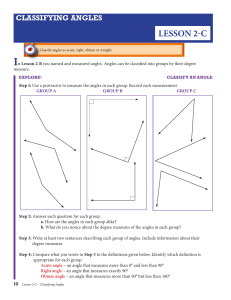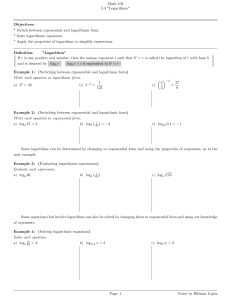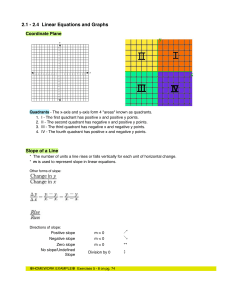
Math 102 5.3 "Logarithms" Objectives: * Switch between exponential
... * Apply the properties of logarithms to simplify expressions. De…nition: "Logarithm" If r is any positive real number, then the unique exponent t such that bt = r is called the logarithm of r with base b logb r = t is equivalent to bt = r and is denoted by logb r ...
... * Apply the properties of logarithms to simplify expressions. De…nition: "Logarithm" If r is any positive real number, then the unique exponent t such that bt = r is called the logarithm of r with base b logb r = t is equivalent to bt = r and is denoted by logb r ...
chemistry 103 - chem.uwec.edu
... We make use of two symbolic reactions. Note these symbolic reactions are not real reactions, and they are not balanced in the conventional sense. They are simply useful ways to think about removal of an “O” atom from a species in different conditions. 2 H+(aq) + “O” H2O (use this for acidic conditi ...
... We make use of two symbolic reactions. Note these symbolic reactions are not real reactions, and they are not balanced in the conventional sense. They are simply useful ways to think about removal of an “O” atom from a species in different conditions. 2 H+(aq) + “O” H2O (use this for acidic conditi ...
Lesson15 Solutions - Adjective Noun Math
... Notes on #3 In simplifying q/7 + 3/7 + 6 = q/2 + 5, it was not necessary to multiply by the least common multiple of 7 and 2. Any other common multiple would have worked as well. The main reason for choosing the least common multiple is to keep the arithmetic as simple as possible. However, if it is ...
... Notes on #3 In simplifying q/7 + 3/7 + 6 = q/2 + 5, it was not necessary to multiply by the least common multiple of 7 and 2. Any other common multiple would have worked as well. The main reason for choosing the least common multiple is to keep the arithmetic as simple as possible. However, if it is ...
Asymptotes, Holes, and Graphing Rational Functions
... Substitute this number into y=mx+b and solve for y. This will give us the point where the rational function crosses the slant asymptote. Plot this point. 7) Choose an x value in each section created by the asymptotes, substitute the x value into the rational function to get the y-value. Plot these p ...
... Substitute this number into y=mx+b and solve for y. This will give us the point where the rational function crosses the slant asymptote. Plot this point. 7) Choose an x value in each section created by the asymptotes, substitute the x value into the rational function to get the y-value. Plot these p ...