Article Title
... and RTM ) versus the wavelength and the angle of incidence . In the ideal situation where RTE 1 and for grazing incidences, the incident and the reflected plane waves should add themselves, and give a tangential electric field on the surface with amplitude equal to 2. Since the surfaces have me ...
... and RTM ) versus the wavelength and the angle of incidence . In the ideal situation where RTE 1 and for grazing incidences, the incident and the reflected plane waves should add themselves, and give a tangential electric field on the surface with amplitude equal to 2. Since the surfaces have me ...
Sample Paper3
... μ0 = 4 π x 10–7 T m A–1 Mass of neutron mn ≅ 1.675 x 10–27 kg Boltzmann’s constant k = 1.381 x 10–23 J K–1 Avogadro’s number NA = 6.022 x 1023 / mol –1 ...
... μ0 = 4 π x 10–7 T m A–1 Mass of neutron mn ≅ 1.675 x 10–27 kg Boltzmann’s constant k = 1.381 x 10–23 J K–1 Avogadro’s number NA = 6.022 x 1023 / mol –1 ...
presentation source
... Insulator responds to an external field by polarizing Polarization leads to surface charge that offsets imposed field Charges at infinitely distant boundary have local effect due to this offsetting field If the system is embedded in a conducting medium, it will respond in a way the eliminate ...
... Insulator responds to an external field by polarizing Polarization leads to surface charge that offsets imposed field Charges at infinitely distant boundary have local effect due to this offsetting field If the system is embedded in a conducting medium, it will respond in a way the eliminate ...
Literal Equations Project
... sheet to locate formulas) You can use your state’s reference sheet for this activity or the new Common Core Reference Sheet. This will allow the students to be familiar with the reference sheet. This worksheet should be completed before you give them the Literal Equations Project. It is good practic ...
... sheet to locate formulas) You can use your state’s reference sheet for this activity or the new Common Core Reference Sheet. This will allow the students to be familiar with the reference sheet. This worksheet should be completed before you give them the Literal Equations Project. It is good practic ...
Series and parallel Connection of capacitors
... Dielectric constant r may be a function of space coordinates. For anistropic materials, the dielectric constant is different in different directions of the electric field, D and E are related by a permittivity tensor which may be written as: ...
... Dielectric constant r may be a function of space coordinates. For anistropic materials, the dielectric constant is different in different directions of the electric field, D and E are related by a permittivity tensor which may be written as: ...
Determination of Relative Dielectric constant and Thickness (1)
... Practically, quadrature mixers, however, have a nonlinear phase response due to their phase and amplitude imbalances as well as DC offset. A more realistic from of the phase including the nonlinearity effect can be expressed as: ...
... Practically, quadrature mixers, however, have a nonlinear phase response due to their phase and amplitude imbalances as well as DC offset. A more realistic from of the phase including the nonlinearity effect can be expressed as: ...
Electricity Notebook
... the checklist to the side after drawing the schematic. Check off all that apply to your circuit with a Lightning Bolt. ...
... the checklist to the side after drawing the schematic. Check off all that apply to your circuit with a Lightning Bolt. ...
3 - web page for staff
... The EM field is not contained entirely in dielectric so it is not pure TEM mode but a quasi-TEM mode that is valid at lower microwave frequency. The effective relative dielectric constant of the microstrip is related to the relative dielectric constant r of the dielectric and also takes into accoun ...
... The EM field is not contained entirely in dielectric so it is not pure TEM mode but a quasi-TEM mode that is valid at lower microwave frequency. The effective relative dielectric constant of the microstrip is related to the relative dielectric constant r of the dielectric and also takes into accoun ...
PHYS_2326_021709
... property of the dielectric and varies from one material to another. • Breakdown potential—maximum potential difference before sparking • Dielectric strength—maximum E field before dielectric breaks down and acts as a conductor between the plates (sparks) ...
... property of the dielectric and varies from one material to another. • Breakdown potential—maximum potential difference before sparking • Dielectric strength—maximum E field before dielectric breaks down and acts as a conductor between the plates (sparks) ...
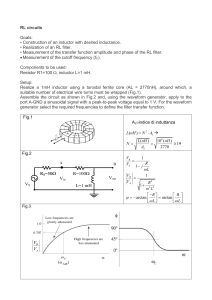
RL circuits Goals: • Construction of an inductor with desired
... • Construction of an inductor with desired inductance. • Realization of an RL filter. • Measurement of the transfer function amplitude and phase of the RL filter. Measurement of the cutoff frequency (fC). Components to be used: Resistor R1=100 inductor L=1 mH. Setup: Realize a 1mH inductor usin ...
... • Construction of an inductor with desired inductance. • Realization of an RL filter. • Measurement of the transfer function amplitude and phase of the RL filter. Measurement of the cutoff frequency (fC). Components to be used: Resistor R1=100 inductor L=1 mH. Setup: Realize a 1mH inductor usin ...
Module 6 : Wave Guides Lecture 43 : Rectangular Wave
... General Approach to Wave Guide Analysis In case of parallel wave guide the modal propagation was visualized as super position of multiply reflected plane wave from the two conducting sheets. This approach although provides better physical understanding of the modal propagation, becomes algebraically ...
... General Approach to Wave Guide Analysis In case of parallel wave guide the modal propagation was visualized as super position of multiply reflected plane wave from the two conducting sheets. This approach although provides better physical understanding of the modal propagation, becomes algebraically ...
Lecture 3: Fiber Modes
... form eiθ. The z function oscillates in space, while the φ function must have the same value at (φ+2π) that it does at φ. • The r function is a combination of Bessel functions of the first and second kinds. The separate solutions for the core and cladding regions must match at the boundary. ...
... form eiθ. The z function oscillates in space, while the φ function must have the same value at (φ+2π) that it does at φ. • The r function is a combination of Bessel functions of the first and second kinds. The separate solutions for the core and cladding regions must match at the boundary. ...
Surge Impedance of Transmission-line Towers: C. A. Jordan`s
... designing transmission lines, engineers need to estimate the surge impedance of the tower in order to estimate voltage of the tower top when the top is struck by lightning carrying huge currents. The large voltage at the tower top causes flush-over phenomena from the tower arm to the transmission li ...
... designing transmission lines, engineers need to estimate the surge impedance of the tower in order to estimate voltage of the tower top when the top is struck by lightning carrying huge currents. The large voltage at the tower top causes flush-over phenomena from the tower arm to the transmission li ...
Slide 1
... or in vacuum (.3 m/ns). Dielectric constants for most dry geologic materials range from 4 (quartz sand) to 7 (shales and carbonates). Water, however, has a dielectric constant of 81 at 20oC and radically alters the velocity of the radar-wave traveling through materials and can cause serious errors i ...
... or in vacuum (.3 m/ns). Dielectric constants for most dry geologic materials range from 4 (quartz sand) to 7 (shales and carbonates). Water, however, has a dielectric constant of 81 at 20oC and radically alters the velocity of the radar-wave traveling through materials and can cause serious errors i ...
The Hydrogen Spectrum
... In this lab we will use a grating spectrometer to measure the visible spectrum of the hydrogen atom. A spectrometer is an instrument used for measuring the wavelength of electromagnetic radiation. It consists of several elements: a slit, a dispersive element, a way to measure angle, and a detector o ...
... In this lab we will use a grating spectrometer to measure the visible spectrum of the hydrogen atom. A spectrometer is an instrument used for measuring the wavelength of electromagnetic radiation. It consists of several elements: a slit, a dispersive element, a way to measure angle, and a detector o ...
Define
... The “Test Result”, “Test”, and “meter setting” Test Result Test Meter Setting 9V battery1K resistor3.3K resistor10K resistorVariable 50Kthree different positions ...
... The “Test Result”, “Test”, and “meter setting” Test Result Test Meter Setting 9V battery1K resistor3.3K resistor10K resistorVariable 50Kthree different positions ...
K0CQ-CSVHF2010
... Low Z TL I have to admit only about half the professional references mention the restriction on the simple formula and no ARRL resources mention that. The close spaced formula comes from work of Harold Wheeler about 1939 where he found that the charges on close spaced wires concentrated where the ...
... Low Z TL I have to admit only about half the professional references mention the restriction on the simple formula and no ARRL resources mention that. The close spaced formula comes from work of Harold Wheeler about 1939 where he found that the charges on close spaced wires concentrated where the ...
HW 6 6340
... aluminum). Do this by assuming a DC current I flowing along the tube in the z direction, and then using Ampere’s law to calculate the magnetic field inside the tube. From this, calculate the stored magnetic energy inside the tube, given by ...
... aluminum). Do this by assuming a DC current I flowing along the tube in the z direction, and then using Ampere’s law to calculate the magnetic field inside the tube. From this, calculate the stored magnetic energy inside the tube, given by ...
Topic 4 Formula - Olympic College
... Topic 4 Formula Introduction: In many situations in science and business we use formulas. these formula are essentially just an algebraic expression where the variables used have very specific meanings. In order to evaluate a formula we essentially just evaluate the algebraic expression that is the ...
... Topic 4 Formula Introduction: In many situations in science and business we use formulas. these formula are essentially just an algebraic expression where the variables used have very specific meanings. In order to evaluate a formula we essentially just evaluate the algebraic expression that is the ...
Fiber Optics Communication
... metallic waveguide, only transverse electric (TE) and transverse magnetic (TM) modes are found • In optical fibers, the core cladding boundary conditions lead to a coupling between electric and magnetic field components. This results in hybrid modes • Hybrid modes HE means (E is larger) or HM means ...
... metallic waveguide, only transverse electric (TE) and transverse magnetic (TM) modes are found • In optical fibers, the core cladding boundary conditions lead to a coupling between electric and magnetic field components. This results in hybrid modes • Hybrid modes HE means (E is larger) or HM means ...
CP Worksheet - Charges and Coulomb`s Law
... 3. The same two resistors, 10 and 50, and now placed into a parallel circuit with a 120 v battery. a. What is the total equivalent resistance of the circuit? Formula: b. What is the total electrical current of the circuit? Formula: c. What is the voltage across the 10 resistor? d. What is th ...
... 3. The same two resistors, 10 and 50, and now placed into a parallel circuit with a 120 v battery. a. What is the total equivalent resistance of the circuit? Formula: b. What is the total electrical current of the circuit? Formula: c. What is the voltage across the 10 resistor? d. What is th ...
Isolating a Variable in a Formula:
... 1. What would you do to isolate w in the formula l = w – 2? Why? ______________________ __________________________________________________________________________ 2. What would you do to isolate p in the formula C = np? Why? ________________________ __________________________________________________ ...
... 1. What would you do to isolate w in the formula l = w – 2? Why? ______________________ __________________________________________________________________________ 2. What would you do to isolate p in the formula C = np? Why? ________________________ __________________________________________________ ...
F = qvB sin θ
... identify that moving charged particles in a magnetic field experience a force identify that charged plates produce an electric field describe quantitatively the force acting on a charge moving through a magnetic field ...
... identify that moving charged particles in a magnetic field experience a force identify that charged plates produce an electric field describe quantitatively the force acting on a charge moving through a magnetic field ...
Non-radiative dielectric waveguide
The non-radiative dielectric (NRD) waveguide has been introduced by Yoneyama in 1981. In Fig. 1 the cross section of NRD guide is shown: it consists of a dielectric rectangular slab of height a and width b, which is placed between two metallic parallel plates of suitable width. The structure is practically the same as the H waveguide, proposed by Tischer in 1953. Due to the dielectric slab, the electromagnetic field is confined in the vicinity of the dielectric region, whereas in the outside region, for suitable frequencies, the electromagnetic field decays exponentially. Therefore, if the metallic plates are sufficiently extended, the field is practically negligible at the end of the plates and therefore the situation does not greatly differ from the ideal case in which the plates are infinitely extended. The polarization of the electric field in the required mode is mainly parallel to the conductive walls. As it is known, if the electric field is parallel to the walls, the conduction losses decrease in the metallic walls at the increasing frequency, whereas, if the field is perpendicular to the walls, losses increase at the increasing frequency. Since the NRD waveguide has been deviced for its implementation at millimeter waves, the selected polarization minimizes the ohmic losses in the metallic walls.The essential difference between the H waveguide and the NRD guide is that in the latter the spacing between the metallic plates is less than half the wavelength in a vacuum, whereas in the H waveguide the spacing is greater. In fact the conduction losses in the metallic plates decrease at the increasing spacing. Therefore, this spacing is larger in the H waveguide, used as a transmission medium for long distances; instead, the NRD waveguide is used for millimeter wave integrated circuit applications in which very short distances are typical. Thus an increase in losses is not of great importance.The choice of a little spacing between the metallic plates has as a fundamental consequence that the required mode results below cut-off in the outside air-regions. In this way, any discontinuity, as a bend or a junction, is purely reactive. This permits radiation and interference to be minimized (hence the name of non-radiative guide); this fact is of vital importance in integrated circuit applications. Instead, in the case of the H waveguide, the above-mentioned discontinuities cause radiation and interference phenomena, as the desired mode, being above cutoff, can propagate towards the outside. In any case, it is important to notice that, if these discontinuities modify the symmetry of the structure with reference to the median horizontal plane, there is anyway radiation in the form of TEM mode in the parallel metallic plate guide and this mode results above cutoff, the distance between the plates may be no matter short. This aspect must always be considered in the design of the various components and junctions, and at the same time much attention has to be paid to the adherence of the dielectric slab to the metallic walls, because it is possible that the above-mentioned phenomena of losses are generated. This occurs when in general any asymmetry in the cross section transforms a confined mode into a ""leaky"" mode.