–1200 Christian Europe Emerges, 300 CHAPTER 10
... 1. While Roman rule and the traditions of Rome died in the west, they were preserved in the Byzantine Empire and in its capital, Constantinople. 2. While the popes in Rome were independent of secular power, the Byzantine emperor appointed the patriarch of Constantinople and intervened in doctrinal d ...
... 1. While Roman rule and the traditions of Rome died in the west, they were preserved in the Byzantine Empire and in its capital, Constantinople. 2. While the popes in Rome were independent of secular power, the Byzantine emperor appointed the patriarch of Constantinople and intervened in doctrinal d ...
Text Ch.9 - Christian Europe Emerges
... 1. While Roman rule and the traditions of Rome died in the west, they were preserved in the Byzantine Empire and in its capital, Constantinople. 2. While the popes in Rome were independent of secular power, the Byzantine emperor appointed the patriarch of Constantinople and intervened in doctrinal d ...
... 1. While Roman rule and the traditions of Rome died in the west, they were preserved in the Byzantine Empire and in its capital, Constantinople. 2. While the popes in Rome were independent of secular power, the Byzantine emperor appointed the patriarch of Constantinople and intervened in doctrinal d ...
Chapter 1 The First Humans Prehistory – 3500 BC
... choosing (in 962) to crown a German king as “Holy Roman Emperor.” The Holy Roman Empire was in fact no more than a loose coalition of German princes. 2. Even within the Holy Roman Empire, secular rulers argued that they should have the power to appoint bishops who held land in fief. Popes disagreed ...
... choosing (in 962) to crown a German king as “Holy Roman Emperor.” The Holy Roman Empire was in fact no more than a loose coalition of German princes. 2. Even within the Holy Roman Empire, secular rulers argued that they should have the power to appoint bishops who held land in fief. Popes disagreed ...
Chapter 13 - cloudfront.net
... Western Roman Empire. Barbarian invasions and settlement/ new customs, and lifestyles to many parts of western Europe. 400’s-1500s’ as a transition in the development of ...
... Western Roman Empire. Barbarian invasions and settlement/ new customs, and lifestyles to many parts of western Europe. 400’s-1500s’ as a transition in the development of ...
Music History World Music - Ancient Music Lecture Notes Prehistoric
... b. Area of land located between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers in modern day Iraq. c. Home to some of the most advanced ancient peoples. d. In this region, societies made music a central part of their religious rites and festivals. e. Beginning around 1800 B.C., Babylonians included psalms and hymn ...
... b. Area of land located between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers in modern day Iraq. c. Home to some of the most advanced ancient peoples. d. In this region, societies made music a central part of their religious rites and festivals. e. Beginning around 1800 B.C., Babylonians included psalms and hymn ...
Middle Ages Review
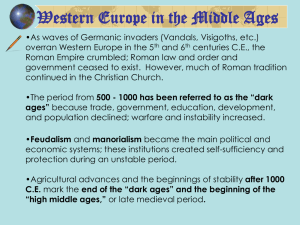
... developed after the fall of the Roman Empire in medieval Europe came about as a consequence of the civil disorder, economic instability and a lack of centralized authority. This led to the development of feudalism and the manorial system which allowed societies to adapt to a symbiotic relationship b ...
... developed after the fall of the Roman Empire in medieval Europe came about as a consequence of the civil disorder, economic instability and a lack of centralized authority. This led to the development of feudalism and the manorial system which allowed societies to adapt to a symbiotic relationship b ...
13.1 Germanic Kingdoms Unite Under Charlemagne
... The Decline of Learning The Germanic invaders could not read or write o Rich oral tradition – no language Learning declined in Rome as others fled to rural areas Only priests and church officials were literate Greek culture lost language Loss of a Common Language As German speaking people ...
... The Decline of Learning The Germanic invaders could not read or write o Rich oral tradition – no language Learning declined in Rome as others fled to rural areas Only priests and church officials were literate Greek culture lost language Loss of a Common Language As German speaking people ...
Lesson 1 An Empire in Decline
... • Problems followed death of Emperor Marcus Aurelius in A.D. 180 • Empire couldnʼt feed everyone and food shortages caused unrest - warfare destroyed some farmland - plantations used slaves instead of finding new farming technology - land wore out, became unproductive; harvests decreased • People di ...
... • Problems followed death of Emperor Marcus Aurelius in A.D. 180 • Empire couldnʼt feed everyone and food shortages caused unrest - warfare destroyed some farmland - plantations used slaves instead of finding new farming technology - land wore out, became unproductive; harvests decreased • People di ...
Slide 1
... Feudalism: a decentralized, localized form of government based on land and military service. It began to take hold in Europe around the 8th century and became standard after the breakup of Charlemagne’s empire. Manorialism: is the economic system that accompanied feudalism. It dealt more with the re ...
... Feudalism: a decentralized, localized form of government based on land and military service. It began to take hold in Europe around the 8th century and became standard after the breakup of Charlemagne’s empire. Manorialism: is the economic system that accompanied feudalism. It dealt more with the re ...
Crusades - kwamekstith
... in the Crusades? “For knights, this was a chance to use their fighting skills, something they enjoyed and did well. They were delighted to have such a worthy battle to fight. For peasants, this was a chance to escape from their dreary life in the feudal system. The pope promised that if they died wh ...
... in the Crusades? “For knights, this was a chance to use their fighting skills, something they enjoyed and did well. They were delighted to have such a worthy battle to fight. For peasants, this was a chance to escape from their dreary life in the feudal system. The pope promised that if they died wh ...
The High Middle Ages - Ms. Sheets` AP World History Class
... • Try to free church from interference from states • Quarrels with HRE Henry IV over investiture (whose right is it to appoint bishops? King or Pope?) • Proves Church is superior to state • Several reform movements created to combat perceived corruption in Church • Mendicant friar groups, 13th centu ...
... • Try to free church from interference from states • Quarrels with HRE Henry IV over investiture (whose right is it to appoint bishops? King or Pope?) • Proves Church is superior to state • Several reform movements created to combat perceived corruption in Church • Mendicant friar groups, 13th centu ...
Name: _______KEY____________ Date: End of Course
... 5. What area of land did Sargon conquer? He also set up the world’s first empire. What is an empire? Sargon conquered all of Mesopotamia. An empire is a group of many different lands under one ruler. Sargon’s empire lasted for more than 200 years before falling to invaders. 6. Read about Hammurabi o ...
... 5. What area of land did Sargon conquer? He also set up the world’s first empire. What is an empire? Sargon conquered all of Mesopotamia. An empire is a group of many different lands under one ruler. Sargon’s empire lasted for more than 200 years before falling to invaders. 6. Read about Hammurabi o ...
Charlemagne
... Downfall of Cities—cities abandoned as centers of administration Population Shifts—lords and commoners leave cities and move to suburbs ...
... Downfall of Cities—cities abandoned as centers of administration Population Shifts—lords and commoners leave cities and move to suburbs ...
Unit 3 Study Guide Fannin/Price Fall 2009 Which European
... In which two countries was Calvinism the dominant religion? What was the dominant religion between 1500 and 1600 in the greatest number of countries? In what year did Denmark adopt Lutheranism as its chief religion? Around what body of water did the Lutherans dominate? In which state were three diff ...
... In which two countries was Calvinism the dominant religion? What was the dominant religion between 1500 and 1600 in the greatest number of countries? In what year did Denmark adopt Lutheranism as its chief religion? Around what body of water did the Lutherans dominate? In which state were three diff ...
Germanic Kingdoms in the West
... The Germans’ long history of migration and their constant fights with the other peoples of the eastern plains had made them into a warriorhunter society. War was necessary to defend the tribe, and the people devoted all their resources to it. All free men were expected to learn the use of arms—spear ...
... The Germans’ long history of migration and their constant fights with the other peoples of the eastern plains had made them into a warriorhunter society. War was necessary to defend the tribe, and the people devoted all their resources to it. All free men were expected to learn the use of arms—spear ...
Document
... Loss of scholarship, literacy Latin was no longer a common language Eastern Roman Empire (Byzantines) preferred Greek As people went rural, dialects formed – What is a dialect? French, Spanish, Italian, Romanian developed Germanic Kingdoms Much smaller, decentralized Franks, Goths, V ...
... Loss of scholarship, literacy Latin was no longer a common language Eastern Roman Empire (Byzantines) preferred Greek As people went rural, dialects formed – What is a dialect? French, Spanish, Italian, Romanian developed Germanic Kingdoms Much smaller, decentralized Franks, Goths, V ...
Early Middle Ages
... Middle Ages, Medieval ages , Dark ages ? • Middle as in time between the end of the Roman Empire and ancient civilization and the rebirth (Renaissance) of progress/growth in Europe • Medieval is “middle” in Latin • Early Middle Ages is called the Dark Age because it was not a great time in Europe: ...
... Middle Ages, Medieval ages , Dark ages ? • Middle as in time between the end of the Roman Empire and ancient civilization and the rebirth (Renaissance) of progress/growth in Europe • Medieval is “middle” in Latin • Early Middle Ages is called the Dark Age because it was not a great time in Europe: ...
H007-014 Review for Test 1/19/2015 Name: ANSWERS __ DUE
... 2. They enjoyed ransacking and destroying Europe. 3. They believed that it was their divine right to rule Europe. 4. Their land was mountainous and rocky, making farming difficult at best. 18. The rapid changes that occurred during the late Middle Ages in Europe had the effect of 1. expanding the in ...
... 2. They enjoyed ransacking and destroying Europe. 3. They believed that it was their divine right to rule Europe. 4. Their land was mountainous and rocky, making farming difficult at best. 18. The rapid changes that occurred during the late Middle Ages in Europe had the effect of 1. expanding the in ...
Western Europe after the Fall of the Western Roman
... such as Corinth, Galatia, and Ephesus, Saul, who would come to be known by his Greco-Roman name Paul, was able to travel and spread the message of Jesus to people throughout the many regions of the empire because of the peace and prosperity that existed there during the first-century. His extremely ...
... such as Corinth, Galatia, and Ephesus, Saul, who would come to be known by his Greco-Roman name Paul, was able to travel and spread the message of Jesus to people throughout the many regions of the empire because of the peace and prosperity that existed there during the first-century. His extremely ...
Rome after its Empire: From the Germanic Middle Ages to the early
... Imperial power in Rome & Western provinces of Empire granted to Pope becomes official basis for claims of secular power by Pope probably 8th C forgery (circa 750, modeled on actual Donation of Pepin) following Frankish invasion of Italy against Lombards ...
... Imperial power in Rome & Western provinces of Empire granted to Pope becomes official basis for claims of secular power by Pope probably 8th C forgery (circa 750, modeled on actual Donation of Pepin) following Frankish invasion of Italy against Lombards ...
Syllabus - Institute for the Study of the Ancient World
... 2.) Final paper (50%) A final research paper is expected at the end of the semester. This paper should incorporate some of the conceptual themes discussed in the seminar section of the course, and ...
... 2.) Final paper (50%) A final research paper is expected at the end of the semester. This paper should incorporate some of the conceptual themes discussed in the seminar section of the course, and ...
File
... days in 410 CE—beginning of the end Next 60 years are a series of good harvests followed by sacks by various Germanic tribes (Goths, Visigoths, Ostrogoths Franks, Magyars, Saxons, Jutes, Lombards, etc.) Romulus Augustus is overthrown in 476 C.E. ...
... days in 410 CE—beginning of the end Next 60 years are a series of good harvests followed by sacks by various Germanic tribes (Goths, Visigoths, Ostrogoths Franks, Magyars, Saxons, Jutes, Lombards, etc.) Romulus Augustus is overthrown in 476 C.E. ...
Early Middle Ages (476 C.E.
... created beautiful religious books by hand. Monasteries were the only centers of learning during the early Middle Ages. ...
... created beautiful religious books by hand. Monasteries were the only centers of learning during the early Middle Ages. ...
reading.one - Dr. Albrecht Classen
... vast majority of Europeans probably never traveled far from the place of their birth, pilgrims, scholars and soldiers also helped to spread goods, news and ideas. The fourteenth and fifteenth centuries, known as the "Later Middle Ages," are best known for the traumas they brought. Population growth ...
... vast majority of Europeans probably never traveled far from the place of their birth, pilgrims, scholars and soldiers also helped to spread goods, news and ideas. The fourteenth and fifteenth centuries, known as the "Later Middle Ages," are best known for the traumas they brought. Population growth ...
The Middle Ages - Harrison Humanities
... With nationalism beginning to take hold in Europe, there arose a natural antagonism between the single most important international office, the Catholic Church, and the various kingdoms. This conflict of interest between the papacy and the secular order reshaped the political landscape of Europe. On ...
... With nationalism beginning to take hold in Europe, there arose a natural antagonism between the single most important international office, the Catholic Church, and the various kingdoms. This conflict of interest between the papacy and the secular order reshaped the political landscape of Europe. On ...
Migration Period

The Migration Period, better known as the Barbarian Invasions also referred to as the Völkerwanderung (in German), was a period of intensified barbarian invasion in Europe, often defined from the period when it seriously impacted the Roman world, as running from about 376 to 800 AD during the transition from Late Antiquity to the Early Middle Ages. This period was marked by profound changes both within the Roman Empire and beyond its ""barbarian frontier"". The barbarians who came first were Germanic tribes such as the Goths, Vandals, Angles, Saxons, Lombards, Suebi, Frisii, Jutes and Franks; they were later pushed westwards by the Huns, Avars, Slavs, Bulgars and Alans.Later barbarian invasions (such as the Viking, Norman, Hungarian, Moorish, Turkic, and Mongol invasions) also had significant effects (especially in North Africa, the Iberian peninsula, Anatolia and Central and Eastern Europe); however, they are outside the scope of the Migration Period.