Young Person`s Frequently Asked Questions
... Blood-borne viruses can affect different people in different ways. Some people may have no symptoms at the beginning, while others can be very unwell. HIV can cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). This is where a person’s immune system gradually stops working. Hepatitis B and hepatitis C ...
... Blood-borne viruses can affect different people in different ways. Some people may have no symptoms at the beginning, while others can be very unwell. HIV can cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). This is where a person’s immune system gradually stops working. Hepatitis B and hepatitis C ...
(Macroparasites and microparasites)edited [Recovered]
... • Most are viruses, bacteria and fungi with a smaller number being protists. • Microparasite examples: viruses and bacteria. Human diseases: influenza, HIV/AIDS and tuberculosis. ...
... • Most are viruses, bacteria and fungi with a smaller number being protists. • Microparasite examples: viruses and bacteria. Human diseases: influenza, HIV/AIDS and tuberculosis. ...
first lecture
... disproved spontaneous generation of microorganisms, developed pasteurization, demonstrated what is now known as Germ Theory of Disease, developed a rabies vaccine Robert Koch - established Koch’s postulates - a sequence of experimental steps that verified the germ theory, identified cause of anthrax ...
... disproved spontaneous generation of microorganisms, developed pasteurization, demonstrated what is now known as Germ Theory of Disease, developed a rabies vaccine Robert Koch - established Koch’s postulates - a sequence of experimental steps that verified the germ theory, identified cause of anthrax ...
221_exam_4_2002
... B. hemolysins C. ability to multiply inside phagocytes D. toxins that kill alveolar macrophages _____ Anthrax, brucellosis and rabies have been “controlled” by __. A. immunization of their domestic animal hosts B. elimination of intermediate hosts C. slaughter of all infected animals D. development ...
... B. hemolysins C. ability to multiply inside phagocytes D. toxins that kill alveolar macrophages _____ Anthrax, brucellosis and rabies have been “controlled” by __. A. immunization of their domestic animal hosts B. elimination of intermediate hosts C. slaughter of all infected animals D. development ...
Biology 20 Diversity of Life PowerPoint part 2.pps
... Viruses are infectious particles made only of a strand of DNA or RNA surrounded by protein coat. Viruses are small or very small (50-200 nm) and cannot be seen with a light microscope (you need an electron microscope). Some scientists consider viruses as complex chemicals ...
... Viruses are infectious particles made only of a strand of DNA or RNA surrounded by protein coat. Viruses are small or very small (50-200 nm) and cannot be seen with a light microscope (you need an electron microscope). Some scientists consider viruses as complex chemicals ...
Viruses
... nucleic acid molecule or several nucleic acid segments. The DNA or RNA may be single-stranded or double-stranded, and either linear or circular. Because viruses are so small, the size of the genome is limited. For example, the genome includes coded instructions for making only a few different protei ...
... nucleic acid molecule or several nucleic acid segments. The DNA or RNA may be single-stranded or double-stranded, and either linear or circular. Because viruses are so small, the size of the genome is limited. For example, the genome includes coded instructions for making only a few different protei ...
Pathogens and their effect on humans. Viral pathogens. Bacteria:
... Viral pathogens work by taking over cells and getting them to carry out viral cell replication rather than carrying out the processes they were designed to do. An example of this is “the flu”. The flu can enter the cell of the linings of the lungs and throat and take over the lung lining cells and f ...
... Viral pathogens work by taking over cells and getting them to carry out viral cell replication rather than carrying out the processes they were designed to do. An example of this is “the flu”. The flu can enter the cell of the linings of the lungs and throat and take over the lung lining cells and f ...
Virus - District 128 Moodle
... Substances that contain the weakened or inactive diseasecausing virus When injected into the body, vaccines provide immunity to the disease ...
... Substances that contain the weakened or inactive diseasecausing virus When injected into the body, vaccines provide immunity to the disease ...
Viruses and Monera
... Symptoms may be mild or severe. You usually start to feel sick about 2 to 5 days after you come in contact with the bacteria. Symptoms usually begin suddenly, and can include: •Fever that begins suddenly and is often highest on the second day •Red throat, sometimes with white patches ...
... Symptoms may be mild or severe. You usually start to feel sick about 2 to 5 days after you come in contact with the bacteria. Symptoms usually begin suddenly, and can include: •Fever that begins suddenly and is often highest on the second day •Red throat, sometimes with white patches ...
Bacteria and Viruses C.20 powerpoint
... Jack Nicklaus had polio as a young boy. Fortunately it did not cause any paralysis. Only .5% of people infected would develop a paralytic symptoms. But among millions infected this ended up to be a lot of people. ...
... Jack Nicklaus had polio as a young boy. Fortunately it did not cause any paralysis. Only .5% of people infected would develop a paralytic symptoms. But among millions infected this ended up to be a lot of people. ...
2 - Viruses Scavenger Hunt Solution - kyoussef-mci
... d) Viruses can spread from mother to child or person to person. They can also spread from animals to humans. Viruses can spread through simple contact, sexual contact, contaminated food/water or through mosquitoes. 2. Characteristics of a Virus – “What are the Essential Characteristics of Viruses?” ...
... d) Viruses can spread from mother to child or person to person. They can also spread from animals to humans. Viruses can spread through simple contact, sexual contact, contaminated food/water or through mosquitoes. 2. Characteristics of a Virus – “What are the Essential Characteristics of Viruses?” ...
Viruses in Soil
... dry and windy. There are no higher plants or animals and the soils have very little organic matter. However, bacteria and fungi grow in these soils when conditions ...
... dry and windy. There are no higher plants or animals and the soils have very little organic matter. However, bacteria and fungi grow in these soils when conditions ...
The immune system
... 6.3.2 Explain why antibiotics are effective against bacteria but not against viruses. Viruses reproduce using the host cell metabolic pathways that are not affected by antibiotics. – Viruses do not have metabolic pathways like bacteria and therefore antibiotics do not work on viruses. – Viruses can ...
... 6.3.2 Explain why antibiotics are effective against bacteria but not against viruses. Viruses reproduce using the host cell metabolic pathways that are not affected by antibiotics. – Viruses do not have metabolic pathways like bacteria and therefore antibiotics do not work on viruses. – Viruses can ...
feature feature - Laboratory Medicine
... Initial diagnostic tests should include chest radiograph, pulse oximetry, blood cultures, sputum Gram’s stain and culture, and testing for viral respiratory organisms. As of March 22, 2003, the case number of SARS suspected in the United States stood at 37, while the WHO reported 456 cases worldwide ...
... Initial diagnostic tests should include chest radiograph, pulse oximetry, blood cultures, sputum Gram’s stain and culture, and testing for viral respiratory organisms. As of March 22, 2003, the case number of SARS suspected in the United States stood at 37, while the WHO reported 456 cases worldwide ...
Culture Methods
... Relationship of Infectivity to Virus Particle Count • As little a one or a few intact, functional virus particles are capable of causing infection in a susceptible host. • Ratios of virus particles to infectious units are highly variable and are subject to change: – Passage of viruses in susceptible ...
... Relationship of Infectivity to Virus Particle Count • As little a one or a few intact, functional virus particles are capable of causing infection in a susceptible host. • Ratios of virus particles to infectious units are highly variable and are subject to change: – Passage of viruses in susceptible ...
Spring 2015-Chapter 14
... Noninfectious diseases are caused by any other agents than infectious organisms. Contagious disease-A contagious disease is a subset category of infectious diseases (or communicable diseases), which are easily transmitted by physical contact (hence the name-origin) with the person suffering the dise ...
... Noninfectious diseases are caused by any other agents than infectious organisms. Contagious disease-A contagious disease is a subset category of infectious diseases (or communicable diseases), which are easily transmitted by physical contact (hence the name-origin) with the person suffering the dise ...
How bacteria cause disease
... • Bacteria can be toxigenic (produce toxins) – Bacteria may not spread, but release soluble toxins which dissolve in body fluids, damaging cells. – Gram negative contain endotoxin (LPS) ...
... • Bacteria can be toxigenic (produce toxins) – Bacteria may not spread, but release soluble toxins which dissolve in body fluids, damaging cells. – Gram negative contain endotoxin (LPS) ...
Section 2: Energy Flow in Ecosystems
... physicians must switch to using different antibiotics. • As new antibiotics are used, bacteria will probably develop resistance to those as well. ...
... physicians must switch to using different antibiotics. • As new antibiotics are used, bacteria will probably develop resistance to those as well. ...
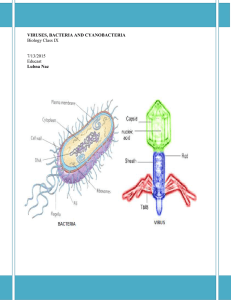
viruses, bacteria and cyanobacteria
... A virus is a small infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of other organisms. Viruses can infect all types of life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. The word is from the Latin virus referring to poison. By 1800's many biologists ...
... A virus is a small infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of other organisms. Viruses can infect all types of life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. The word is from the Latin virus referring to poison. By 1800's many biologists ...
TAXONOMY of VIRUSES
... – Diploid cell lines: derived from human embryos, multiply for about 50 – 100 generations and then die. – Continuous cell lines: Immortal lines are derived from transformed or cancerous cells. Can multiply indefinitely in culture and are immortal. These are commonly used in propagation of viruses. ...
... – Diploid cell lines: derived from human embryos, multiply for about 50 – 100 generations and then die. – Continuous cell lines: Immortal lines are derived from transformed or cancerous cells. Can multiply indefinitely in culture and are immortal. These are commonly used in propagation of viruses. ...
Lecture GuideViruses(Ch13)–7e
... Can you make viral proteins and more genetic material from the following types of viruses? ss (-) DNA ss (+) RNA ss (-) RNA ds (+/-) RNA With all of these viruses, we have been following the flow of information in the following manner: DNA RNA protein This flow of information is called t ...
... Can you make viral proteins and more genetic material from the following types of viruses? ss (-) DNA ss (+) RNA ss (-) RNA ds (+/-) RNA With all of these viruses, we have been following the flow of information in the following manner: DNA RNA protein This flow of information is called t ...
History of virology

The history of virology – the scientific study of viruses and the infections they cause – began in the closing years of the 19th century. Although Louis Pasteur and Edward Jenner developed the first vaccines to protect against viral infections, they did not know that viruses existed. The first evidence of the existence of viruses came from experiments with filters that had pores small enough to retain bacteria. In 1892, Dmitry Ivanovsky used one of these filters to show that sap from a diseased tobacco plant remained infectious to healthy tobacco plants despite having been filtered. Martinus Beijerinck called the filtered, infectious substance a ""virus"" and this discovery is considered to be the beginning of virology. By the 20th century many viruses were discovered.
![(Macroparasites and microparasites)edited [Recovered]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000701227_1-e77fabc78bd26bd6dffe57ed2eb3168d-300x300.png)