UNIT 7: Trigonometric Identities and Solving Trigonometric Equations
... UNIT 7: Trigonometric Identities and Solving Trigonometric Equations Objectives: Upon completion of the unit, students will be able to: • Simplify trigonometric expressions involving trig identities • Use trig identities to determine the exact value of an expression • Solve trig equations (use trig ...
... UNIT 7: Trigonometric Identities and Solving Trigonometric Equations Objectives: Upon completion of the unit, students will be able to: • Simplify trigonometric expressions involving trig identities • Use trig identities to determine the exact value of an expression • Solve trig equations (use trig ...
Unit 4 Review Package - Linear Equations And Systems
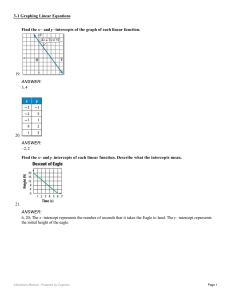
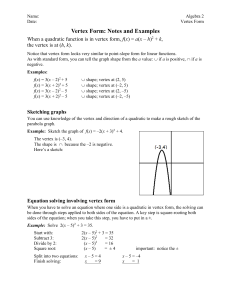
... Count how many units the line goes up or down (rise) and… Count how many units the line goes left or right (run) until you hit another point on the graph What is the formula to calculate slope? m= ...
... Count how many units the line goes up or down (rise) and… Count how many units the line goes left or right (run) until you hit another point on the graph What is the formula to calculate slope? m= ...
Applying Gauss elimination from boolean equation systems to
... Example 8. Consider the following boolean equation system: (µx = (y ∧ z) ∨ x) (νy = true) This is not in standard recursive form, as the first equation has “∧” and “∨” symbols in the same equation and a boolean constant still appears in the second equation. We first introduce a new equation for the ...
... Example 8. Consider the following boolean equation system: (µx = (y ∧ z) ∨ x) (νy = true) This is not in standard recursive form, as the first equation has “∧” and “∨” symbols in the same equation and a boolean constant still appears in the second equation. We first introduce a new equation for the ...
x that passes through the point (2, 4)
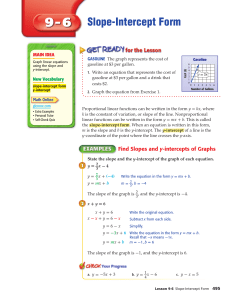
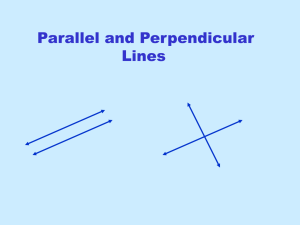
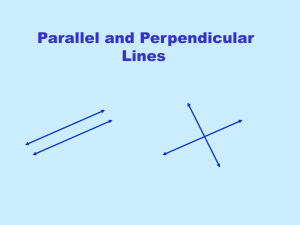
... The slope of the first line is still –1. The slope of a line perpendicular is the negative reciporical so take –1 and "flip" it over and ...
... The slope of the first line is still –1. The slope of a line perpendicular is the negative reciporical so take –1 and "flip" it over and ...