The Middle Ages - Mr. Lilly
... is a social system where king’s give nobles fiefs (land) in exchange for soldiers to serve the king. Nobles give the land to vassals to manage, who distribute the work to serfs (peasants) in exchange for protection. ...
... is a social system where king’s give nobles fiefs (land) in exchange for soldiers to serve the king. Nobles give the land to vassals to manage, who distribute the work to serfs (peasants) in exchange for protection. ...
Name: Period: ______ Homework Sheet Miss Bush Language Arts
... Language Arts: 1. Revise and edit Rough Draft for What caused the fall of the Roman Empire? Paragraph Social Studies: 1. Feudalism Notes- margin questions THURSDAY (10/13) Language Arts: 1. Final Draft: What caused the fall of the Roman Empire? Use a blue or black pen. Social Studies: 1. Pink Sheet ...
... Language Arts: 1. Revise and edit Rough Draft for What caused the fall of the Roman Empire? Paragraph Social Studies: 1. Feudalism Notes- margin questions THURSDAY (10/13) Language Arts: 1. Final Draft: What caused the fall of the Roman Empire? Use a blue or black pen. Social Studies: 1. Pink Sheet ...
European Synthesis
... Patrick carried Christianity to the Irish by transforming their sacred groves, wells, and mounds into centers of worship for the new faith. He also adopted the ancient Celtic deities into the new faith, demoting them to saints Brigit,the goddess of healing and fertility became St. Bridgit in t ...
... Patrick carried Christianity to the Irish by transforming their sacred groves, wells, and mounds into centers of worship for the new faith. He also adopted the ancient Celtic deities into the new faith, demoting them to saints Brigit,the goddess of healing and fertility became St. Bridgit in t ...
Name - Athens Academy
... in the Roman Empire? 4. What was the significance of Charlemagne’s coronation as emperor? 5. What was the basic message of Islam? How was it able to spread so quickly? 6. Describe feudalism. It has been said that feudalism was the perfect political system for the Middles Ages. Explain. 7. Why was th ...
... in the Roman Empire? 4. What was the significance of Charlemagne’s coronation as emperor? 5. What was the basic message of Islam? How was it able to spread so quickly? 6. Describe feudalism. It has been said that feudalism was the perfect political system for the Middles Ages. Explain. 7. Why was th ...
History: Pre - Renaissance
... Issues in Western Civilization, 2 vols., N.Y.: McGraw-Hill, 1992), p. xi. ...
... Issues in Western Civilization, 2 vols., N.Y.: McGraw-Hill, 1992), p. xi. ...
Western Civilization: Antiquity to 1300 What is Western Civilization
... For five thousand years a “Western Civilization” has been growing, changing, reflecting on itself, and sharing ideas with its neighbors. The “West” deserves to be studied because its tale is old and compelling, but demands to be studied because its story has been central to the development of the wo ...
... For five thousand years a “Western Civilization” has been growing, changing, reflecting on itself, and sharing ideas with its neighbors. The “West” deserves to be studied because its tale is old and compelling, but demands to be studied because its story has been central to the development of the wo ...
Chapter 7 notes - Plainview Public Schools
... • After collapse or Rome Western Europe declined politically, socially, and economically • 500 to 1000 was known as dark ages • However, many aspects of Greco Roman, Christian, and Germanic traditions blended • Called Middle Ages ...
... • After collapse or Rome Western Europe declined politically, socially, and economically • 500 to 1000 was known as dark ages • However, many aspects of Greco Roman, Christian, and Germanic traditions blended • Called Middle Ages ...
The Early Middle Ages and The High Middle Ages
... The Medieval Church *After the fall of Rome, the Christian Church split into eastern and western churches. The western church, became known as the Roman Catholic Church • The most powerful secular force in medieval Europe – *The pope claimed authority over all men – Taught all men were sinners and d ...
... The Medieval Church *After the fall of Rome, the Christian Church split into eastern and western churches. The western church, became known as the Roman Catholic Church • The most powerful secular force in medieval Europe – *The pope claimed authority over all men – Taught all men were sinners and d ...
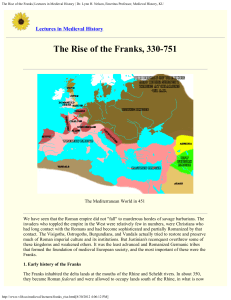
The Rise of the Franks| Lectures in Medieval History | Dr. Lynn H
... fashion, in five years, he had united the Franks under his personal rule. In 486, he attacked the lands of Syagrius, a Roman general holding out in hopes that the Western imperial government would be restored. He defeated Syagrius in a single battle, and moved his capital to the more central and str ...
... fashion, in five years, he had united the Franks under his personal rule. In 486, he attacked the lands of Syagrius, a Roman general holding out in hopes that the Western imperial government would be restored. He defeated Syagrius in a single battle, and moved his capital to the more central and str ...
Emerging Europe and the Middle Ages 500-1500 AD
... Emerging Europe and the Middle Ages 500-1500 A.D. ...
... Emerging Europe and the Middle Ages 500-1500 A.D. ...
European Chaos, Byzantine Empire and the Spread of Islam
... Sicily-- Rome is reclaimed, then lost again to the Lombards – Barbarians take over in the West--Eastern Roman empire will no longer attempt to reclaim lands of the old Roman Empire. – last Latin Emperor--successors were Greeks, influenced by Greek language and customs ...
... Sicily-- Rome is reclaimed, then lost again to the Lombards – Barbarians take over in the West--Eastern Roman empire will no longer attempt to reclaim lands of the old Roman Empire. – last Latin Emperor--successors were Greeks, influenced by Greek language and customs ...
PERIOD 3 CIVILIZATIONS!
... Small communities governed by unwritten rules and traditions replaced loyalty to a centralized government and written laws No centralized rule due to emphasis on personal ties rather than loyalty to an unfamiliar king Clovis brought Christianity to the Franks (Germanic people of Gaul) 511: Clovis un ...
... Small communities governed by unwritten rules and traditions replaced loyalty to a centralized government and written laws No centralized rule due to emphasis on personal ties rather than loyalty to an unfamiliar king Clovis brought Christianity to the Franks (Germanic people of Gaul) 511: Clovis un ...
Byzantine Empire
... • Huge harbor and guarded on three sides by water • Linked Europe and Asia with trade routes • Europe’s busiest marketplace for centuries ...
... • Huge harbor and guarded on three sides by water • Linked Europe and Asia with trade routes • Europe’s busiest marketplace for centuries ...
Classical Civilizations of the West: Persia, Greece and Rome
... Many Greek cities supported philosophers who would lay the ...
... Many Greek cities supported philosophers who would lay the ...
Summary: The Middle Ages
... broke down. People left the towns and cities. Travel and trade became unsafe. The people of Rome turned to military leaders and the Catholic Church for help. The military leader Charlemagne brought order to much of the Roman Empire. The Pope made Charlemagne emperor. The government grew strong again ...
... broke down. People left the towns and cities. Travel and trade became unsafe. The people of Rome turned to military leaders and the Catholic Church for help. The military leader Charlemagne brought order to much of the Roman Empire. The Pope made Charlemagne emperor. The government grew strong again ...
Western Europe During the High Middle Ages
... Both the French and English consolidated their feudal estates into the centralized governments of French kings. ...
... Both the French and English consolidated their feudal estates into the centralized governments of French kings. ...
The Middle Ages in Western Europe
... – Crusades (11th – 13th centuries) – Hundred Years War (14th century): Though primarily a dynastic conflict, the war gave impetus to ideas of both French and English nationality. Militarily, it saw the introduction of new weapons and tactics, which eroded the older system of feudal armies dominated ...
... – Crusades (11th – 13th centuries) – Hundred Years War (14th century): Though primarily a dynastic conflict, the war gave impetus to ideas of both French and English nationality. Militarily, it saw the introduction of new weapons and tactics, which eroded the older system of feudal armies dominated ...
Political Developments of the Middle Ages
... was captured and executed by the English as a witch; but her impact on the war could not be stopped. The French rallied around Charles and the memory of Joan and pushed the English forces from France by 1453. There were some positives that came out of the Hundred Years’ War. The French had developed ...
... was captured and executed by the English as a witch; but her impact on the war could not be stopped. The French rallied around Charles and the memory of Joan and pushed the English forces from France by 1453. There were some positives that came out of the Hundred Years’ War. The French had developed ...
Middle Ages
... • Trade and education declined during the early Middle Ages. • The population of towns also declined when serfs moved to villages near lords’ castles. • Consequently, kings also became weaker as countries were divided into areas controlled by the feudal lords. • Wars often broke out between lords wh ...
... • Trade and education declined during the early Middle Ages. • The population of towns also declined when serfs moved to villages near lords’ castles. • Consequently, kings also became weaker as countries were divided into areas controlled by the feudal lords. • Wars often broke out between lords wh ...
Europe During the Early Middle Ages
... 8. Although the eastern half of the former Roman Empire thrived as the Byzantine Empire, the western half was controlled by many different groups of a) b) c) d) ...
... 8. Although the eastern half of the former Roman Empire thrived as the Byzantine Empire, the western half was controlled by many different groups of a) b) c) d) ...
The Barbarians
... – improved military technology (easier to defend from invaders and to control subjects) – more intense agricultural investment (higher motivation to stand one’s ground against invaders) • All new states convert to Christianity in order to be admitted to the club of European states ...
... – improved military technology (easier to defend from invaders and to control subjects) – more intense agricultural investment (higher motivation to stand one’s ground against invaders) • All new states convert to Christianity in order to be admitted to the club of European states ...
The Development of Feudalism in Western Europe
... knights were expected to live by. ► At around age 7, a boy would start training to be a knight. ...
... knights were expected to live by. ► At around age 7, a boy would start training to be a knight. ...
Chapter 13
... Invasion Triggers Change • The Germanic invaders could not read & write, and the knowledge of Greek & Roman culture almost disappeared. ...
... Invasion Triggers Change • The Germanic invaders could not read & write, and the knowledge of Greek & Roman culture almost disappeared. ...
Migration Period

The Migration Period, better known as the Barbarian Invasions also referred to as the Völkerwanderung (in German), was a period of intensified barbarian invasion in Europe, often defined from the period when it seriously impacted the Roman world, as running from about 376 to 800 AD during the transition from Late Antiquity to the Early Middle Ages. This period was marked by profound changes both within the Roman Empire and beyond its ""barbarian frontier"". The barbarians who came first were Germanic tribes such as the Goths, Vandals, Angles, Saxons, Lombards, Suebi, Frisii, Jutes and Franks; they were later pushed westwards by the Huns, Avars, Slavs, Bulgars and Alans.Later barbarian invasions (such as the Viking, Norman, Hungarian, Moorish, Turkic, and Mongol invasions) also had significant effects (especially in North Africa, the Iberian peninsula, Anatolia and Central and Eastern Europe); however, they are outside the scope of the Migration Period.