Indirect Evidence of Evolution
... Features are rudimentary structures with no apparent useful function This suggests that they once served some function in an ancient ancestor, but the organism evolved to function without the structure. ...
... Features are rudimentary structures with no apparent useful function This suggests that they once served some function in an ancient ancestor, but the organism evolved to function without the structure. ...
Evolution Reading Updated 2008
... II: Explain the history of life in terms of biodiversity, ancestry, and the rates of evolution The work of Charles Darwin and Gregor Mendel laid a foundation to explain the large diversity of species found today. Adaptive radiation is when species diversity occurs in a relatively short time. It occu ...
... II: Explain the history of life in terms of biodiversity, ancestry, and the rates of evolution The work of Charles Darwin and Gregor Mendel laid a foundation to explain the large diversity of species found today. Adaptive radiation is when species diversity occurs in a relatively short time. It occu ...
"evolution" is best described as
... bacterial infections. After a number of years, there were outbreaks of staphylococcal infections that did not respond to treatment with penicillin. The best explanation for this situation is that members of the original population of bacteria that were penicillin resistant survived and reproduced, c ...
... bacterial infections. After a number of years, there were outbreaks of staphylococcal infections that did not respond to treatment with penicillin. The best explanation for this situation is that members of the original population of bacteria that were penicillin resistant survived and reproduced, c ...
Origins of Life
... variations will gradually lead to the appearance of new species better adapted to their environment. • Weakness in Darwin’s Theory is that it does not account for genetic basis of variations. At the time, not much was known about the mechanisms of genetic inheritance. ...
... variations will gradually lead to the appearance of new species better adapted to their environment. • Weakness in Darwin’s Theory is that it does not account for genetic basis of variations. At the time, not much was known about the mechanisms of genetic inheritance. ...
Important Concepts - Alaska K-12 Science Curricular Initiative (AKSCI)
... should know and understand by the end of eighth grade are: By the end of 8th grade, students should know that: · One of the most general distinctions among organisms is between plants, which use sunlight to make their own food, and animals, which consume energy-rich foods. Some kinds of organisms, m ...
... should know and understand by the end of eighth grade are: By the end of 8th grade, students should know that: · One of the most general distinctions among organisms is between plants, which use sunlight to make their own food, and animals, which consume energy-rich foods. Some kinds of organisms, m ...
Big Idea 1 - Amundsen High School
... • Phylogenetic trees and cladograms are dynamic (i.e. they are constantly being revised), based on the biological data used, new mathematical and computational ideas, and current and emerging knowledge. ...
... • Phylogenetic trees and cladograms are dynamic (i.e. they are constantly being revised), based on the biological data used, new mathematical and computational ideas, and current and emerging knowledge. ...
Life Sciences 11 with elaborations - BC Curriculum
... • How might the range of abiotic and biotic characteristics on Earth help us to understand space exploration (e.g., extreme environments — Mars, moon)? Taxonomy Sample opportunities to support student inquiry: • Why do two organisms compete to coexist in the same niche? • How is DNA analysis used to ...
... • How might the range of abiotic and biotic characteristics on Earth help us to understand space exploration (e.g., extreme environments — Mars, moon)? Taxonomy Sample opportunities to support student inquiry: • Why do two organisms compete to coexist in the same niche? • How is DNA analysis used to ...
Origins of Life - Amazon Web Services
... Random events produced stable molecules that would reproduce themselves. Then Natural Selection favored changes that increased their rate of reproduction. This eventually lead to the first cell. Organic acids came together to form organisms. ...
... Random events produced stable molecules that would reproduce themselves. Then Natural Selection favored changes that increased their rate of reproduction. This eventually lead to the first cell. Organic acids came together to form organisms. ...
Evolution
... Random events produced stable molecules that would reproduce themselves. Then Natural Selection favored changes that increased their rate of reproduction. This eventually lead to the first cell. Organic acids came together to form organisms. ...
... Random events produced stable molecules that would reproduce themselves. Then Natural Selection favored changes that increased their rate of reproduction. This eventually lead to the first cell. Organic acids came together to form organisms. ...
Natural selection and evolution
... 9. During the nineteenth and early twentieth centuries, the Hessian fly repeatedly wiped out wheat crops in the US. Eventually, scientists developed a strain of wheat that made a toxin that repelled the Hessian fly. What most likely happened to the Hessian fly population after farmers began growing ...
... 9. During the nineteenth and early twentieth centuries, the Hessian fly repeatedly wiped out wheat crops in the US. Eventually, scientists developed a strain of wheat that made a toxin that repelled the Hessian fly. What most likely happened to the Hessian fly population after farmers began growing ...
Biology and the Living World
... possible explanations of these observations that can be used in forming predictions that can be tested experimentally. Some hypotheses are rejected based on experimentation, while others are tentatively accepted. Scientific investigations use a series of six stages, called the scientific process, to ...
... possible explanations of these observations that can be used in forming predictions that can be tested experimentally. Some hypotheses are rejected based on experimentation, while others are tentatively accepted. Scientific investigations use a series of six stages, called the scientific process, to ...
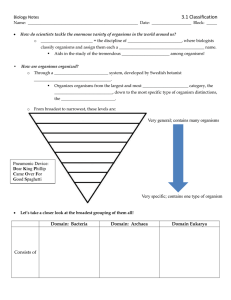
3.1 Classification
... Name: _____________________________________________________ Date: ___________________ Block: _____ ...
... Name: _____________________________________________________ Date: ___________________ Block: _____ ...
Fitness and Life Histories
... acclimate to the food and nutrients • LOG PHASE: metabolic machinery is running, exponentially multiplication of population density, doubling in number every few minutes. • STATIONARY PHASE: competition for food and nutrients causes number of bacteria to ...
... acclimate to the food and nutrients • LOG PHASE: metabolic machinery is running, exponentially multiplication of population density, doubling in number every few minutes. • STATIONARY PHASE: competition for food and nutrients causes number of bacteria to ...
Overproduction
... • Genotype is the alleles, or variations, of a gene that are carried by an organism. Organisms inherit one copy of each gene from each parent. • Genotypes are represented using letters for each allele. Capital letters represent the dominant allele, lower case letters represent the recessive allele. ...
... • Genotype is the alleles, or variations, of a gene that are carried by an organism. Organisms inherit one copy of each gene from each parent. • Genotypes are represented using letters for each allele. Capital letters represent the dominant allele, lower case letters represent the recessive allele. ...
Evolution Ch. 15&16
... Change in a species due to mutation of the DNA code that occurs over a long time ...
... Change in a species due to mutation of the DNA code that occurs over a long time ...
Divergent evolution - Miss Williams` Weebly
... • There are several ways that species can change to adapt to their environment ...
... • There are several ways that species can change to adapt to their environment ...
Alief ISD Biology STAAR EOC Review Reporting Category 3
... The environment may pose many challenges. Resources are scarce and predators and competitors are numerous. Many organisms will die before they reproduce. However, certain phenotypes can give some individuals a fitness advantage. Fitness refers to an organism’s ability to survive, attract a mate, and ...
... The environment may pose many challenges. Resources are scarce and predators and competitors are numerous. Many organisms will die before they reproduce. However, certain phenotypes can give some individuals a fitness advantage. Fitness refers to an organism’s ability to survive, attract a mate, and ...
What causes inherited variation among individuals in a population?
... The environment may pose many challenges. Resources are scarce and predators and competitors are numerous. Many organisms will die before they reproduce. However, certain phenotypes can give some individuals a fitness advantage. Fitness refers to an organism’s ability to survive, attract a mate, and ...
... The environment may pose many challenges. Resources are scarce and predators and competitors are numerous. Many organisms will die before they reproduce. However, certain phenotypes can give some individuals a fitness advantage. Fitness refers to an organism’s ability to survive, attract a mate, and ...
Evolution PowerPoint
... Well developed molar teeth 2. Use the information to Sharp, bony tusks on face ...
... Well developed molar teeth 2. Use the information to Sharp, bony tusks on face ...
File - Gander biology
... The environment may pose many challenges. Resources are scarce and predators and competitors are numerous. Many organisms will die before they reproduce. However, certain phenotypes can give some individuals a fitness advantage. Fitness refers to an organism’s ability to survive, attract a mate, and ...
... The environment may pose many challenges. Resources are scarce and predators and competitors are numerous. Many organisms will die before they reproduce. However, certain phenotypes can give some individuals a fitness advantage. Fitness refers to an organism’s ability to survive, attract a mate, and ...
Evolution . . . .
... characteristics that help an organism survive. Sharp teeth help to eat meat ...
... characteristics that help an organism survive. Sharp teeth help to eat meat ...
10th abbreviated evolution - Hatboro
... • Artificial selection- nature provides the variation among different organisms, and humans select those variations they find useful. – Ex. BREEDING ...
... • Artificial selection- nature provides the variation among different organisms, and humans select those variations they find useful. – Ex. BREEDING ...
Darwin*s Theory of Evolution
... Individuals best suited for the environment survive and reproduce most successful Species change over time ...
... Individuals best suited for the environment survive and reproduce most successful Species change over time ...
Evolving digital ecological networks
Evolving digital ecological networks are webs of interacting, self-replicating, and evolving computer programs (i.e., digital organisms) that experience the same major ecological interactions as biological organisms (e.g., competition, predation, parasitism, and mutualism). Despite being computational, these programs evolve quickly in an open-ended way, and starting from only one or two ancestral organisms, the formation of ecological networks can be observed in real-time by tracking interactions between the constantly evolving organism phenotypes. These phenotypes may be defined by combinations of logical computations (hereafter tasks) that digital organisms perform and by expressed behaviors that have evolved. The types and outcomes of interactions between phenotypes are determined by task overlap for logic-defined phenotypes and by responses to encounters in the case of behavioral phenotypes. Biologists use these evolving networks to study active and fundamental topics within evolutionary ecology (e.g., the extent to which the architecture of multispecies networks shape coevolutionary outcomes, and the processes involved).