Lecture 12
... A current of 3.60 A flows through an automobile headlight. How many coulombs of charge flow through the headlight in a time of 2.60 hrs? Dimensional analysis: 3.6 C/s and so we want in the end an answer in C How? Figure out number of seconds in 2.6 hours 60s/min * 60min/hr * 2.6 hr = 3600 * 2.6 = 9, ...
... A current of 3.60 A flows through an automobile headlight. How many coulombs of charge flow through the headlight in a time of 2.60 hrs? Dimensional analysis: 3.6 C/s and so we want in the end an answer in C How? Figure out number of seconds in 2.6 hours 60s/min * 60min/hr * 2.6 hr = 3600 * 2.6 = 9, ...
Basic mathematical concepts from probability and information theory.
... and so we conclude that for that case the density % regarded as a function of the 2N co-ordinates qi and pi , must be an invariant of the system. This is clearly also the case for any function of the density in particular the logarithm of the density i.e. log % Now this particular function has anoth ...
... and so we conclude that for that case the density % regarded as a function of the 2N co-ordinates qi and pi , must be an invariant of the system. This is clearly also the case for any function of the density in particular the logarithm of the density i.e. log % Now this particular function has anoth ...
Distortion of bulk-electron distribution function and its effect on core
... during the calculation. The coefficient c is obtained from the fast-electron density, and the broadness of the fast-electron distribution function toward v k direction can be determined by parameter Tk . (Throughout the calculations T⊥ is fixed at 1keV.) In this paper we choose the vpeak as electron ...
... during the calculation. The coefficient c is obtained from the fast-electron density, and the broadness of the fast-electron distribution function toward v k direction can be determined by parameter Tk . (Throughout the calculations T⊥ is fixed at 1keV.) In this paper we choose the vpeak as electron ...
Lecture 9
... Muons: very high energy muons can travel kilometres in matter before losing all energy Positrons: same behaviour of electrons, but after coming to rest, a positron will annihilate with electrons that are always present. This annihilation gives rise to a pair of back-to-back gamma rays of 511 keV. Ex ...
... Muons: very high energy muons can travel kilometres in matter before losing all energy Positrons: same behaviour of electrons, but after coming to rest, a positron will annihilate with electrons that are always present. This annihilation gives rise to a pair of back-to-back gamma rays of 511 keV. Ex ...
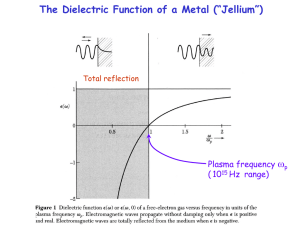
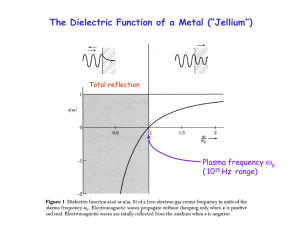
Lecture 2 - The Dionne Group
... Properties of metallic-bonded materials • ionic cores tend to pack closely, like stacked oranges, i.e. hexagonal close close-packed, packed, face face-centered centered cubic • bond is non-directional under an applied force, metal ions can move with respect p to each other • as a result, metals a ...
... Properties of metallic-bonded materials • ionic cores tend to pack closely, like stacked oranges, i.e. hexagonal close close-packed, packed, face face-centered centered cubic • bond is non-directional under an applied force, metal ions can move with respect p to each other • as a result, metals a ...
Chapter 5 Photoelectric Emission
... Figure 5.10 shows on the left-hand side the multiplet manifolds of the 4f 7 , 4f 8 , and 4f 9 final states in Gd, Tb, and Dy, respectively.5 In localized systems, the occupation is always an integer number, like in atoms, because these states do not mix with others. The binding energy of the localiz ...
... Figure 5.10 shows on the left-hand side the multiplet manifolds of the 4f 7 , 4f 8 , and 4f 9 final states in Gd, Tb, and Dy, respectively.5 In localized systems, the occupation is always an integer number, like in atoms, because these states do not mix with others. The binding energy of the localiz ...
Density of states
In solid-state and condensed matter physics, the density of states (DOS) of a system describes the number of states per interval of energy at each energy level that are available to be occupied. Unlike isolated systems, like atoms or molecules in gas phase, the density distributions are not discrete like a spectral density but continuous. A high DOS at a specific energy level means that there are many states available for occupation. A DOS of zero means that no states can be occupied at that energy level. In general a DOS is an average over the space and time domains occupied by the system. Localvariations, most often due to distortions of the original system, are often called local density of states (LDOS). If the DOS of an undisturbedsystem is zero, the LDOS can locally be non-zero due to the presence of a local potential.