Pro Matcha - Vibrant Health
... Algal, Sacha Inchi, Yellow Pea, and Spirulina provide 21 grams of protein. This strong protein combination curbs hunger, provides Omega 3,6,9 fatty acids (in proper ratios), detoxifies, is low in carbs, boosts immunity, and is easily absorbed. Pro Matcha protein contains all essential amino acids an ...
... Algal, Sacha Inchi, Yellow Pea, and Spirulina provide 21 grams of protein. This strong protein combination curbs hunger, provides Omega 3,6,9 fatty acids (in proper ratios), detoxifies, is low in carbs, boosts immunity, and is easily absorbed. Pro Matcha protein contains all essential amino acids an ...
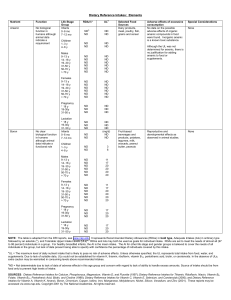
MNND Training Overheads
... niacin deficiency was a known problem. If no nutrient rich foods are available to include in the general ration, increasing the cereal allocation may allow beneficiaries the opportunity to trade the excess and diversify their diet. For this to happen they need access to ...
... niacin deficiency was a known problem. If no nutrient rich foods are available to include in the general ration, increasing the cereal allocation may allow beneficiaries the opportunity to trade the excess and diversify their diet. For this to happen they need access to ...
Nutrition and Osteoporosis
... Upper daily limits: calcium & vitamin D The National Academy of Sciences (1997) suggests the following tolerable daily upper intake levels (UL) from foods and supplements combined: • Calcium: The UL for 1 year and older (including pregnant and lactating women) is 2,500 mg/day. It was not possible t ...
... Upper daily limits: calcium & vitamin D The National Academy of Sciences (1997) suggests the following tolerable daily upper intake levels (UL) from foods and supplements combined: • Calcium: The UL for 1 year and older (including pregnant and lactating women) is 2,500 mg/day. It was not possible t ...
Nutrition and Osteoporosis - Washington State Dairy Council
... Upper daily limits: calcium & vitamin D The National Academy of Sciences (1997) suggests the following tolerable daily upper intake levels (UL) from foods and supplements combined: • Calcium: The UL for 1 year and older (including pregnant and lactating women) is 2,500 mg/day. It was not possible t ...
... Upper daily limits: calcium & vitamin D The National Academy of Sciences (1997) suggests the following tolerable daily upper intake levels (UL) from foods and supplements combined: • Calcium: The UL for 1 year and older (including pregnant and lactating women) is 2,500 mg/day. It was not possible t ...
Conclusions of a WHO Technical Consultation on folate and vitamin
... of depression. Vitamin B12 deficiency Hematology ...
... of depression. Vitamin B12 deficiency Hematology ...
Soups Salads & LTH A
... This book highlights simple ways to make healthy and delectable soups and salads with the use of flavourful herbs and spices while avoiding the fat laden ingredients and yet maintaining the original taste. 48 recipes rich in Vitamin A, Vitamin B complex, Vitamin C, Iron, Calcium, Protein and Fibre h ...
... This book highlights simple ways to make healthy and delectable soups and salads with the use of flavourful herbs and spices while avoiding the fat laden ingredients and yet maintaining the original taste. 48 recipes rich in Vitamin A, Vitamin B complex, Vitamin C, Iron, Calcium, Protein and Fibre h ...
ESTABLISHING A SUGGESTED OPTIMAL NUTRIENT
... (deficiency of niacin) and beriberi (deficiency of thiamine) in the general population. Since then, nutritionists, dieticians and physicians have relied on this reference standard and its many revisions commonly referred to by its abbreviation, the RDA. The RDAs (Council, 1980 544) (Council 1989 120 ...
... (deficiency of niacin) and beriberi (deficiency of thiamine) in the general population. Since then, nutritionists, dieticians and physicians have relied on this reference standard and its many revisions commonly referred to by its abbreviation, the RDA. The RDAs (Council, 1980 544) (Council 1989 120 ...
The Fat-Soluble Vitamins
... needed for important metabolic reactions in the body. • They are not a source of energy. Instead, they promote many energy-yielding and other reactions in the body, thereby aiding in the growth, development, and maintenance of ...
... needed for important metabolic reactions in the body. • They are not a source of energy. Instead, they promote many energy-yielding and other reactions in the body, thereby aiding in the growth, development, and maintenance of ...
Osteoporosis
... The main dietary sources of vitamin D are fortified milk (400 IU per quart), some fortified cereals, cold saltwater fish (for example: salmon, halibut, herring, tuna, oysters and shrimp) and some calcium and vitamin/mineral supplements. ...
... The main dietary sources of vitamin D are fortified milk (400 IU per quart), some fortified cereals, cold saltwater fish (for example: salmon, halibut, herring, tuna, oysters and shrimp) and some calcium and vitamin/mineral supplements. ...
Calcium - European Food Safety
... The main dietary sources of vitamin D are fortified milk (400 IU per quart), some fortified cereals, cold saltwater fish (for example: salmon, halibut, herring, tuna, oysters and shrimp) and some calcium and vitamin/mineral supplements. Also, vitamin D can be manufactured in your skin following dire ...
... The main dietary sources of vitamin D are fortified milk (400 IU per quart), some fortified cereals, cold saltwater fish (for example: salmon, halibut, herring, tuna, oysters and shrimp) and some calcium and vitamin/mineral supplements. Also, vitamin D can be manufactured in your skin following dire ...
Dietary Reference Intakes: Elements
... caution should be taken when using manganese supplements especially among those persons already consuming large amounts of manganese from diets high in plant products. In addition, individuals with liver disease may be distinctly susceptible to the adverse effects of excess manganese intake. ...
... caution should be taken when using manganese supplements especially among those persons already consuming large amounts of manganese from diets high in plant products. In addition, individuals with liver disease may be distinctly susceptible to the adverse effects of excess manganese intake. ...
Carotenemia
... anorexia nervosa, nephrotic syndrome, and liver disease. In hypothyroidism and diabetes mellitus, the underlying mechanism of hypercarotenemia is through both impaired conversion of beta-carotene into retinol and the associated increased serum lipids. Diabetes mellitus has also been associated with ...
... anorexia nervosa, nephrotic syndrome, and liver disease. In hypothyroidism and diabetes mellitus, the underlying mechanism of hypercarotenemia is through both impaired conversion of beta-carotene into retinol and the associated increased serum lipids. Diabetes mellitus has also been associated with ...
Floradix - Red Seal
... Floradix contains 15mg iron per 20ml (125% RDA*) Floravital contains 19mg iron per 20ml (158% RDA*) ...
... Floradix contains 15mg iron per 20ml (125% RDA*) Floravital contains 19mg iron per 20ml (158% RDA*) ...
Victory Over Diabetes - Image Awareness> Home
... • Obesity did not appear to be a risk factor for diabetes if levels of these pollutants were undetectable in the blood. • Obesity was associated with diabetes when pollutant accumulation was above the 25th percentile. ...
... • Obesity did not appear to be a risk factor for diabetes if levels of these pollutants were undetectable in the blood. • Obesity was associated with diabetes when pollutant accumulation was above the 25th percentile. ...
Ruminant milk: A source of vitamins in human nutrition
... concern. Its deficiency is by far the most common; it was estimated that 3 million children developed xerophthalmia annually whereas the estimation increased to 250 million when considering sub-clinical deficiencies detected by blood measurements (FAO/WHO, 2001). At-risk subjects are children under ...
... concern. Its deficiency is by far the most common; it was estimated that 3 million children developed xerophthalmia annually whereas the estimation increased to 250 million when considering sub-clinical deficiencies detected by blood measurements (FAO/WHO, 2001). At-risk subjects are children under ...