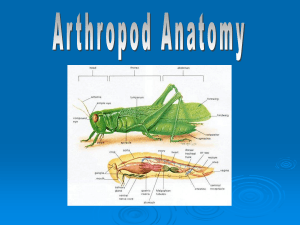
Here
... Before Darwin’s time, others believed that organisms changed over time and tried to explain this change. Jean-Baptiste Lamark is probably the most famous of these. Lamark’s theory proposes that by selective use or disuse of organs, organisms acquired or lost certain traits during their lifetime. The ...
... Before Darwin’s time, others believed that organisms changed over time and tried to explain this change. Jean-Baptiste Lamark is probably the most famous of these. Lamark’s theory proposes that by selective use or disuse of organs, organisms acquired or lost certain traits during their lifetime. The ...
Darwin`s Theory of Evolution
... However, because some animals on each continent were living under similar ecological conditions, they were exposed to similar pressures of natural selection Because of this, different animals ended up evolving certain common features. ...
... However, because some animals on each continent were living under similar ecological conditions, they were exposed to similar pressures of natural selection Because of this, different animals ended up evolving certain common features. ...
Nothing in Biology Makes Sense Except in the Light of Evolution
... truly cosmopolitan species but, owing to his technologic achievements, can survive for at least a limited time on the surface of the moon and in cosmic spaces. By contrast, some organisms are amazingly specialized. Perhaps the narrowest ecologic niche of all is that of a species of the fungus family ...
... truly cosmopolitan species but, owing to his technologic achievements, can survive for at least a limited time on the surface of the moon and in cosmic spaces. By contrast, some organisms are amazingly specialized. Perhaps the narrowest ecologic niche of all is that of a species of the fungus family ...
Chapter 13
... Darwin proposed natural selection as the mechanism of evolution – Darwin observed that organisms z Produce more offspring than the environment can support z Vary in many characteristics that can be inherited – Darwin reasoned that natural selection z Results in favored traits being represented more ...
... Darwin proposed natural selection as the mechanism of evolution – Darwin observed that organisms z Produce more offspring than the environment can support z Vary in many characteristics that can be inherited – Darwin reasoned that natural selection z Results in favored traits being represented more ...
7.Evolution - Check Your Accuracy
... Explain antibiotic resistance observed in bacteria in light of Darwinian selection theory. Answer 1: Darwinian selection theory states that individuals with favourable variations are better adapted than individuals with less favourable variation. It means that nature selects the individuals with use ...
... Explain antibiotic resistance observed in bacteria in light of Darwinian selection theory. Answer 1: Darwinian selection theory states that individuals with favourable variations are better adapted than individuals with less favourable variation. It means that nature selects the individuals with use ...
Nothing in Biology Makes Sense Except in the Light of Evolution
... many other possible ways of living as yet unexploited by any existing species; but one thing is clear: with less organic diversity, some opportunities for living would remain unexploited. The evolutionary process tends to fill up the available ecologic niches. It does not do so consciously or delibe ...
... many other possible ways of living as yet unexploited by any existing species; but one thing is clear: with less organic diversity, some opportunities for living would remain unexploited. The evolutionary process tends to fill up the available ecologic niches. It does not do so consciously or delibe ...
Lecture 11: Phylogenetic tree inference: introduction Evolution
... their order be? • In the real world, a species can go extinct without leaving any descendants. If it leaves fossil evidence, it goes into our tree as a leaf, not an imaginary ancestor. In the real world, a species can split off one new species, and then go extinct. • The only justification we have f ...
... their order be? • In the real world, a species can go extinct without leaving any descendants. If it leaves fossil evidence, it goes into our tree as a leaf, not an imaginary ancestor. In the real world, a species can split off one new species, and then go extinct. • The only justification we have f ...
Alex Heffron, Jake Jongewaard, and Katie Kerwin
... evolution. The sickle cells are a genetic blood disorder in which red blood cells are characterized as abnormal, ridged sickle shapes. ...
... evolution. The sickle cells are a genetic blood disorder in which red blood cells are characterized as abnormal, ridged sickle shapes. ...
Evolution Quiz Week 9
... o 1859, 12 rabbit brought to Oz. 6 years later there were 30,000 o 1950’s, myxoma virus brought to control rabbits & kill most of them o Within 15 years, virus evolves to be less virulent & rabbits recover Coincidental evolution hypothesis: Different environment, different virulence ...
... o 1859, 12 rabbit brought to Oz. 6 years later there were 30,000 o 1950’s, myxoma virus brought to control rabbits & kill most of them o Within 15 years, virus evolves to be less virulent & rabbits recover Coincidental evolution hypothesis: Different environment, different virulence ...
Self-study Problems #1: Evolution
... The view that geological strata and fossils are explicable by the action of the same processes we observe today, like deposition of sand by a river, accumulating their effects over a very long period of time. 5. Is Darwin’s theory of evolution catastrophist, or uniformitarian? Why? Uniformitarian, b ...
... The view that geological strata and fossils are explicable by the action of the same processes we observe today, like deposition of sand by a river, accumulating their effects over a very long period of time. 5. Is Darwin’s theory of evolution catastrophist, or uniformitarian? Why? Uniformitarian, b ...
Evolution History
... i. Geological processes are constant through time ii. Challenged the prevailing thought that the earth was young iii. Darwin needed large periods of time for natural selection to work iv. Uniformitarinism provided Darwin the time element needed for his theory ...
... i. Geological processes are constant through time ii. Challenged the prevailing thought that the earth was young iii. Darwin needed large periods of time for natural selection to work iv. Uniformitarinism provided Darwin the time element needed for his theory ...
Unit 7: Evolution - Blue Valley Schools
... _____ 15. As shown in the diagram above, analysis of forelimb anatomy of humans, bats, and whales shows that humans and bats have fairly similar skeletal structures, while whales have diverged considerably in the shapes and proportions of their bones. However, analysis of several genes in these spec ...
... _____ 15. As shown in the diagram above, analysis of forelimb anatomy of humans, bats, and whales shows that humans and bats have fairly similar skeletal structures, while whales have diverged considerably in the shapes and proportions of their bones. However, analysis of several genes in these spec ...
Déjà Vu: How and Why Evolution Repeats Itself
... chance,” explain somewhat carefully just where that number 750 years comes from. That is, explain how one can estimate that about once in 750 years a herring gull chick will be born able to see UV light. The answer of a herring gull chick born with UV light once in750 years comes from simple, basic ...
... chance,” explain somewhat carefully just where that number 750 years comes from. That is, explain how one can estimate that about once in 750 years a herring gull chick will be born able to see UV light. The answer of a herring gull chick born with UV light once in750 years comes from simple, basic ...
Origins of Bacterial Species-
... de Queiroz, K. 1998. The general lineage concept of species, species criteria, and the process of speciation. In Endless Forms: Species and Speciation, (D. J. Howard and S. H. Berlocher, eds.), pp. 57-75., Oxford University Press, Oxford. Kevin de Queiroz argues that despite the large number of spec ...
... de Queiroz, K. 1998. The general lineage concept of species, species criteria, and the process of speciation. In Endless Forms: Species and Speciation, (D. J. Howard and S. H. Berlocher, eds.), pp. 57-75., Oxford University Press, Oxford. Kevin de Queiroz argues that despite the large number of spec ...
Darwin`s Theory of Evolution notesheet
... born faster than people were dying. He reasoned that if the human population continued to grow, sooner or later there would be ...
... born faster than people were dying. He reasoned that if the human population continued to grow, sooner or later there would be ...
Ch.16 and 17 notes
... • 8. First eukaryotes may have been communities of prokaryotes. – Complex eukaryotic cells probably evolved from prokaryotic cells. – The endosymbiont theory, proposed by American biologist Lynn Margulis explains how eukaryotic cells may have arisen. The theory proposes that eukaryotes evolved thro ...
... • 8. First eukaryotes may have been communities of prokaryotes. – Complex eukaryotic cells probably evolved from prokaryotic cells. – The endosymbiont theory, proposed by American biologist Lynn Margulis explains how eukaryotic cells may have arisen. The theory proposes that eukaryotes evolved thro ...
Section 3 notes
... Natural selection does not make organisms “better.” Adaptations don’t have to be perfect—just good enough to enable an organism to reproduce. Natural selection also doesn’t move in a fixed direction. There is no one, perfect way of doing something. Natural selection is simply enables organisms to su ...
... Natural selection does not make organisms “better.” Adaptations don’t have to be perfect—just good enough to enable an organism to reproduce. Natural selection also doesn’t move in a fixed direction. There is no one, perfect way of doing something. Natural selection is simply enables organisms to su ...
05 Lecture Evolution LO.10
... 4) Natural selection acts on phenotypic variation in population and results from differences in survival and reproduction among phenotypes. 5) The extent to which phenotypic variation is due to genetic variation determines the potential for evolution by natural selection. 6) Adaptations result from ...
... 4) Natural selection acts on phenotypic variation in population and results from differences in survival and reproduction among phenotypes. 5) The extent to which phenotypic variation is due to genetic variation determines the potential for evolution by natural selection. 6) Adaptations result from ...
The Evolution of Populations
... A closer look at natural selection as the mechanism of adaptive evolution ...
... A closer look at natural selection as the mechanism of adaptive evolution ...
1-4 Evolution and Classification.notebook
... Darwin thought evolution occurred by natural selection Natural selection the process by which individuals that are better adapted to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce than other members of the same species As understanding of evolution increased, biologists changed how ...
... Darwin thought evolution occurred by natural selection Natural selection the process by which individuals that are better adapted to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce than other members of the same species As understanding of evolution increased, biologists changed how ...
Plant and Animal Adaptations
... grasslands Adaptations: It is able to go with out drinking as long as green grass is available and it adapts well to drought. They can hop as fast as 40 mph (64 km). They use this as their first line of defense. Kangaroos have a tendon in the leg which acts like a rubber band, conserving energy as t ...
... grasslands Adaptations: It is able to go with out drinking as long as green grass is available and it adapts well to drought. They can hop as fast as 40 mph (64 km). They use this as their first line of defense. Kangaroos have a tendon in the leg which acts like a rubber band, conserving energy as t ...
Bio 152 – Summer 2006 Week 2 OBJECTIVES: Lecture 5 1. What is
... 1. Describe reproduction in prokaryotes. 2. Briefly summarize the mitosis cycle. 3. What is the purpose of mitosis? 4. Briefly summarize the meiosis cycle. 5. What are the unique features of meiosis? 6. When do mitosis and meiosis occur during the life of an organism? 7. Explain the term nondisjunct ...
... 1. Describe reproduction in prokaryotes. 2. Briefly summarize the mitosis cycle. 3. What is the purpose of mitosis? 4. Briefly summarize the meiosis cycle. 5. What are the unique features of meiosis? 6. When do mitosis and meiosis occur during the life of an organism? 7. Explain the term nondisjunct ...