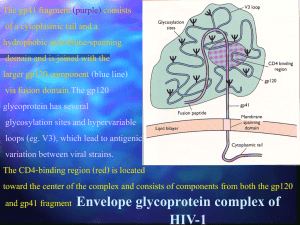
UNIT 8: MICROBIOLOGY STUDY Guide with Test Objectives
... 1. AIDS (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome) 2. common cold 3. Smallpox ** 4. Influenza (Flu) 5. Warts (host cell transforms into wart cell) 11. Describe the purpose of endospore formation and its role in bacterial survival. a. Bacteria need moisture, rely on temperature, pH and nutrition to grow. ...
... 1. AIDS (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome) 2. common cold 3. Smallpox ** 4. Influenza (Flu) 5. Warts (host cell transforms into wart cell) 11. Describe the purpose of endospore formation and its role in bacterial survival. a. Bacteria need moisture, rely on temperature, pH and nutrition to grow. ...
File - Peter Litsas
... Bacteria are responsible for a number of diseases, but they are also responsible for many antibiotics. Anaerobic bacteria survive without oxygen, and they get energy from fermentation. There are many types of plankton that are considered bacteria. Cyanobacteria produce much of the world’s oxygen, th ...
... Bacteria are responsible for a number of diseases, but they are also responsible for many antibiotics. Anaerobic bacteria survive without oxygen, and they get energy from fermentation. There are many types of plankton that are considered bacteria. Cyanobacteria produce much of the world’s oxygen, th ...
Viruses and Bacteria What are they and how they affect us?
... 1. What is step one the purpose of it? 2. What does the tissue culture act as for the virus? 3. Why is the culture kept at a low temperature? 4. Why are the strains that have a more difficult time growing in the warmer environment of the human selected? 5. How many years did it take to create the me ...
... 1. What is step one the purpose of it? 2. What does the tissue culture act as for the virus? 3. Why is the culture kept at a low temperature? 4. Why are the strains that have a more difficult time growing in the warmer environment of the human selected? 5. How many years did it take to create the me ...
Instrumentation and Process Control
... genome. The following examples from should make this clear: (1) poliovirus makes a negative-strand intermediate, which is the template for the positive-strand genome; (2) influenza, measles, and rabies viruses make a positive strand intermediate, which is the template for the negative-strand genome; ...
... genome. The following examples from should make this clear: (1) poliovirus makes a negative-strand intermediate, which is the template for the positive-strand genome; (2) influenza, measles, and rabies viruses make a positive strand intermediate, which is the template for the negative-strand genome; ...
Organ System Power Point
... In almost all cases, those infected with H5N1 had extensive physical contact with infected birds. Still, around 60% of humans known to have been infected with the current Asian strain of HPAI A(H5N1) have died from it ...
... In almost all cases, those infected with H5N1 had extensive physical contact with infected birds. Still, around 60% of humans known to have been infected with the current Asian strain of HPAI A(H5N1) have died from it ...
2.7 - mikrobiol unsoed
... showed that muscle tumors in chickens were caused by a filterable virus ...
... showed that muscle tumors in chickens were caused by a filterable virus ...
Chapter Outline
... about inactivation of host genes not necessary to viral replication. iv. During maturation, viral DNA and capsids are assembled to produce several hundred viral particles and lysozyme, coded by the virus, is produced. v. When lysozyme disrupts the cell wall, release of the viral particles occurs and ...
... about inactivation of host genes not necessary to viral replication. iv. During maturation, viral DNA and capsids are assembled to produce several hundred viral particles and lysozyme, coded by the virus, is produced. v. When lysozyme disrupts the cell wall, release of the viral particles occurs and ...
Infectivity of blood Adham
... AIDS, the infectivity by homologous blood transfusion has received renewed attention. In fact, for many years, blood banks use one or two tests (i.e., syphilis and hepatitis B surface antigen) to screen blood. In recent years, many more tests have been added. Overall, blood is probably safer than it ...
... AIDS, the infectivity by homologous blood transfusion has received renewed attention. In fact, for many years, blood banks use one or two tests (i.e., syphilis and hepatitis B surface antigen) to screen blood. In recent years, many more tests have been added. Overall, blood is probably safer than it ...
6SC09 Bacteria and Viruses
... There are two different types of virus: active and hidden. The active virus takes charge of the cell immediately, telling the cell’s DNA to make new virus proteins and replicate the virus’ DNA. The DNA and proteins become new viruses. This process will continue until the cell has produced so many ne ...
... There are two different types of virus: active and hidden. The active virus takes charge of the cell immediately, telling the cell’s DNA to make new virus proteins and replicate the virus’ DNA. The DNA and proteins become new viruses. This process will continue until the cell has produced so many ne ...
Chapter 10 Active Lecture Questions
... a. Viruses are not composed of cells b. Viruses are obligate parasites c. Some viruses can incorporate their genome into a host’s genome d. Viruses direct anabolic pathways of host cells ...
... a. Viruses are not composed of cells b. Viruses are obligate parasites c. Some viruses can incorporate their genome into a host’s genome d. Viruses direct anabolic pathways of host cells ...
Virology
... genome enters the cell is that the (-) sense genome is copied by the polymerase, forming either (+)sense transcripts which are used directly as mRNA, or a double-stranded molecule known either as the replicative intermediate (RI) or replicative form (RF), which serves as a template for further round ...
... genome enters the cell is that the (-) sense genome is copied by the polymerase, forming either (+)sense transcripts which are used directly as mRNA, or a double-stranded molecule known either as the replicative intermediate (RI) or replicative form (RF), which serves as a template for further round ...
Micro 280 Introduction
... • Biotechnology, the use of microbes to produce foods and chemicals, is centuries old. • Genetic engineering is a new technique for biotechnology. Through genetic engineering, bacteria and fungi can produce a variety of proteins including vaccines and enzymes. • Missing or defective genes in human c ...
... • Biotechnology, the use of microbes to produce foods and chemicals, is centuries old. • Genetic engineering is a new technique for biotechnology. Through genetic engineering, bacteria and fungi can produce a variety of proteins including vaccines and enzymes. • Missing or defective genes in human c ...
Document
... 20 million people have died from AIDS and about 3 million are infected with HIV Disease mechanism • Virus infects and replicated inside white blood cells (WBC) • WBC die decreased immune response ...
... 20 million people have died from AIDS and about 3 million are infected with HIV Disease mechanism • Virus infects and replicated inside white blood cells (WBC) • WBC die decreased immune response ...
Science Forward--Evolution
... Flora Lichtman: [2:43] What's it like to be a bacterium? What's it like to live in the habitat of the human body? Think about how you move around and sense the environment. Now imagine you're microscopic. The rules can be different. Laura Broughton: [2:55] Bacteria on average are about 50 times smal ...
... Flora Lichtman: [2:43] What's it like to be a bacterium? What's it like to live in the habitat of the human body? Think about how you move around and sense the environment. Now imagine you're microscopic. The rules can be different. Laura Broughton: [2:55] Bacteria on average are about 50 times smal ...
THE GENETICS OF VIRUSES
... Bacteria so small it passed through filter made a filterable toxin which then caused the disease Martinus Beijerinck-tested Ivanowsky’s 2nd hypothesis o sprayed plants with filtered sap through a series of infections ability to cause disease undiluted from plant to plant, generation to gener ...
... Bacteria so small it passed through filter made a filterable toxin which then caused the disease Martinus Beijerinck-tested Ivanowsky’s 2nd hypothesis o sprayed plants with filtered sap through a series of infections ability to cause disease undiluted from plant to plant, generation to gener ...
DNA-notes
... In 1918, Dr. Lancefield joined the Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research, commencing her studies of the hemolytic streptococci, known then as Streptococcus haemolyticus. Following in the path of Oswald Avery, who had previously developed a serum (or precipitation) system for differentiating amo ...
... In 1918, Dr. Lancefield joined the Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research, commencing her studies of the hemolytic streptococci, known then as Streptococcus haemolyticus. Following in the path of Oswald Avery, who had previously developed a serum (or precipitation) system for differentiating amo ...
microbe mission test
... 32. Which of the following statements BEST describes the Endosymbiotic Theory? a. prokaryotic cells evolved from specialized eukaryotes living inside one another. b. viruses evolved from protein-infectious particles. c. eukaryotic cells evolved from specialized prokaryotes living inside one another. ...
... 32. Which of the following statements BEST describes the Endosymbiotic Theory? a. prokaryotic cells evolved from specialized eukaryotes living inside one another. b. viruses evolved from protein-infectious particles. c. eukaryotic cells evolved from specialized prokaryotes living inside one another. ...
BACTERIOPHAGE
... +) It acts also as cell regulatory activity ( activation of natural killer cells, activation of monocytes and macrophages and inhibition of cell growth. ,) Recombinant DNA techniques now allow production of inexpensive large amount of interferon by yeast and bacteria. CLINICAL USES: • Used in treatm ...
... +) It acts also as cell regulatory activity ( activation of natural killer cells, activation of monocytes and macrophages and inhibition of cell growth. ,) Recombinant DNA techniques now allow production of inexpensive large amount of interferon by yeast and bacteria. CLINICAL USES: • Used in treatm ...
Clinical Group - Chulabhorn Research Institute
... Disrupting the assembly line Protease Enz cut viral proteins into shorter pieces so that they can incorporated into new viruses -Protease inhibitors block this stage of reproduction by neutralizing the enzyme. They’re even more effective when combined with RT inhibitors ...
... Disrupting the assembly line Protease Enz cut viral proteins into shorter pieces so that they can incorporated into new viruses -Protease inhibitors block this stage of reproduction by neutralizing the enzyme. They’re even more effective when combined with RT inhibitors ...
Leaving Certificate Biology Photosynthesis Quiz
... is naturally produced by living microorganisms and destroys or inhibits the growth of other micro-organisms, especially bacteria or fungi? Antiseptic ...
... is naturally produced by living microorganisms and destroys or inhibits the growth of other micro-organisms, especially bacteria or fungi? Antiseptic ...
History of virology

The history of virology – the scientific study of viruses and the infections they cause – began in the closing years of the 19th century. Although Louis Pasteur and Edward Jenner developed the first vaccines to protect against viral infections, they did not know that viruses existed. The first evidence of the existence of viruses came from experiments with filters that had pores small enough to retain bacteria. In 1892, Dmitry Ivanovsky used one of these filters to show that sap from a diseased tobacco plant remained infectious to healthy tobacco plants despite having been filtered. Martinus Beijerinck called the filtered, infectious substance a ""virus"" and this discovery is considered to be the beginning of virology. By the 20th century many viruses were discovered.