Spring 2008 Qualifying Exam
... In a vacuum diode, electrons are emitted from a hot cathode, at potential zero, and accelerated across a gap to the anode, which is held at positive potential V. The cloud of moving electrons within the gap rapidly builds up to the point where it reduces the field at the surface of the cathode to ze ...
... In a vacuum diode, electrons are emitted from a hot cathode, at potential zero, and accelerated across a gap to the anode, which is held at positive potential V. The cloud of moving electrons within the gap rapidly builds up to the point where it reduces the field at the surface of the cathode to ze ...
Feathers vs Rocks (pg 45)
... • Mass is the amount of matter (“stuff”) in a substance • Measured with a scale ...
... • Mass is the amount of matter (“stuff”) in a substance • Measured with a scale ...
Solid State 3, Problem Set 2 Lecturer: Eytan Grosfeld
... for the clean 1D tight-binding chain (use the exact spectrum). 2. Transport on the surface of a topological insulator Electrons confined to the two-dimensional surface of a topological insulator tuned to the Dirac point are described by the continuum limit Hamiltonian H = vσ · p where σa are Pauli m ...
... for the clean 1D tight-binding chain (use the exact spectrum). 2. Transport on the surface of a topological insulator Electrons confined to the two-dimensional surface of a topological insulator tuned to the Dirac point are described by the continuum limit Hamiltonian H = vσ · p where σa are Pauli m ...
problem set #5 – s
... 1. A material has a dielectric constant of εr = 3 and has an atomic density of 1028 atoms per cubic meter. If only two electrons in the outer orbital shell will distort with an applied Efield, and both electrons follow the same orbital path as a pair, find the spacing between the center of the nucle ...
... 1. A material has a dielectric constant of εr = 3 and has an atomic density of 1028 atoms per cubic meter. If only two electrons in the outer orbital shell will distort with an applied Efield, and both electrons follow the same orbital path as a pair, find the spacing between the center of the nucle ...
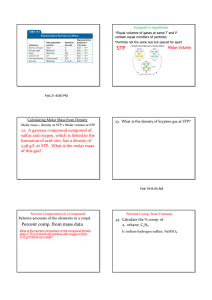
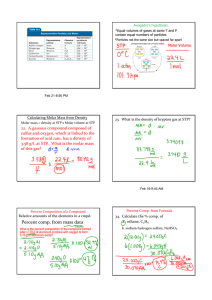
Lecture 3: Electronic Band Theory: A Many
... If we add up the number of states for each energy (at different momentum) we get the density of states, N (E). Depending on the number of electrons in our system, we can be in a conducting or insulating state. The equilibrium state of the system is the one where we put all our electrons into the low ...
... If we add up the number of states for each energy (at different momentum) we get the density of states, N (E). Depending on the number of electrons in our system, we can be in a conducting or insulating state. The equilibrium state of the system is the one where we put all our electrons into the low ...
Solid State 2 – Exercise 3
... Assume that in time coll , electrons can cover a maximal distance v coll . Show that (Fick’s law): j Dn ...
... Assume that in time coll , electrons can cover a maximal distance v coll . Show that (Fick’s law): j Dn ...
Density of states
In solid-state and condensed matter physics, the density of states (DOS) of a system describes the number of states per interval of energy at each energy level that are available to be occupied. Unlike isolated systems, like atoms or molecules in gas phase, the density distributions are not discrete like a spectral density but continuous. A high DOS at a specific energy level means that there are many states available for occupation. A DOS of zero means that no states can be occupied at that energy level. In general a DOS is an average over the space and time domains occupied by the system. Localvariations, most often due to distortions of the original system, are often called local density of states (LDOS). If the DOS of an undisturbedsystem is zero, the LDOS can locally be non-zero due to the presence of a local potential.