unif - orsagouge
... Once you know a Z, you can accurately predict the entire future sequence (not really random) If a Z ever repeats, the whole sequence starts ...
... Once you know a Z, you can accurately predict the entire future sequence (not really random) If a Z ever repeats, the whole sequence starts ...
From Rainbow to the Lonely Runner
... Let G be a graph. Let r be a real number and Sr be a circle on the xy-plane centered at (0,0) with circumference r. An r-coloring of G is a function f : V(G) => Sr such that for adjacent vertices u and v, the circular distance (shorter distance on Sr) between f(u) and f(v) is at least 1. The circula ...
... Let G be a graph. Let r be a real number and Sr be a circle on the xy-plane centered at (0,0) with circumference r. An r-coloring of G is a function f : V(G) => Sr such that for adjacent vertices u and v, the circular distance (shorter distance on Sr) between f(u) and f(v) is at least 1. The circula ...
Compare and Order Integers
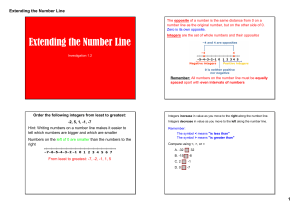
... Put this set of numbers in order, from least to greatest: +3, -5, +4, -9, 2, +7, -1, +6. Which number has the greatest absolute value? ...
... Put this set of numbers in order, from least to greatest: +3, -5, +4, -9, 2, +7, -1, +6. Which number has the greatest absolute value? ...
Solve when r = 7 - Stoughton Public Schools
... when you are given 2 of the variables in the formula and asked to find the 3rd. ...
... when you are given 2 of the variables in the formula and asked to find the 3rd. ...
Collatz conjecture

The Collatz conjecture is a conjecture in mathematics named after Lothar Collatz, who first proposed it in 1937. The conjecture is also known as the 3n + 1 conjecture, the Ulam conjecture (after Stanisław Ulam), Kakutani's problem (after Shizuo Kakutani), the Thwaites conjecture (after Sir Bryan Thwaites), Hasse's algorithm (after Helmut Hasse), or the Syracuse problem; the sequence of numbers involved is referred to as the hailstone sequence or hailstone numbers (because the values are usually subject to multiple descents and ascents like hailstones in a cloud), or as wondrous numbers.Take any natural number n. If n is even, divide it by 2 to get n / 2. If n is odd, multiply it by 3 and add 1 to obtain 3n + 1. Repeat the process (which has been called ""Half Or Triple Plus One"", or HOTPO) indefinitely. The conjecture is that no matter what number you start with, you will always eventually reach 1. The property has also been called oneness.Paul Erdős said about the Collatz conjecture: ""Mathematics may not be ready for such problems."" He also offered $500 for its solution.