Chapter_03_4E
... – Spinal cord – Lower regions of the brain – Motor areas of the cerebral cortex • Motor responses for more complex movement patterns typically originate in the motor cortex • A motor reflex is a preprogrammed response that is integrated by the spinal cord without conscious thought ...
... – Spinal cord – Lower regions of the brain – Motor areas of the cerebral cortex • Motor responses for more complex movement patterns typically originate in the motor cortex • A motor reflex is a preprogrammed response that is integrated by the spinal cord without conscious thought ...
Brain
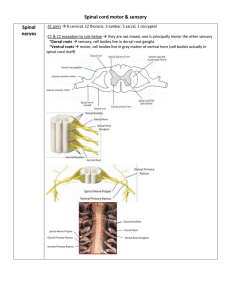
... Each column is filled with named tracts (fibers with a similar origin, destination and function) Ascending and descending tract head up or down Contralateral means origin and destination are on opposite sides while ipsilateral means on same side ...
... Each column is filled with named tracts (fibers with a similar origin, destination and function) Ascending and descending tract head up or down Contralateral means origin and destination are on opposite sides while ipsilateral means on same side ...
memory and learning
... stimuli that have not been paired with an unconditioned stimulus. For example, if a bell tone were the conditioned stimulus, discrimination would involve being able to tell the difference between the bell tone and other similar sounds ...
... stimuli that have not been paired with an unconditioned stimulus. For example, if a bell tone were the conditioned stimulus, discrimination would involve being able to tell the difference between the bell tone and other similar sounds ...
Psychology as a Science
... able to hum the tune (pattern) but won’t know the words. If damaged on right side, cannot hum tune but can say the words. ...
... able to hum the tune (pattern) but won’t know the words. If damaged on right side, cannot hum tune but can say the words. ...
Changes in spinal cord
... *from reticular regions of pons & medulla to ventral horn *descend in ipsilateral cord; but exert bilateral motor control *branches or interneurons at terminal level *mainly function to control “automatic functions” such as walking or posture -tectospinal *from superior colliculus to ventral horn of ...
... *from reticular regions of pons & medulla to ventral horn *descend in ipsilateral cord; but exert bilateral motor control *branches or interneurons at terminal level *mainly function to control “automatic functions” such as walking or posture -tectospinal *from superior colliculus to ventral horn of ...
Motor neuron
... skin of much of the lower limb and sends motor commands to hamstring muscles as well as other muscles of the lower leg Sciatic and feet. ...
... skin of much of the lower limb and sends motor commands to hamstring muscles as well as other muscles of the lower leg Sciatic and feet. ...
NEURAL CONTROL AND COORDINATION
... Cerebellum is attached to the brain stem by cerebellar peduncles. It is the motor area of the brain responsible for subconscious movements of skeletal muscles. It also maintains body balance and posture. The medulla oblongata lies between pons and spinal cord. It contains centers which control resp ...
... Cerebellum is attached to the brain stem by cerebellar peduncles. It is the motor area of the brain responsible for subconscious movements of skeletal muscles. It also maintains body balance and posture. The medulla oblongata lies between pons and spinal cord. It contains centers which control resp ...
Class 10- Control and Coordination
... The nervous system consists of the brain, spinal cord and nerves. a) Receptors :- These are the sense organs which receive the stimuli and pass the message to the brain or spinal cord through the sensory nerves. Eg :- Photoreceptors in the eyes to detect light. Phonoreceptors in the ears to detect s ...
... The nervous system consists of the brain, spinal cord and nerves. a) Receptors :- These are the sense organs which receive the stimuli and pass the message to the brain or spinal cord through the sensory nerves. Eg :- Photoreceptors in the eyes to detect light. Phonoreceptors in the ears to detect s ...
The nervous system - Sonoma Valley High School
... outside is positive Na+ and K+ ions move across the cell Membrane via the sodium-potassium pump ...
... outside is positive Na+ and K+ ions move across the cell Membrane via the sodium-potassium pump ...
The Somatic Motor System
... •Motor cortex commands do not reach muscles and muscles atrophy. •Electrodes can artificially activate muscles and prevent atrophy UPPER MOTOR NEURON SYNDROME DAMAGE TO DESENDING PATHWAYS Damage to the pathways driving the motor neurons •Spasticity ...
... •Motor cortex commands do not reach muscles and muscles atrophy. •Electrodes can artificially activate muscles and prevent atrophy UPPER MOTOR NEURON SYNDROME DAMAGE TO DESENDING PATHWAYS Damage to the pathways driving the motor neurons •Spasticity ...
For your acute ischemic stroke patients The first 24 hours are critical
... References: 1. Jauch EC, Saver JL, Adams HP Jr, et al. Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2013;44(3):870-947. 2. Summers D, Leonard A, Wentworth ...
... References: 1. Jauch EC, Saver JL, Adams HP Jr, et al. Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2013;44(3):870-947. 2. Summers D, Leonard A, Wentworth ...
Motor neuron
... 1. Receptors to pressure & pain are stimulated 2. Sensory neurons carry the impulses to the spinal cord by way of the dorsal root 3. The sensory neuron synapses with many neurons in the spinal cord of the CNS: - an interneuron may carry the signal to the brain to ’advise it’ about the situation. - a ...
... 1. Receptors to pressure & pain are stimulated 2. Sensory neurons carry the impulses to the spinal cord by way of the dorsal root 3. The sensory neuron synapses with many neurons in the spinal cord of the CNS: - an interneuron may carry the signal to the brain to ’advise it’ about the situation. - a ...
DSM-5 proposed diagnostic criteria changes
... employment in occupations exposed to war (such as soldiers) or disaster (such as emergency service workers);[8] or getting a diagnosis of a life-threatening illness.[1] Children or adults may develop PTSD symptoms by experiencing bullying or mobbing.[9][10] Approximately 25% of children exposed to f ...
... employment in occupations exposed to war (such as soldiers) or disaster (such as emergency service workers);[8] or getting a diagnosis of a life-threatening illness.[1] Children or adults may develop PTSD symptoms by experiencing bullying or mobbing.[9][10] Approximately 25% of children exposed to f ...
The Neural Optimal Control Hierarchy
... that comprise the Neural Optimal Control Hierarchy (NOCH). The numbering on this figure is used to aid description, and does not indicate sequential information flow. See text for details. state acceleration by dividing the state space up into areas where the dynamics can be captured with a simple l ...
... that comprise the Neural Optimal Control Hierarchy (NOCH). The numbering on this figure is used to aid description, and does not indicate sequential information flow. See text for details. state acceleration by dividing the state space up into areas where the dynamics can be captured with a simple l ...
Regulation Notes Activity Page 38: Endocrine/Nerve Cell Coloring
... B.10A - describe the interactions that occur among systems that perform the functions of regulation, nutrient absorption, reproduction, and defense from injury or illness in animals ...
... B.10A - describe the interactions that occur among systems that perform the functions of regulation, nutrient absorption, reproduction, and defense from injury or illness in animals ...
NVCC Bio 211 - gserianne.com
... • Memories are not stored in individual “memory cells” or neurons; they are stored as pathways called engrams, or memory traces that use strengthened or altered synapses. • Immediate memory lasts a few seconds, e.g., remembering the earliest part of a sentence to make sense of it. • Short-term memor ...
... • Memories are not stored in individual “memory cells” or neurons; they are stored as pathways called engrams, or memory traces that use strengthened or altered synapses. • Immediate memory lasts a few seconds, e.g., remembering the earliest part of a sentence to make sense of it. • Short-term memor ...
Skeletal Muscle
... Visceral reflexes (also known as autonomic reflexes) refer to reflexes such as those which affect the gland secretion or smooth muscle of the cardiac system to contract. The main purpose of the visceral reflexes is to ensure that the involuntary process of the body are in full operating condition an ...
... Visceral reflexes (also known as autonomic reflexes) refer to reflexes such as those which affect the gland secretion or smooth muscle of the cardiac system to contract. The main purpose of the visceral reflexes is to ensure that the involuntary process of the body are in full operating condition an ...
The Central Nervous System
... – The body is represented spatially and upside-down according to the site of stimulus – The right hemisphere receives input from the left side of the body – The amount of sensory cortex devoted to a body region is related to the region’s sensitivity – The face and fingertips are the most sensitive ...
... – The body is represented spatially and upside-down according to the site of stimulus – The right hemisphere receives input from the left side of the body – The amount of sensory cortex devoted to a body region is related to the region’s sensitivity – The face and fingertips are the most sensitive ...
A Journey Through the Central Nervous System
... – Extension of conus (covered by pia mater) – anchors spinal cord to coccyx – Denticulate ligaments (saw-tooth like pia mater) attach to dura mater ...
... – Extension of conus (covered by pia mater) – anchors spinal cord to coccyx – Denticulate ligaments (saw-tooth like pia mater) attach to dura mater ...
Red Eyes and Ocular Emergencies - Heart of America Contact Lens
... Spreading of infection / inflammation into surrounding eyelid tissue or into orbital socket and into brain ...
... Spreading of infection / inflammation into surrounding eyelid tissue or into orbital socket and into brain ...
MRS study on lentiform nucleus in idiopathic Parkinson`s disease
... disease is about eighty percent; the differentiation of IPD from alternative diagnosis such as multiple system atrophy and progressive supranuclear palsy in life is crucial. Early diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease is even more difficult. But the prognosis will be better if the patients receive accura ...
... disease is about eighty percent; the differentiation of IPD from alternative diagnosis such as multiple system atrophy and progressive supranuclear palsy in life is crucial. Early diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease is even more difficult. But the prognosis will be better if the patients receive accura ...
Allochiria

Allochiria (from the Greek meaning ""other hand"") is a neurological disorder in which the patient responds to stimuli presented to one side of their body as if the stimuli had been presented at the opposite side. It is associated with spatial transpositions, usually symmetrical, of stimuli from one side of the body (or of the space) to the opposite one. Thus a touch to the left arm will be reported as a touch to the right arm, which is also known as somatosensory allochiria. If the auditory or visual senses are affected, sounds (a person's voice for instance) will be reported as being heard on the opposite side to that on which they occur and objects presented visually will be reported as having been presented on the opposite side. Often patients may express allochiria in their drawing while copying an image. Allochiria often co-occurs with unilateral neglect and, like hemispatial neglect, the disorder arises commonly from damage to the right parietal lobe.Allochiria is often confused with alloesthesia, also known as false allochiria. True allochiria is a symptom of dyschiria and unilateral neglect. Dyschiria is a disorder in the localization of sensation due to various degrees of dissociation and cause impairment in one side causing the inability to tell which side of the body was touched.