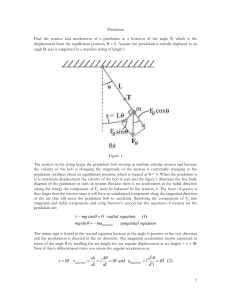
Chapter 5
... 7. x + y = -2 x-y=0 Solve the first equation for y, y = -2 - x . Substitute -2 - x for y in the second equation. x - (-2 - x) = 0 x +2 + x = 0 2x = -2 x = -1 Substitute –1 for x in the equation y = -2 - x . y = -2 - (-1) y = -2 + 1 y = -1 The solution is (–1, –1). ...
... 7. x + y = -2 x-y=0 Solve the first equation for y, y = -2 - x . Substitute -2 - x for y in the second equation. x - (-2 - x) = 0 x +2 + x = 0 2x = -2 x = -1 Substitute –1 for x in the equation y = -2 - x . y = -2 - (-1) y = -2 + 1 y = -1 The solution is (–1, –1). ...
5.1 A Formula for Slope
... In Chapter 4, you saw that the rate of change of a line can be a numerical and graphical representation of a real-world change like a car’s speed. Look at the lines and equation shown on page 251 of your book. Because the coefficient of x represents the rate of change of the line, you can match the ...
... In Chapter 4, you saw that the rate of change of a line can be a numerical and graphical representation of a real-world change like a car’s speed. Look at the lines and equation shown on page 251 of your book. Because the coefficient of x represents the rate of change of the line, you can match the ...