Lesson 1
... water retention and air circulation structures while increasing microbial activity and the availability of nutrients. Because the most fertile soil is alive with organisms that work in tandem with plants, soil structure and microbial balance is continually adapting to environmental conditions and nu ...
... water retention and air circulation structures while increasing microbial activity and the availability of nutrients. Because the most fertile soil is alive with organisms that work in tandem with plants, soil structure and microbial balance is continually adapting to environmental conditions and nu ...
File
... Note how this tree has raised the sidewalk. (B) This tree is surviving by growing roots into tiny joints and cracks, which become larger as the tree grows. ...
... Note how this tree has raised the sidewalk. (B) This tree is surviving by growing roots into tiny joints and cracks, which become larger as the tree grows. ...
Abiotic Disorders Presentation Part II
... controlled simply by reducing pH and EC levels. - High pH (above 7.5) can tie up nutrients such as zinc, iron, and manganese. - Add elemental sulfur or fertilizer with nitrogen sulfate to reduce a high pH - Add organic matter to your soil or garden in raised beds amended with organic matter and/or p ...
... controlled simply by reducing pH and EC levels. - High pH (above 7.5) can tie up nutrients such as zinc, iron, and manganese. - Add elemental sulfur or fertilizer with nitrogen sulfate to reduce a high pH - Add organic matter to your soil or garden in raised beds amended with organic matter and/or p ...
Dissolving rocks - Lockland Local Schools
... 4.1 Rocks and Weathering • Plant Growth 1. __________ of plants grow into spaces or cracks Roots 2. They make the cracks bigger and spreads them apart _____________ 3. As the roots get bigger they pry the spaces or wider open cracks ___________ ...
... 4.1 Rocks and Weathering • Plant Growth 1. __________ of plants grow into spaces or cracks Roots 2. They make the cracks bigger and spreads them apart _____________ 3. As the roots get bigger they pry the spaces or wider open cracks ___________ ...
chapter1
... Depending upon the composition of the starting material, some liquid may be produced. ...
... Depending upon the composition of the starting material, some liquid may be produced. ...
Soil and Compost Enrichment Lessons
... Background information: Soil is made of a variety of inorganic and organic components. Some inorganic components come from rocks, such as sand (larger particles), silt (medium particles), and clay (small particles). Others inorganic compounds include air, water and occasionally heavy metals. Living ...
... Background information: Soil is made of a variety of inorganic and organic components. Some inorganic components come from rocks, such as sand (larger particles), silt (medium particles), and clay (small particles). Others inorganic compounds include air, water and occasionally heavy metals. Living ...
OUTDOOR SCIENCE SCHOOL VOC (#1 – Test)
... 8. (Pg 6) ROCK – a non-living (abiotic) material composed of one or more minerals (a) “3” types of rocks: igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic 9. (Pg 7; 195) MINERAL – an inorganic (non-living/abiotic) substance found in nature (not human made) which forms rocks (a) has a definite chemical compositi ...
... 8. (Pg 6) ROCK – a non-living (abiotic) material composed of one or more minerals (a) “3” types of rocks: igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic 9. (Pg 7; 195) MINERAL – an inorganic (non-living/abiotic) substance found in nature (not human made) which forms rocks (a) has a definite chemical compositi ...
Annual News Letter 2013 - Critical Zone Hydrology Group
... a happy and successful New Year! The first full year of operation of the ACZHG has been dynamic. This letter aims to inform you about successes and developments in the group ...
... a happy and successful New Year! The first full year of operation of the ACZHG has been dynamic. This letter aims to inform you about successes and developments in the group ...
EARTH SCIENCE FINAL EXAM REVIEW SHEET
... 1. What are some examples of a composite volcano? 2. How are hot spot volcanoes different from other volcanoes? 3.Compare the amount of silica in lava with the eruption type of a volcano. 4. Calculate the speed of a tectonic plate from hot spot islands. ...
... 1. What are some examples of a composite volcano? 2. How are hot spot volcanoes different from other volcanoes? 3.Compare the amount of silica in lava with the eruption type of a volcano. 4. Calculate the speed of a tectonic plate from hot spot islands. ...
Nutrient Recycling Worksheet
... There is a _______________________________________ on earth e.g. you are probably aware of the water cycle – where water is _____________________________________ in nature. There are similar cycles for all nutrients. When plants and animals die, their ________________________________________________ ...
... There is a _______________________________________ on earth e.g. you are probably aware of the water cycle – where water is _____________________________________ in nature. There are similar cycles for all nutrients. When plants and animals die, their ________________________________________________ ...
Earth History – Study Guide Investigations: Sedimentary Rocks +
... 10. Where do river sediments often accumulate? 11. Where do windblown sediments often accumulate? 12. Name two other places where sediments can accumulate. 13. What type of rock is most easily broken down by carbonic acid? 14. What are the four natural forces that cause erosion? 15. Of the four from ...
... 10. Where do river sediments often accumulate? 11. Where do windblown sediments often accumulate? 12. Name two other places where sediments can accumulate. 13. What type of rock is most easily broken down by carbonic acid? 14. What are the four natural forces that cause erosion? 15. Of the four from ...
Geology study guide
... 3. transform fault is were 1 plate is going up and the other going down and there grinding ...
... 3. transform fault is were 1 plate is going up and the other going down and there grinding ...
variation of steady state infiltration rate with land use type
... considered were: turf area, forest area and shrub area. The study aimed at examining the effect of various land use types on infiltration and determining the degree of relationship between infiltration rates and selected soil properties under different land use types. The soil properties selected we ...
... considered were: turf area, forest area and shrub area. The study aimed at examining the effect of various land use types on infiltration and determining the degree of relationship between infiltration rates and selected soil properties under different land use types. The soil properties selected we ...
OUTDOOR SCIENCE SCHOOL VOC (#1 – Test)
... 8. (Pg 195; 10) OXYGEN [O] – is a colorless, odorless, gaseous element found in our atmosphere (a) 21% of the gas making up our air is oxygen [O] (b) O2 allows aerobic (oxygenated environment) organisms to efficiently convert food into energy (through cellular respiration) (c) O2 is a chemical agent ...
... 8. (Pg 195; 10) OXYGEN [O] – is a colorless, odorless, gaseous element found in our atmosphere (a) 21% of the gas making up our air is oxygen [O] (b) O2 allows aerobic (oxygenated environment) organisms to efficiently convert food into energy (through cellular respiration) (c) O2 is a chemical agent ...
Soils and Land-Use Research Workshop Dr. Brian Donlon EPA Research Programme
... The overall aim of these research areas are to: “help to protect and ensure a sustainable use of soil by getting a better understanding of soil and its functions and by preventing the threats to soil and mitigating their effects. Research activities will aim at supporting sustainable urban and land- ...
... The overall aim of these research areas are to: “help to protect and ensure a sustainable use of soil by getting a better understanding of soil and its functions and by preventing the threats to soil and mitigating their effects. Research activities will aim at supporting sustainable urban and land- ...
Magma
... *Type I - Igneous rock forms when hot magma or lava cools and solidifies. 2. Magma is melted rock found below the Earth’s crust, where temperatures and pressures are very high. Any rock heated at great depths can melt into magma. Magma can push away or dissolve surrounding rocks. 3. When magma break ...
... *Type I - Igneous rock forms when hot magma or lava cools and solidifies. 2. Magma is melted rock found below the Earth’s crust, where temperatures and pressures are very high. Any rock heated at great depths can melt into magma. Magma can push away or dissolve surrounding rocks. 3. When magma break ...
Chapter 2: The Earliest Human Societies pp
... B. By 8,000 B.C. Agricultural revolution 1. Humans learned to change their environment a. Hunter-gatherers to farming i. ii. Created many tools for farming d. Slash-and-burn agriculture i ii When soil was ruined farmers moved to new land C. New tools Better farming Permanent settlements 1. Farmi ...
... B. By 8,000 B.C. Agricultural revolution 1. Humans learned to change their environment a. Hunter-gatherers to farming i. ii. Created many tools for farming d. Slash-and-burn agriculture i ii When soil was ruined farmers moved to new land C. New tools Better farming Permanent settlements 1. Farmi ...
Newsletter
... purchase. To begin a long-term solution to iron chlorosis, you must work at modifying the soil environment to make iron more available. Usually this means lowering the soil pH. This can be done by (1) added compost, (2) adding sulfur – sulfur reacts with elements in the soil to produce acid and in t ...
... purchase. To begin a long-term solution to iron chlorosis, you must work at modifying the soil environment to make iron more available. Usually this means lowering the soil pH. This can be done by (1) added compost, (2) adding sulfur – sulfur reacts with elements in the soil to produce acid and in t ...
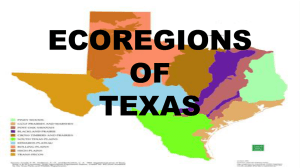
Texas eco regions 2016
... The shape of the hills in this region is rounded due to increased precipitation and chemical weathering. Central Texas' Flash Flood Alley is one of the most flood-prone areas nationwide. When rocks and soil can absorb no more rainfall, it gets carried off into a stream or at the bottom of a lake ...
... The shape of the hills in this region is rounded due to increased precipitation and chemical weathering. Central Texas' Flash Flood Alley is one of the most flood-prone areas nationwide. When rocks and soil can absorb no more rainfall, it gets carried off into a stream or at the bottom of a lake ...
Eons, Eras, Periods and Epochs Dating by radioactive isotopes
... •Concave at the bottom (debris slope and waning slope lead to pediment in the depositional zone) ...
... •Concave at the bottom (debris slope and waning slope lead to pediment in the depositional zone) ...
Earth Science 2007-2008 Final Study Guide
... Igneous rocks are formed by cooling magma Intrusive rocks form inside the crust, extrusive rocks form by cooling rapidly on the surface and are more fine grained Sediment is deposited and through lithification become sedimentary rocks When rocks go through intense heat and pressure they beco ...
... Igneous rocks are formed by cooling magma Intrusive rocks form inside the crust, extrusive rocks form by cooling rapidly on the surface and are more fine grained Sediment is deposited and through lithification become sedimentary rocks When rocks go through intense heat and pressure they beco ...
Soil test reports by AAT
... global cultivation of rice, wheat, sugarcane, pulses and vegetables. Sustainable agriculture should carefully consider maintaining and improving the existing soil structure and innate productive capacity of this soil. Mere application of chemical fertilizer and over working with soil without taking ...
... global cultivation of rice, wheat, sugarcane, pulses and vegetables. Sustainable agriculture should carefully consider maintaining and improving the existing soil structure and innate productive capacity of this soil. Mere application of chemical fertilizer and over working with soil without taking ...