172 The shortest life expectancy is associated with which clinical
... A. Injury of the skull and brain with contusions and wounds of the soft tissues without lesion of the aponeurosis B. Injury of the skull and brain with contusions and wounds of the soft tissues with the lesion of aponeurosis C. All cases of CCT with liquorrhoea D. Head injury with any types of calva ...
... A. Injury of the skull and brain with contusions and wounds of the soft tissues without lesion of the aponeurosis B. Injury of the skull and brain with contusions and wounds of the soft tissues with the lesion of aponeurosis C. All cases of CCT with liquorrhoea D. Head injury with any types of calva ...
somatic sensory system
... T F 2. The largest diameter sensory fibers innervate muscle spindles and tendon organs, but not the skin. T F 3. Group III afferent fibers mediate slow pain. T F 4. Some of the primary sensory fibers entering the pons with the trigeminal nerve make synapses in the lower medulla. T F 5. All Group III ...
... T F 2. The largest diameter sensory fibers innervate muscle spindles and tendon organs, but not the skin. T F 3. Group III afferent fibers mediate slow pain. T F 4. Some of the primary sensory fibers entering the pons with the trigeminal nerve make synapses in the lower medulla. T F 5. All Group III ...
Ascending Tracts - Bell`s Palsy
... Peripheral process extends to skin or other tissues and ends as free nerve endings (receptors). Cell body is situated in the posterior root ganglion. Central process extends into the posterior grey column and synapses with the 2nd order neuron. ...
... Peripheral process extends to skin or other tissues and ends as free nerve endings (receptors). Cell body is situated in the posterior root ganglion. Central process extends into the posterior grey column and synapses with the 2nd order neuron. ...
“AWAKE” ANESTHESIA FOR SHOULDER SURGERY The goal of
... the problems with thinking associated with general anesthesia. Patients therefore tend to recover faster and feel less drowsy after surgery. In addition to the block, the patient may be given a sedative to help make him (or her) relaxed and to reduce anxiety. This will be different from general anes ...
... the problems with thinking associated with general anesthesia. Patients therefore tend to recover faster and feel less drowsy after surgery. In addition to the block, the patient may be given a sedative to help make him (or her) relaxed and to reduce anxiety. This will be different from general anes ...
Parts of the nervous system
... her allergy from attacking again. 1. Improper use of antibiotics often leads to deafness. Therefore it destroys the sensory neurons/receptors in the ears that receive sound waves. True ...
... her allergy from attacking again. 1. Improper use of antibiotics often leads to deafness. Therefore it destroys the sensory neurons/receptors in the ears that receive sound waves. True ...
Control and Coordination
... sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. It controls the involuntary actions of the internal organs of the body like heart etc. You will learn more about autonomic nervous system in higher classes. 28.6 REFLEX ACTION AND REFLEX ARC There are many actions in our body which are spontaneous and ...
... sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. It controls the involuntary actions of the internal organs of the body like heart etc. You will learn more about autonomic nervous system in higher classes. 28.6 REFLEX ACTION AND REFLEX ARC There are many actions in our body which are spontaneous and ...
The BRAIN - davis.k12.ut.us
... Integrating Center - a region within the CNS (spinal cord or brain) that interprets the information from the sensory neuron and initiates an appropriate response ...
... Integrating Center - a region within the CNS (spinal cord or brain) that interprets the information from the sensory neuron and initiates an appropriate response ...
Done by : Noor Bjant.hala Dr: loai zghol
... proprioceptor from the leg it self : muscle length , muscle tension , joint position in movement . Each nerve has it’s own pathway , our brain can detect anyone if this pathway always give him pain ! so it’s pain pathway , if it’s always give him pressure it’s pressure path way and so on .. *s ...
... proprioceptor from the leg it self : muscle length , muscle tension , joint position in movement . Each nerve has it’s own pathway , our brain can detect anyone if this pathway always give him pain ! so it’s pain pathway , if it’s always give him pressure it’s pressure path way and so on .. *s ...
Life span chapter 3-1 File
... Auditory Perception: The World of Sound Infants – Hear before birth and have good auditory perception after they are born – Are more sensitive to certain frequencies – Reach adult accuracy in sound localization by age 1 – Can discriminate between groups of different sounds – React to changes in mus ...
... Auditory Perception: The World of Sound Infants – Hear before birth and have good auditory perception after they are born – Are more sensitive to certain frequencies – Reach adult accuracy in sound localization by age 1 – Can discriminate between groups of different sounds – React to changes in mus ...
Applying Lean Six Sigma to your Compliance Program
... Value ‐ an activity that administers care or provides a service or information to meet customer/ patient needs and requirements (usually something that the customer/ patient is willing to pay for) Value Stream Map – A graphic map of steps that occur from a request for a product or service to ...
... Value ‐ an activity that administers care or provides a service or information to meet customer/ patient needs and requirements (usually something that the customer/ patient is willing to pay for) Value Stream Map – A graphic map of steps that occur from a request for a product or service to ...
Summary
... In chapter 3 we investigated the relation between the coding of attention and reward in area V1 with a curve-tracing task where we varied the amounts of reward associated with the curves. Similar to previous studies (Platt & Glimcher 1999; Leon & Shadlen 1999; Ikeda & Hikosaka 2003; Sugrue et al 20 ...
... In chapter 3 we investigated the relation between the coding of attention and reward in area V1 with a curve-tracing task where we varied the amounts of reward associated with the curves. Similar to previous studies (Platt & Glimcher 1999; Leon & Shadlen 1999; Ikeda & Hikosaka 2003; Sugrue et al 20 ...
Nervous System - Thephysicsteacher
... (i) Distinguish between the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. Include a clear reference to each in your answer. (ii) Give one way in which a nervous response differs from a hormonal response. (b) (i) Draw a large labelled diagram of a motor neuron. (ii) Give one function each ...
... (i) Distinguish between the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. Include a clear reference to each in your answer. (ii) Give one way in which a nervous response differs from a hormonal response. (b) (i) Draw a large labelled diagram of a motor neuron. (ii) Give one function each ...
A Dynamic Field Theory of Visual Recognition in Infant Looking... Gregor Schöner Sammy Perone () and John P. Spencer ()
... only difference across simulations was in the distribution of the inputs. Mareschal and colleagues (e.g., Mareschal, French, & Quinn, 2000; French et al., 2004) have extensively examined the role of input distribution in asymmetric categorization and have tested predictions of an autoencoder network ...
... only difference across simulations was in the distribution of the inputs. Mareschal and colleagues (e.g., Mareschal, French, & Quinn, 2000; French et al., 2004) have extensively examined the role of input distribution in asymmetric categorization and have tested predictions of an autoencoder network ...
Motor functions
... These axons constitute corticospinal tract, known also as the pyramidal tract. • This tract descends from the cerebral cortex (frontal motor and premotor cortices, ...
... These axons constitute corticospinal tract, known also as the pyramidal tract. • This tract descends from the cerebral cortex (frontal motor and premotor cortices, ...
Lecture 26 revised 03/10 Upper Motor Control Last lecture we
... note how much the disproportions relative to body size look like those in the somatosensory map- corresponds to need for finer motor control of some structures (ears?) Box 17D A difference from how somatotopy works in the somatosensory system, where a point on the surface of the body is processed in ...
... note how much the disproportions relative to body size look like those in the somatosensory map- corresponds to need for finer motor control of some structures (ears?) Box 17D A difference from how somatotopy works in the somatosensory system, where a point on the surface of the body is processed in ...
M555 Medical Neuroscience
... Corticospinal Tract Damage corticospinal tract alone loss of ability to make precise movements of digits more experimental primate studies than actual clinical cases corticospinal tract along with other structures strokes, tumors, traumatic brain injuries motor cortex/corticospinal tract plus other ...
... Corticospinal Tract Damage corticospinal tract alone loss of ability to make precise movements of digits more experimental primate studies than actual clinical cases corticospinal tract along with other structures strokes, tumors, traumatic brain injuries motor cortex/corticospinal tract plus other ...
Richard G. Schuster, DO
... Pain is the conscious perception of inputs to the cortex which results in what is called pain. ...
... Pain is the conscious perception of inputs to the cortex which results in what is called pain. ...
Neurophysiology
... Cerebral Dominance/Laterality • Language Processing in the left hemisphere. (Remember the right ear has the strongest connections to the left hemisphere) • Most people show a right-ear advantage in processing linguistic stimuli ...
... Cerebral Dominance/Laterality • Language Processing in the left hemisphere. (Remember the right ear has the strongest connections to the left hemisphere) • Most people show a right-ear advantage in processing linguistic stimuli ...
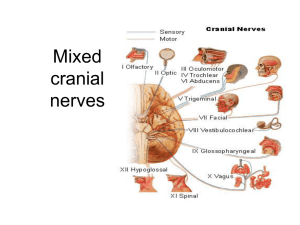
26. Mixed cranial nervest
... combination and function in parasympathetic nervous system. • Cranial nerves I, II and VIII are purely sensory. • Cranial nerves III, IV, VI, XI and XII are motor (although also function balance). ...
... combination and function in parasympathetic nervous system. • Cranial nerves I, II and VIII are purely sensory. • Cranial nerves III, IV, VI, XI and XII are motor (although also function balance). ...
Allochiria

Allochiria (from the Greek meaning ""other hand"") is a neurological disorder in which the patient responds to stimuli presented to one side of their body as if the stimuli had been presented at the opposite side. It is associated with spatial transpositions, usually symmetrical, of stimuli from one side of the body (or of the space) to the opposite one. Thus a touch to the left arm will be reported as a touch to the right arm, which is also known as somatosensory allochiria. If the auditory or visual senses are affected, sounds (a person's voice for instance) will be reported as being heard on the opposite side to that on which they occur and objects presented visually will be reported as having been presented on the opposite side. Often patients may express allochiria in their drawing while copying an image. Allochiria often co-occurs with unilateral neglect and, like hemispatial neglect, the disorder arises commonly from damage to the right parietal lobe.Allochiria is often confused with alloesthesia, also known as false allochiria. True allochiria is a symptom of dyschiria and unilateral neglect. Dyschiria is a disorder in the localization of sensation due to various degrees of dissociation and cause impairment in one side causing the inability to tell which side of the body was touched.