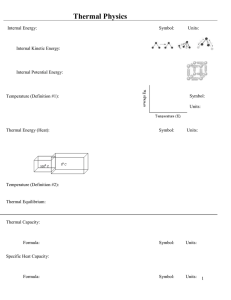
Calculation of Mass Attenuation Coefficients of
... radiation. (b) The energy level diagram of an atom, illustrating the excitation of K, L, M and The binding energy of a K-electron increases with increasing atomic number. It is only 13.6 eV in the lightest element hydrogen, but increases to 88 keV in lead. The probability of photoelectric absorption ...
... radiation. (b) The energy level diagram of an atom, illustrating the excitation of K, L, M and The binding energy of a K-electron increases with increasing atomic number. It is only 13.6 eV in the lightest element hydrogen, but increases to 88 keV in lead. The probability of photoelectric absorption ...
Modification of Coulomb law and energy levels of hydrogen atom in
... LLL corresponds to nρ = 0, σz = −1, m = 0, −1, −2, .... A wave function factorizes on those describing free motion along a magnetic field with momentum pz and those describing motion in perpendicular to magnetic field plane: ...
... LLL corresponds to nρ = 0, σz = −1, m = 0, −1, −2, .... A wave function factorizes on those describing free motion along a magnetic field with momentum pz and those describing motion in perpendicular to magnetic field plane: ...
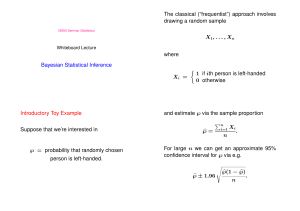
Bayesian Statistical Inference Introductory Toy Example Suppose
... A common interval answer in Bayesian statistics is a 95% credible interval posterior density function ...
... A common interval answer in Bayesian statistics is a 95% credible interval posterior density function ...
transparencies - Rencontres de Blois
... • Average absorbing column (from X-rays) 5 to 6 1021 cm-2. • Likely distance is 1 to 1.5 kpc (association with clouds in the West and absorption value). Radius is then 8 to 13 pc. • Might be remnant of SN 393 (1600 years old). • Central compact object is present, therefore SN II. Possibly exploded i ...
... • Average absorbing column (from X-rays) 5 to 6 1021 cm-2. • Likely distance is 1 to 1.5 kpc (association with clouds in the West and absorption value). Radius is then 8 to 13 pc. • Might be remnant of SN 393 (1600 years old). • Central compact object is present, therefore SN II. Possibly exploded i ...
for week 5 general science review
... • EM energy is a continuous range from lower energy AMFM radio to gamma rays. • EM travels in the sine wave and oscillates from magnetic to electric fields • If you get enough energy it can penetrate matter.These generally have shorter wavelengths and increased frequency. • Each can be described as ...
... • EM energy is a continuous range from lower energy AMFM radio to gamma rays. • EM travels in the sine wave and oscillates from magnetic to electric fields • If you get enough energy it can penetrate matter.These generally have shorter wavelengths and increased frequency. • Each can be described as ...
Exercises - Tiwariacademy.net
... Monochromatic light of wavelength 632.8 nm is produced by a helium-neon laser. The power emitted is 9.42 mW. (a) Find the energy and momentum of each photon in the light beam, (b) How many photons per second, on the average, arrive at a target irradiated by this beam? (Assume the beam to have unifor ...
... Monochromatic light of wavelength 632.8 nm is produced by a helium-neon laser. The power emitted is 9.42 mW. (a) Find the energy and momentum of each photon in the light beam, (b) How many photons per second, on the average, arrive at a target irradiated by this beam? (Assume the beam to have unifor ...
Document
... to be one-atom tunnelling states (e.g. Smith 1979). In our present paper we draw attention to a distinct and general class of possible tunnelling centres, and one which has particular promise for such systems produced during radiation amorphisation. Since we are concerned primarily with the initiati ...
... to be one-atom tunnelling states (e.g. Smith 1979). In our present paper we draw attention to a distinct and general class of possible tunnelling centres, and one which has particular promise for such systems produced during radiation amorphisation. Since we are concerned primarily with the initiati ...
Teknologi Solid State - Universitas Brawijaya
... • Mechanical waves are waves which propagate through a material medium (solid, liquid, or gas) at a wave speed which depends on the elastic and inertial properties of that medium. There are two basic types of wave motion for mechanical waves: longitudinal waves and transverse waves. • It corresponds ...
... • Mechanical waves are waves which propagate through a material medium (solid, liquid, or gas) at a wave speed which depends on the elastic and inertial properties of that medium. There are two basic types of wave motion for mechanical waves: longitudinal waves and transverse waves. • It corresponds ...
Density of states
In solid-state and condensed matter physics, the density of states (DOS) of a system describes the number of states per interval of energy at each energy level that are available to be occupied. Unlike isolated systems, like atoms or molecules in gas phase, the density distributions are not discrete like a spectral density but continuous. A high DOS at a specific energy level means that there are many states available for occupation. A DOS of zero means that no states can be occupied at that energy level. In general a DOS is an average over the space and time domains occupied by the system. Localvariations, most often due to distortions of the original system, are often called local density of states (LDOS). If the DOS of an undisturbedsystem is zero, the LDOS can locally be non-zero due to the presence of a local potential.