into families. • Families may be one column, or several columns put together. • Families have names rather than numbers. (Just like your family has a common last name.) ...
... • Columns are also grouped into families. • Families may be one column, or several columns put together. • Families have names rather than numbers. (Just like your family has a common last name.) ...
Study Sheet for Unit Test
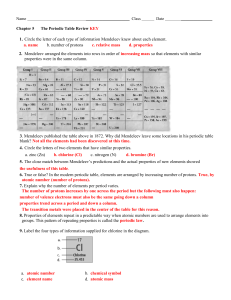
... 7. Know the main types of elements in the periodic table (metals, semimetals, non-metals, inert gases)? Where are they generally located on the table? What are some of the properties of each? 8. What is the reactivity of the groups in the periodic table? Which ones are most reactive? Which group rar ...
... 7. Know the main types of elements in the periodic table (metals, semimetals, non-metals, inert gases)? Where are they generally located on the table? What are some of the properties of each? 8. What is the reactivity of the groups in the periodic table? Which ones are most reactive? Which group rar ...
Chapter 5 – The Periodic Law
... Correctly predicted the physical and chemical properties of the missing elements based on the trends he saw in the groups…they were all discovered by 1886 ...
... Correctly predicted the physical and chemical properties of the missing elements based on the trends he saw in the groups…they were all discovered by 1886 ...
Document
... Review atomic theory and the major contributions by Democritus, Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford, and Bohr. Place their atomic models in a sequence according to the timeline. Know the mass (a.m.u), location, and charge of each particle in the atom. Determine the mass number of an atom given the number of ...
... Review atomic theory and the major contributions by Democritus, Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford, and Bohr. Place their atomic models in a sequence according to the timeline. Know the mass (a.m.u), location, and charge of each particle in the atom. Determine the mass number of an atom given the number of ...
Sample Questions Sample Questions Standard Atomic Notation
... breakthrough in the understanding of the elements. However, it was discovered later on that using the atomic mass was not the proper way to organize the elements. • The key was to use the atomic number or the number of protons. • Therefore, a new law was born. • The modern periodic law states ...
... breakthrough in the understanding of the elements. However, it was discovered later on that using the atomic mass was not the proper way to organize the elements. • The key was to use the atomic number or the number of protons. • Therefore, a new law was born. • The modern periodic law states ...
Periodic table
... (ISBN 0-85404-381-0), written by Keith Taber, The Royal Society of Chemistry Fellow 20002001. This book includes many useful classroom activities that can be used to identify student misconceptions, and to help students construct chemical concepts. The exercise below is based on concept mapping. It ...
... (ISBN 0-85404-381-0), written by Keith Taber, The Royal Society of Chemistry Fellow 20002001. This book includes many useful classroom activities that can be used to identify student misconceptions, and to help students construct chemical concepts. The exercise below is based on concept mapping. It ...
"Part 1" Resource
... table, and his first work was published in 1924. This was known as the "Periodic Chart of the Atoms". Into the 1930s the heaviest elements were being put up in the body of the periodic table, and Glenn Seaborg "plucked those out" while working with Fermi in Chicago, naming them the Actinide series, ...
... table, and his first work was published in 1924. This was known as the "Periodic Chart of the Atoms". Into the 1930s the heaviest elements were being put up in the body of the periodic table, and Glenn Seaborg "plucked those out" while working with Fermi in Chicago, naming them the Actinide series, ...
PT objectives
... including highly reactive metals, less reactive metals, highly reactive nonmetals, less reactive non-metals, and some almost completely non-reactive gases. Students understand that substances are often placed in categories together if they react in similar ways. Examples of this in the periodic tabl ...
... including highly reactive metals, less reactive metals, highly reactive nonmetals, less reactive non-metals, and some almost completely non-reactive gases. Students understand that substances are often placed in categories together if they react in similar ways. Examples of this in the periodic tabl ...
Name - TeacherWeb
... The number of protons increases by one across the period but the following must also happen: number of valence electrons must also be the same going down a column properties trend across a period and down a column. The transition metals were placed in the center of the table for this reason. 8. Prop ...
... The number of protons increases by one across the period but the following must also happen: number of valence electrons must also be the same going down a column properties trend across a period and down a column. The transition metals were placed in the center of the table for this reason. 8. Prop ...
File
... names or symbols, are written on these cards. As the cards are arranged and rearranged based on logical trends in some of these properties, the nature of the periodic law should reveal itself. ...
... names or symbols, are written on these cards. As the cards are arranged and rearranged based on logical trends in some of these properties, the nature of the periodic law should reveal itself. ...
Introduction to the Periodic Table
... * electrons – negatively charged particle that surrounds the nucleus ...
... * electrons – negatively charged particle that surrounds the nucleus ...
02 The structure of the periodic table II
... Development of the Periodic Table discovery of the atomic number clarified some inconsistencies in Mendeleev’s periodic table It made sense for iodine (I) to come ...
... Development of the Periodic Table discovery of the atomic number clarified some inconsistencies in Mendeleev’s periodic table It made sense for iodine (I) to come ...
Chapter 6
... • arranged in order of atomic mass • appeared to be a repetition of properties every eighth element • arranged elements into groups of 7 • Law of Octaves – same properties repeat every 8th element • (but it didn’t account for Noble gases and transition metals) ...
... • arranged in order of atomic mass • appeared to be a repetition of properties every eighth element • arranged elements into groups of 7 • Law of Octaves – same properties repeat every 8th element • (but it didn’t account for Noble gases and transition metals) ...
Episode 7 - The Periodic Table
... 14. Why are the electrons in the outer shell of an atom important? They are the electrons involved in the formation of chemical bonds ...
... 14. Why are the electrons in the outer shell of an atom important? They are the electrons involved in the formation of chemical bonds ...
The Periodic Table - Teach-n-Learn-Chem
... 14. Why are the electrons in the outer shell of an atom important? They are the electrons involved in the formation of chemical bonds ...
... 14. Why are the electrons in the outer shell of an atom important? They are the electrons involved in the formation of chemical bonds ...
Basics of the Periodic Table
... *Directions: Use the Periodic Table in your textbook to answer the following questions. Read carefully! ...
... *Directions: Use the Periodic Table in your textbook to answer the following questions. Read carefully! ...
CPA Study Guide for Chapter 6 Test The Periodic Table Know the
... Trend in atomic radius; comparing radii in an isoelectronic series; comparing the radius of a parent atom to its ion Be able to identify the number of valence electrons in each family of the representative elements Be able to predict the charge on an ion based on the atoms tendency to obtain a noble ...
... Trend in atomic radius; comparing radii in an isoelectronic series; comparing the radius of a parent atom to its ion Be able to identify the number of valence electrons in each family of the representative elements Be able to predict the charge on an ion based on the atoms tendency to obtain a noble ...
Section 5.1 Review
... 3. _____ The modern periodic law states that (a) no two electrons with the same spin can be found in the same place in an atom. (b) the physical and chemical properties of an element are functions of its atomic number. (c) electrons exhibit properties of both particles and waves. (d) the chemical pr ...
... 3. _____ The modern periodic law states that (a) no two electrons with the same spin can be found in the same place in an atom. (b) the physical and chemical properties of an element are functions of its atomic number. (c) electrons exhibit properties of both particles and waves. (d) the chemical pr ...
Dmitri Mendeleev

Dmitri Ivanovich Mendeleev (/ˌmɛndəlˈeɪəf/; Russian: Дми́трий Ива́нович Менделе́ев; IPA: [ˈdmʲitrʲɪj ɪˈvanəvʲɪtɕ mʲɪndʲɪˈlʲejɪf]; 8 February 1834 – 2 February 1907 O.S. 27 January 1834 – 20 January 1907) was a Russian chemist and inventor. He formulated the Periodic Law, created his own version of the periodic table of elements, and used it to correct the properties of some already discovered elements and also to predict the properties of eight elements yet to be discovered.