Chapter #12.2
... varied from island to island noted both similarities and differences between the islands and other parts of the world Began working on an idea that new organisms develop from preexisting organisms over time This is the traditional definition for evolution ...
... varied from island to island noted both similarities and differences between the islands and other parts of the world Began working on an idea that new organisms develop from preexisting organisms over time This is the traditional definition for evolution ...
Content Standards
... Students who demonstrate understanding can: MS-LS4-1. Analyze and interpret data for patterns in the fossil record that document the existence, diversity, extinction, and change of life forms throughout the history of life on Earth under the assumption that natural laws operate today as in the past. ...
... Students who demonstrate understanding can: MS-LS4-1. Analyze and interpret data for patterns in the fossil record that document the existence, diversity, extinction, and change of life forms throughout the history of life on Earth under the assumption that natural laws operate today as in the past. ...
EVOLUTION AND CHANGE POWERPOINT
... 3. Evolution is gradual, taking place over a long time. 4. The mechanism of evolution is natural selection. ...
... 3. Evolution is gradual, taking place over a long time. 4. The mechanism of evolution is natural selection. ...
a. artificial selection.
... homologous vestigial dichotomous fossilized 4. In science, theories are: an educated guess a known fact absolute and unchangeable the best explanation for a set of data or observations 7. Any variation that can help an organism survive in its environment is called a(n): adaptation characteristic com ...
... homologous vestigial dichotomous fossilized 4. In science, theories are: an educated guess a known fact absolute and unchangeable the best explanation for a set of data or observations 7. Any variation that can help an organism survive in its environment is called a(n): adaptation characteristic com ...
Evolution - Coach Blair`s Biology Website
... Each new generation is largely made up of offspring ...
... Each new generation is largely made up of offspring ...
Evolution Notes 3
... Evolution Lecture Notes Part III Microevolution When organisms change in _____________________ over time (their traits change) Does not create a NEW species Ex: _________________________________________ Macroevolution Much bigger evolutionary changes that ____________________________________ ...
... Evolution Lecture Notes Part III Microevolution When organisms change in _____________________ over time (their traits change) Does not create a NEW species Ex: _________________________________________ Macroevolution Much bigger evolutionary changes that ____________________________________ ...
12/18/06
... organisms become evident when we look at embryonic development. For example, all vertebrate embryos have structures called pharyngeal pouches in their throat at some stage in their development. ...
... organisms become evident when we look at embryonic development. For example, all vertebrate embryos have structures called pharyngeal pouches in their throat at some stage in their development. ...
Week 2
... B.8.1 Explain how anatomical and molecular similarities among organisms suggests that life on earth began as simple, one-celled organisms about 4 billion years ago and multicellular organisms evolved later. B.8.3 Use anatomical and molecular evidence to establish evolutionary relationships among org ...
... B.8.1 Explain how anatomical and molecular similarities among organisms suggests that life on earth began as simple, one-celled organisms about 4 billion years ago and multicellular organisms evolved later. B.8.3 Use anatomical and molecular evidence to establish evolutionary relationships among org ...
PPT
... Adaptation (def.) – inherited characteristic that improves an organism's ability to survive and reproduce in a particular environment EXAMPLES?? ...
... Adaptation (def.) – inherited characteristic that improves an organism's ability to survive and reproduce in a particular environment EXAMPLES?? ...
Environmental AP
... 78. The role a species plays in the community is called 79. When 2 species with the same role in the community occupy the same habitat and one species is eventually removed from the habitat, it is called 80. The number of niches a community can have is determined by 81. These two species share the s ...
... 78. The role a species plays in the community is called 79. When 2 species with the same role in the community occupy the same habitat and one species is eventually removed from the habitat, it is called 80. The number of niches a community can have is determined by 81. These two species share the s ...
DO NOT WRITE ON THE EXAM Test: changes over time (100 points
... 18. _____ selection favors one extreme form of a trait in a population. a. directional b. stabilizing c. disruptive ...
... 18. _____ selection favors one extreme form of a trait in a population. a. directional b. stabilizing c. disruptive ...
Evolution
... • Physical adaptations – size, shape, color and structure of organisms or parts of organisms – Example: camels have extremely wide two toed feet to avoid sinking in sand ...
... • Physical adaptations – size, shape, color and structure of organisms or parts of organisms – Example: camels have extremely wide two toed feet to avoid sinking in sand ...
Mechanisms of Evolution Practice Write the term or phrase that best
... 14. The flying squirrel of North America closely resembles the flying phalanger of Australia. They are similar in size and have long, bushy tails and skin folds that allow them to glide through the air. The squirrel is a placental mammal, while the phalanger is a marsupial. These close resemblances ...
... 14. The flying squirrel of North America closely resembles the flying phalanger of Australia. They are similar in size and have long, bushy tails and skin folds that allow them to glide through the air. The squirrel is a placental mammal, while the phalanger is a marsupial. These close resemblances ...
Evolution
... observed among the diverse species of living organisms. The degree of kinship between organisms or species can be estimated from the similarity of their DNA sequences; this similarity often closely matches organisms' or species' classification based on anatomical similarities. ...
... observed among the diverse species of living organisms. The degree of kinship between organisms or species can be estimated from the similarity of their DNA sequences; this similarity often closely matches organisms' or species' classification based on anatomical similarities. ...
Theory of Evolution
... similar species. The genus Ursus contains five other species of bears, The second part of a scientific name— maritimus for polar bears—is the species and is often a description of the organism’s habitat or of an important trait. The Latin word maritimus refers to the sea: ...
... similar species. The genus Ursus contains five other species of bears, The second part of a scientific name— maritimus for polar bears—is the species and is often a description of the organism’s habitat or of an important trait. The Latin word maritimus refers to the sea: ...
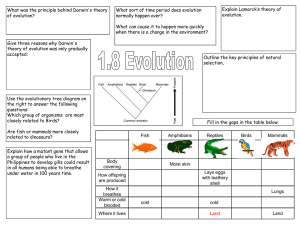
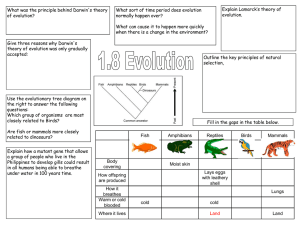
1.8_Evolution
... of evolution? All species evolved from simpler life forms that first developed more than 3 billion years ago Give three reasons why Darwin's theory of evolution was only gradually accepted: •Challenged religion – idea that god made all living organisms •Insufficient evidence at time •Mechanism of in ...
... of evolution? All species evolved from simpler life forms that first developed more than 3 billion years ago Give three reasons why Darwin's theory of evolution was only gradually accepted: •Challenged religion – idea that god made all living organisms •Insufficient evidence at time •Mechanism of in ...
File
... of evolution? All species evolved from simpler life forms that first developed more than 3 billion years ago Give three reasons why Darwin's theory of evolution was only gradually accepted: •Challenged religion – idea that god made all living organisms •Insufficient evidence at time •Mechanism of in ...
... of evolution? All species evolved from simpler life forms that first developed more than 3 billion years ago Give three reasons why Darwin's theory of evolution was only gradually accepted: •Challenged religion – idea that god made all living organisms •Insufficient evidence at time •Mechanism of in ...
Evolution
... • Provides more evidence for descent with modification • Homologous Structures —body structures from different species that originated by heredity from a structure in a common ancestor. • Show that an inherited structural pattern became modified overtime as different populations of descendants adapt ...
... • Provides more evidence for descent with modification • Homologous Structures —body structures from different species that originated by heredity from a structure in a common ancestor. • Show that an inherited structural pattern became modified overtime as different populations of descendants adapt ...
Possible snow day work 3/10 File
... related organisms? a. analogous structures b. embryo development c. genes d. DNA hybridization _______6. A biologist analyzes the DNA sequences in three different primates. The biologist finds that primates A and B have nearly identical DNA sequences. The DNA sequences in primate C are significantly ...
... related organisms? a. analogous structures b. embryo development c. genes d. DNA hybridization _______6. A biologist analyzes the DNA sequences in three different primates. The biologist finds that primates A and B have nearly identical DNA sequences. The DNA sequences in primate C are significantly ...
Biology A
... What allowed mammals to evolve to become larger? What was the first kind of mammal (hint: they’re still alive on Australia)? Why are there so many different mammals when they all started as one kind? ...
... What allowed mammals to evolve to become larger? What was the first kind of mammal (hint: they’re still alive on Australia)? Why are there so many different mammals when they all started as one kind? ...
Evolving digital ecological networks
Evolving digital ecological networks are webs of interacting, self-replicating, and evolving computer programs (i.e., digital organisms) that experience the same major ecological interactions as biological organisms (e.g., competition, predation, parasitism, and mutualism). Despite being computational, these programs evolve quickly in an open-ended way, and starting from only one or two ancestral organisms, the formation of ecological networks can be observed in real-time by tracking interactions between the constantly evolving organism phenotypes. These phenotypes may be defined by combinations of logical computations (hereafter tasks) that digital organisms perform and by expressed behaviors that have evolved. The types and outcomes of interactions between phenotypes are determined by task overlap for logic-defined phenotypes and by responses to encounters in the case of behavioral phenotypes. Biologists use these evolving networks to study active and fundamental topics within evolutionary ecology (e.g., the extent to which the architecture of multispecies networks shape coevolutionary outcomes, and the processes involved).