Slide 1
... • Acquired from host cell during viral replication or release; envelope is portion of membrane system of host • Composed of phospholipid bilayer and proteins; some proteins are virally-coded glycoproteins (spikes) • Envelope’s proteins and glycoproteins often play role in host recognition ...
... • Acquired from host cell during viral replication or release; envelope is portion of membrane system of host • Composed of phospholipid bilayer and proteins; some proteins are virally-coded glycoproteins (spikes) • Envelope’s proteins and glycoproteins often play role in host recognition ...
Viruses Quiz Answer Key
... 8. What does it mean for a virus to “infect” a cell? a) The virus lands on the outside of the cell then completely enters the cell. b) The virus lands on the outside of the cell and injects its genetic material into the cell. c) The virus lands on the outside of the cell and injects its proteins int ...
... 8. What does it mean for a virus to “infect” a cell? a) The virus lands on the outside of the cell then completely enters the cell. b) The virus lands on the outside of the cell and injects its genetic material into the cell. c) The virus lands on the outside of the cell and injects its proteins int ...
Kingdom: Viruses
... their nucleic acid (DNA or RNA), strandedness (single-stranded or double-stranded), and method of replication. Group I: double-stranded DNA viruses Group II: single-stranded DNA viruses Group III: double-stranded RNA viruses Group IV: positive-sense single-stranded RNA viruses Group V: neg ...
... their nucleic acid (DNA or RNA), strandedness (single-stranded or double-stranded), and method of replication. Group I: double-stranded DNA viruses Group II: single-stranded DNA viruses Group III: double-stranded RNA viruses Group IV: positive-sense single-stranded RNA viruses Group V: neg ...
Slide 1
... The virus life cycle can be divided into five stages: 1. attachment (adsorption), 2. penetration (injection), 3. protein and nucleic acid synthesis, 4. assembly and packaging, and 5. virion release. ...
... The virus life cycle can be divided into five stages: 1. attachment (adsorption), 2. penetration (injection), 3. protein and nucleic acid synthesis, 4. assembly and packaging, and 5. virion release. ...
Lecture 16: Spherical Virus Structures
... Capsid Proteins - Bacterial, Plant, insect and animal viruses have a similar motif - an eight-stranded antiparallel b-barrel ...
... Capsid Proteins - Bacterial, Plant, insect and animal viruses have a similar motif - an eight-stranded antiparallel b-barrel ...
B. Nucleic acid
... Viral protein and nucleic acid synthesis 1. Protein synthesis a) Uses host ribosomes, ATP, amino acids, tRNA, etc. b) Function of viral proteins (1) Alter host cell functions (a) Decrease host nucleic acid synthesis and degradation of host nucleic acids (i) This increases resources available to make ...
... Viral protein and nucleic acid synthesis 1. Protein synthesis a) Uses host ribosomes, ATP, amino acids, tRNA, etc. b) Function of viral proteins (1) Alter host cell functions (a) Decrease host nucleic acid synthesis and degradation of host nucleic acids (i) This increases resources available to make ...
Viruses Lecture 16 Fall 2008
... • Many animal viruses have envelopes • Glycoproteins in envelope bind to receptor proteins of host • Production of new glycoproteins ...
... • Many animal viruses have envelopes • Glycoproteins in envelope bind to receptor proteins of host • Production of new glycoproteins ...
notes chap. 24 virsuses - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... d. Doesn’t cause harm immediately but at some point it can become the lytic cycle. e. Causes transduction (spreading of new DNA to another cell) ex. Cancers,cold sores,shingles, AIDS ...
... d. Doesn’t cause harm immediately but at some point it can become the lytic cycle. e. Causes transduction (spreading of new DNA to another cell) ex. Cancers,cold sores,shingles, AIDS ...
Prokaryote vs. Eukaryote
... 1) Classification based on capsid • protein coat that surrounds the genetic material of a virus ...
... 1) Classification based on capsid • protein coat that surrounds the genetic material of a virus ...
Essential Knowledge 3.C.3: Viral replication results in genetic
... latent (lysogenic) infection. These latent viral genomes came result in properties for the host such as increased pathogenicity in bacteria. ...
... latent (lysogenic) infection. These latent viral genomes came result in properties for the host such as increased pathogenicity in bacteria. ...
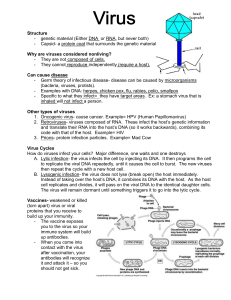
What is a virus
... - genetic material (Either DNA or RNA, but never both) - Capsid- a protein coat that surrounds the genetic material Why are viruses considered nonliving? - They are not composed of cells. - They cannot reproduce independently (require a host). Can cause disease - Germ theory of infectious disease- d ...
... - genetic material (Either DNA or RNA, but never both) - Capsid- a protein coat that surrounds the genetic material Why are viruses considered nonliving? - They are not composed of cells. - They cannot reproduce independently (require a host). Can cause disease - Germ theory of infectious disease- d ...
Viruses
... Only 3 characteristics of life: reproduction, evolution, and genetic code (DNA/RNA) Can only reproduce inside a host cell! Process or reproduction = lytic cycle ...
... Only 3 characteristics of life: reproduction, evolution, and genetic code (DNA/RNA) Can only reproduce inside a host cell! Process or reproduction = lytic cycle ...
(1) Replication of negative ssRNA viruses
... 1-Medically important negative-strand RNA viruses 2- They are all enveloped; . 3-Their virions contain an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (transcriptase) that synthesizes viral mRNAs using the genomic the genomic negative-strand viral negative-strand RNA as a template RNAs are not infectious, 4- Some n ...
... 1-Medically important negative-strand RNA viruses 2- They are all enveloped; . 3-Their virions contain an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (transcriptase) that synthesizes viral mRNAs using the genomic the genomic negative-strand viral negative-strand RNA as a template RNAs are not infectious, 4- Some n ...
Viruses
... metabolism either • They have no binar division • They have a genom (RNA or DNA) + • They are affected by biological evolution + • They interact with living organisms +/- ...
... metabolism either • They have no binar division • They have a genom (RNA or DNA) + • They are affected by biological evolution + • They interact with living organisms +/- ...
virus
... Either single-stranded or double-stranded DNA or RNA - linear, closed circle, or able to assume either shape. Reproduce only within living cells Virion All viruses have a nucleocapsid composed of a nucleic acid surrounded by a protein capsid that may be icosahedral, helical, or complex in structure. ...
... Either single-stranded or double-stranded DNA or RNA - linear, closed circle, or able to assume either shape. Reproduce only within living cells Virion All viruses have a nucleocapsid composed of a nucleic acid surrounded by a protein capsid that may be icosahedral, helical, or complex in structure. ...
Viruses - saddlespace.org
... • Antiviral drugs are available to treat only a few viral diseases. Why is this so??? – Because the drug is likely to be toxic to the host as well as the virus. ...
... • Antiviral drugs are available to treat only a few viral diseases. Why is this so??? – Because the drug is likely to be toxic to the host as well as the virus. ...
ppt presentation
... • Nucleic acid in protein capsid (no membrane envelop) • Protein capsid – protection and transfer of NA • Nucleic acid – infectious (in some viruses together with polymerases) ...
... • Nucleic acid in protein capsid (no membrane envelop) • Protein capsid – protection and transfer of NA • Nucleic acid – infectious (in some viruses together with polymerases) ...
chapt17b_lecture
... Ribosomal RNA is the most abundant form and makes up 80% cellular RNA. Ribosomal RNA molecules are large and are found in the ribososmes. ...
... Ribosomal RNA is the most abundant form and makes up 80% cellular RNA. Ribosomal RNA molecules are large and are found in the ribososmes. ...
VIROLOGY - MCB 5505 VIRUS FAMILY: RHABDOVIRIDAE I
... capped and polyadenylated. Glycoprotein (G) and Matrix protein (M) are both involved in the envelope. The viral core is found to be infectious, which shows that transcript activity is associated with the Largest protein (L), the Nucleocapsid protein (N) and the P protein. This makes the 3 internal p ...
... capped and polyadenylated. Glycoprotein (G) and Matrix protein (M) are both involved in the envelope. The viral core is found to be infectious, which shows that transcript activity is associated with the Largest protein (L), the Nucleocapsid protein (N) and the P protein. This makes the 3 internal p ...
Viruses
... Translates RNA into DNA, integration into cellular DNA called provirus Provirus DNA is transcribed to make new HIV viruses that leave cell Provirus never leaves cell ...
... Translates RNA into DNA, integration into cellular DNA called provirus Provirus DNA is transcribed to make new HIV viruses that leave cell Provirus never leaves cell ...
03-131 Genes, Diseases and Drugs Lecture 1 August 23, 2015
... protease required for maturation of viral proteins and the production of new viruses. Other types of Viruses: 1. Double stranded DNA: Smallpox, DNA replicated in the nucleus of host cell 2. Double-stranded RNA: Plant viruses, replicated in cytoplasm of host cell. 3. Single-stranded RNA.: ...
... protease required for maturation of viral proteins and the production of new viruses. Other types of Viruses: 1. Double stranded DNA: Smallpox, DNA replicated in the nucleus of host cell 2. Double-stranded RNA: Plant viruses, replicated in cytoplasm of host cell. 3. Single-stranded RNA.: ...