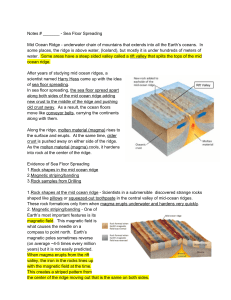
Notes # ______ Sea Floor Spreading Mid Ocean Ridge underwater
... in the central valley of midocean ridges. These rock formations only form when magma erupts underwater and hardens very quickly ...
... in the central valley of midocean ridges. These rock formations only form when magma erupts underwater and hardens very quickly ...
BOPP_WP17_highlights_+
... Whereas regional perturbations in temperature and precipitation by historical emissions and by non-CO2 agents are largely reversible within centuries. In the High case, CO2 remains above 580 ppm and 30% of carbon emissions are still airborne by 2500. ...
... Whereas regional perturbations in temperature and precipitation by historical emissions and by non-CO2 agents are largely reversible within centuries. In the High case, CO2 remains above 580 ppm and 30% of carbon emissions are still airborne by 2500. ...
What is carbon cycle?
... CO2 is also exchanged continuously between the ocean and the atmosphere. This exchange is largely controlled by sea surface temperatures, ocean acidity, circulating currents and the biological processes of photosynthesis and respiration by marine plants and animals. Cold ocean waters favour the up ...
... CO2 is also exchanged continuously between the ocean and the atmosphere. This exchange is largely controlled by sea surface temperatures, ocean acidity, circulating currents and the biological processes of photosynthesis and respiration by marine plants and animals. Cold ocean waters favour the up ...
PosterA0LandscapeFinal3 - The Tidal Irrigation and Electrical System
... enables greater concomitant production of DOW’s other potential products, such as electricity. Unlike an unconstrained release, the open pond system can capture much of the biomaterial from the water, which limits the impact to the surrounding ecosystem. 3. The Tidal Irrigation and Electrical Syste ...
... enables greater concomitant production of DOW’s other potential products, such as electricity. Unlike an unconstrained release, the open pond system can capture much of the biomaterial from the water, which limits the impact to the surrounding ecosystem. 3. The Tidal Irrigation and Electrical Syste ...
Summary of Earth Structure/Geodynamics
... What is the space-time geography of energy input and dissipation in the ocean ? ...
... What is the space-time geography of energy input and dissipation in the ocean ? ...
Marine Sediment Proxy Records
... protists that secrete calcium carbonate shells around their cells. The chemistry of these calcite shells provides information about the chemical and physical conditions in which they grew. Two main types of foraminifera are distinguished, both comprising numerous different species. Planktonic forami ...
... protists that secrete calcium carbonate shells around their cells. The chemistry of these calcite shells provides information about the chemical and physical conditions in which they grew. Two main types of foraminifera are distinguished, both comprising numerous different species. Planktonic forami ...
General Circulation and Climate Zones
... (SST), by way of sea-air heat flux. SST generally cools with increasing latitude, but important deviations from a pure latitudinal dependence occurs. These are generally due to the movement of sea water in both the horizontal and vertical directions. Temperature and density of ocean water are relate ...
... (SST), by way of sea-air heat flux. SST generally cools with increasing latitude, but important deviations from a pure latitudinal dependence occurs. These are generally due to the movement of sea water in both the horizontal and vertical directions. Temperature and density of ocean water are relate ...
Earth Chemistry Quiz Answers
... experiment. 2. Why don’t scientists know for sure how life began? Because no one was around when the first organisms formed. 3. What causes the amount of carbon dioxide to increase rapidly? Increased burning of fossil fuel, deforestation. 4. What do we mean by ‘locked up carbon’? Carbon dioxide that ...
... experiment. 2. Why don’t scientists know for sure how life began? Because no one was around when the first organisms formed. 3. What causes the amount of carbon dioxide to increase rapidly? Increased burning of fossil fuel, deforestation. 4. What do we mean by ‘locked up carbon’? Carbon dioxide that ...
Effects of increasing atmospheric CO on phytoplankton communities
... decreases the ratio of calcification to organic carbon production in two coccolithophore species (Riebesell et al 2000: Nature 2000). Note that the decrease in this ratio is caused by both reduced calcification and enhanced Corg-prduction. A and B have opposing effects on the ratio of calcification ...
... decreases the ratio of calcification to organic carbon production in two coccolithophore species (Riebesell et al 2000: Nature 2000). Note that the decrease in this ratio is caused by both reduced calcification and enhanced Corg-prduction. A and B have opposing effects on the ratio of calcification ...
ángeles garcía pardo
... analysis, as it is the main program funding projects on marine science, although there are other programs also including marine research: i.e. ANT (Polar research), BTE (Earth Science), BOS (Biodiversity) or ACU (Aquaculture). In the last 5 years we have had a progressive reduction in the percentage ...
... analysis, as it is the main program funding projects on marine science, although there are other programs also including marine research: i.e. ANT (Polar research), BTE (Earth Science), BOS (Biodiversity) or ACU (Aquaculture). In the last 5 years we have had a progressive reduction in the percentage ...
Workshop_Ackleson
... conducting a 10-year effort to develop an integrated Earth observing system of systems (GEOSS). 2007-8: International Polar Year, encouraged continued international cooperation in high-latitude research in the context of climate change. 2009: OceanObs 09, international community agreement on GOOS de ...
... conducting a 10-year effort to develop an integrated Earth observing system of systems (GEOSS). 2007-8: International Polar Year, encouraged continued international cooperation in high-latitude research in the context of climate change. 2009: OceanObs 09, international community agreement on GOOS de ...
Evolution of Ocean Observatories
... a 10-year effort to develop an integrated Earth observing system of systems (GEOSS). 2007-8: International Polar Year, encouraged continued international cooperation in high-latitude research in the context of climate change. 2009: OceanObs 09, international community agreement on GOOS decadal visio ...
... a 10-year effort to develop an integrated Earth observing system of systems (GEOSS). 2007-8: International Polar Year, encouraged continued international cooperation in high-latitude research in the context of climate change. 2009: OceanObs 09, international community agreement on GOOS decadal visio ...
International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) 1 Input to SG report on
... Through their bioaccumulation to levels that may adversely affect human health, marine pollutants can adversely affect international trade in these valuable commodities, particularly from the Least Developing Countries and Small Islands Developing States depending heavily on their marine resources. ...
... Through their bioaccumulation to levels that may adversely affect human health, marine pollutants can adversely affect international trade in these valuable commodities, particularly from the Least Developing Countries and Small Islands Developing States depending heavily on their marine resources. ...
Plate tectonics theory
... PBS, Intro to Plate Tectonic Theory, http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/aso/tryit/tectonics/intro.html, accessed ...
... PBS, Intro to Plate Tectonic Theory, http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/aso/tryit/tectonics/intro.html, accessed ...
1. Progress in Understanding c. Calculations of Ocean Circulation
... [Figure 1] Scenario of Radioactivity Concentrations in the Effluent Discharged from the Fukushima Dai-ichi NPP The scenario assumes that radioactive substances diffuse on the sea surface of 8 × 8 km at 1/100 of the concentrations observed at the coast based on “Results of Nuclide Analysis of Seawate ...
... [Figure 1] Scenario of Radioactivity Concentrations in the Effluent Discharged from the Fukushima Dai-ichi NPP The scenario assumes that radioactive substances diffuse on the sea surface of 8 × 8 km at 1/100 of the concentrations observed at the coast based on “Results of Nuclide Analysis of Seawate ...
1. Progress in Understanding c. Calculations of Ocean Circulation
... [Figure 1] Scenario of Radioactivity Concentrations in the Effluent Discharged from the Fukushima Dai-ichi NPP The scenario assumes that radioactive substances diffuse on the sea surface of 8 × 8 km at 1/100 of the concentrations observed at the coast based on “Results of Nuclide Analysis of Seawate ...
... [Figure 1] Scenario of Radioactivity Concentrations in the Effluent Discharged from the Fukushima Dai-ichi NPP The scenario assumes that radioactive substances diffuse on the sea surface of 8 × 8 km at 1/100 of the concentrations observed at the coast based on “Results of Nuclide Analysis of Seawate ...
Chapter 7-2 Ocean Currents and Climate
... seawater sinks beneath less dense coldwater. • Seawater becomes more dense when it gets colder. ...
... seawater sinks beneath less dense coldwater. • Seawater becomes more dense when it gets colder. ...
Geology - Fetlar
... years ago. The assembly of this jigsaw was the result of a massive collision as plate tectonic forces drove three ancient continents and the ocean between them together to form a supercontinent. As a result the vast Caledonian Mountain Chain was thrust up in a process known as the Caledonian Orogeny ...
... years ago. The assembly of this jigsaw was the result of a massive collision as plate tectonic forces drove three ancient continents and the ocean between them together to form a supercontinent. As a result the vast Caledonian Mountain Chain was thrust up in a process known as the Caledonian Orogeny ...
E.S. Ch. 3 Study Guide
... Wegener’s hypothesis was that all the continents were once joined together in a single landmass and have since drifted apart. Continental Drift— Wegener’s idea; the continents slowly move over Earth’s Surface. Pangaea—The Super Continent. Fossil—is any trace of an ancient organism that has been pres ...
... Wegener’s hypothesis was that all the continents were once joined together in a single landmass and have since drifted apart. Continental Drift— Wegener’s idea; the continents slowly move over Earth’s Surface. Pangaea—The Super Continent. Fossil—is any trace of an ancient organism that has been pres ...
Sea-Floor Spreading
... 1. Magnetic field and rocks --NORMAL POLARITY state in which magnetized objects such as compass needles, will orient themselves to point north. --Magnetic Reversal occurs and the magnetic field reverse direction. And is called REVERSED POLARITY. This is where objects orient themselves to point south ...
... 1. Magnetic field and rocks --NORMAL POLARITY state in which magnetized objects such as compass needles, will orient themselves to point north. --Magnetic Reversal occurs and the magnetic field reverse direction. And is called REVERSED POLARITY. This is where objects orient themselves to point south ...
Chapter 5: The Biogeochemical Cycles
... • When a body of water becomes polluted, how can we reduce the pollution and its effects? ...
... • When a body of water becomes polluted, how can we reduce the pollution and its effects? ...
... Midocean ridge rocks are _____________ than surrounding ocean floor rocks Midocean ridge volcanoes are _________________ than volcanoes further away Ocean floor sediments are _______ on the ridges and get ____________ as the distance from the ridges increase Polar reversal magnetism proves that the ...
The Blue Planet
... Nearly 71 percent of Earth’s surface is covered by the global ocean. Oceanography is a science that draws on the methods and knowledge of geology, chemistry, physics, and biology to study all aspects of the world ocean. Geography of the Oceans The world ocean can be divided into four main ocea ...
... Nearly 71 percent of Earth’s surface is covered by the global ocean. Oceanography is a science that draws on the methods and knowledge of geology, chemistry, physics, and biology to study all aspects of the world ocean. Geography of the Oceans The world ocean can be divided into four main ocea ...
Ocean acidification

Ocean acidification is the ongoing decrease in the pH of the Earth's oceans, caused by the uptake of carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere. An estimated 30–40% of the carbon dioxide from human activity released into the atmosphere dissolves into oceans, rivers and lakes. To achieve chemical equilibrium, some of it reacts with the water to form carbonic acid. Some of these extra carbonic acid molecules react with a water molecule to give a bicarbonate ion and a hydronium ion, thus increasing ocean acidity (H+ ion concentration). Between 1751 and 1994 surface ocean pH is estimated to have decreased from approximately 8.25 to 8.14, representing an increase of almost 30% in H+ ion concentration in the world's oceans. Since current and projected ocean pH levels are above 7.0, the oceans are technically alkaline now and will remain so; referring to this effect as ""decreasing ocean alkalinity"" would be equally correct if less politically useful. Earth System Models project that within the last decade ocean acidity exceeded historical analogs and in combination with other ocean biogeochemical changes could undermine the functioning of marine ecosystems and disrupt the provision of many goods and services associated with the ocean.Increasing acidity is thought to have a range of possibly harmful consequences, such as depressing metabolic rates and immune responses in some organisms, and causing coral bleaching. This also causes decreasing oxygen levels as it kills off algae.Other chemical reactions are triggered which result in a net decrease in the amount of carbonate ions available. This makes it more difficult for marine calcifying organisms, such as coral and some plankton, to form biogenic calcium carbonate, and such structures become vulnerable to dissolution. Ongoing acidification of the oceans threatens food chains connected with the oceans. As members of the InterAcademy Panel, 105 science academies have issued a statement on ocean acidification recommending that by 2050, global CO2 emissions be reduced by at least 50% compared to the 1990 level.Ocean acidification has been called the ""evil twin of global warming"" and ""the other CO2 problem"".Ocean acidification has occurred previously in Earth's history. The most notable example is the Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum (PETM), which occurred approximately 56 million years ago. For reasons that are currently uncertain, massive amounts of carbon entered the ocean and atmosphere, and led to the dissolution of carbonate sediments in all ocean basins.























