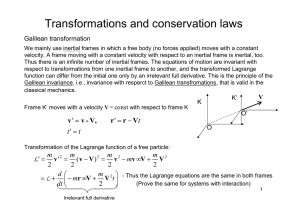
Dual energy solution and supercausality
... foreseen by Pauli’s exclusion principle. Einstein had not predicted that the information between the two electrons could travel at a speed greater than light, but he had suggested this experiment in order to show that it was possible to know all the information about particles (position and speed), ...
... foreseen by Pauli’s exclusion principle. Einstein had not predicted that the information between the two electrons could travel at a speed greater than light, but he had suggested this experiment in order to show that it was possible to know all the information about particles (position and speed), ...
Assignment #1
... permittivity of free space, respectively. Write these equations using index notation. 4. For a gas currently not in thermodynamic equilibrium, all of the gas molecules have their velocity vectors uniformly, but still randomly distributed inside a cubical volume in velocity space, such that there are ...
... permittivity of free space, respectively. Write these equations using index notation. 4. For a gas currently not in thermodynamic equilibrium, all of the gas molecules have their velocity vectors uniformly, but still randomly distributed inside a cubical volume in velocity space, such that there are ...
Solutions
... 2. Note that the annul axis mentioned in this question is perpendicular to the plane of the disc, that is, we want to find the potential a perpendicular distance y from the center of the disc. [The case is similar to Chp 25, Example 10.] So for part (a), let’s first compute the charge density: Q 4Q ...
... 2. Note that the annul axis mentioned in this question is perpendicular to the plane of the disc, that is, we want to find the potential a perpendicular distance y from the center of the disc. [The case is similar to Chp 25, Example 10.] So for part (a), let’s first compute the charge density: Q 4Q ...
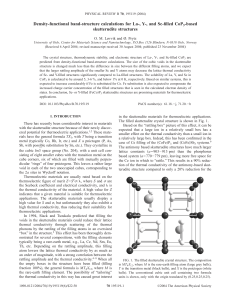
Density-functional band-structure calculations for La-, Y
... is general, and even for several different materials the thermal conductivity decreases by an order of magnitude almost monotonically when the rattling amplitude increases from 15 pm (in CeFe4P12) to 29 pm (in CeFe4Sb12).2 It is evident that the smaller unit cell of the phosphorusbased skutterudite ...
... is general, and even for several different materials the thermal conductivity decreases by an order of magnitude almost monotonically when the rattling amplitude increases from 15 pm (in CeFe4P12) to 29 pm (in CeFe4Sb12).2 It is evident that the smaller unit cell of the phosphorusbased skutterudite ...
Density of states
In solid-state and condensed matter physics, the density of states (DOS) of a system describes the number of states per interval of energy at each energy level that are available to be occupied. Unlike isolated systems, like atoms or molecules in gas phase, the density distributions are not discrete like a spectral density but continuous. A high DOS at a specific energy level means that there are many states available for occupation. A DOS of zero means that no states can be occupied at that energy level. In general a DOS is an average over the space and time domains occupied by the system. Localvariations, most often due to distortions of the original system, are often called local density of states (LDOS). If the DOS of an undisturbedsystem is zero, the LDOS can locally be non-zero due to the presence of a local potential.