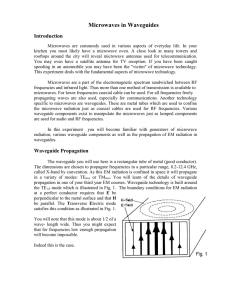
How to Simulate the Whispering-Gallery-Modes of Dielectric Microresonators in FEMLAB/COMSOL Mark Oxborrow
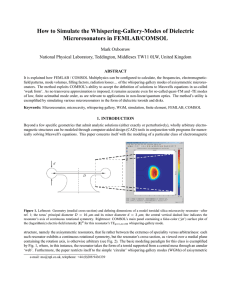
... the (necessarily finite) domain in the medial half-plane that the FEM model is defined to simulate (and ‘mesh’). In the case of open resonators and their unbounded WG modes, sufficient accuracy generally requires that this boundary lie either in the radiation zone or at least deep into the evanescen ...
... the (necessarily finite) domain in the medial half-plane that the FEM model is defined to simulate (and ‘mesh’). In the case of open resonators and their unbounded WG modes, sufficient accuracy generally requires that this boundary lie either in the radiation zone or at least deep into the evanescen ...
Review Powerpoint (including Ex Problem Answers)
... • A capacitor has an area of 15 square centimeters. The plates are separated by .5 mm. What is its capacitance? • What would the capacitance be if water was plates between the plates (dielectric constant of 80)? ...
... • A capacitor has an area of 15 square centimeters. The plates are separated by .5 mm. What is its capacitance? • What would the capacitance be if water was plates between the plates (dielectric constant of 80)? ...
Rosensweig, R.E., M. Zahn, and R. Shumovich, Labyrinthine Instability in Magnetic and Dielectric Fluids, Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 39, 127-132, November 198
... W h e n the spacer is reinserted, the labyrinth pattern occurs, growing more convoluted as the voltage is increased. The dielectric spacer gives rise to depolarizing fields with n o n - u n i f o r m field components tangential and perpendicular to the fluid interface causing interracial instability ...
... W h e n the spacer is reinserted, the labyrinth pattern occurs, growing more convoluted as the voltage is increased. The dielectric spacer gives rise to depolarizing fields with n o n - u n i f o r m field components tangential and perpendicular to the fluid interface causing interracial instability ...
Analysing Electric Field Distribution in Non
... SV software [9] in an axisymmetric approximation with the mesh size of about 20,000 triangles. Only half of the coil was modeled owing to mirror image symmetry in the R-θ-plane. The outer boundary is maintained at zero potential (except the R-θ-plane, where the normal component of the E-vector is ze ...
... SV software [9] in an axisymmetric approximation with the mesh size of about 20,000 triangles. Only half of the coil was modeled owing to mirror image symmetry in the R-θ-plane. The outer boundary is maintained at zero potential (except the R-θ-plane, where the normal component of the E-vector is ze ...
high voltage engineering
... The design of power devices particularly at high voltages is governed by their transient behavior. The transient high voltages or surge voltages originate in power systems due to lightning and switching operations. The effect of surge voltages is severe in all power apparatus. The response of a powe ...
... The design of power devices particularly at high voltages is governed by their transient behavior. The transient high voltages or surge voltages originate in power systems due to lightning and switching operations. The effect of surge voltages is severe in all power apparatus. The response of a powe ...
Wednesday, Feb. 15, 2012
... and are separated by d=4.0mm. (a) Find the capacitance, the charge on the capacitor, the electric field strength, and the energy stored in the capacitor. (b) The dielectric is carefully removed, without changing the plate separation nor does any charge leave the capacitor. Find the new value of capa ...
... and are separated by d=4.0mm. (a) Find the capacitance, the charge on the capacitor, the electric field strength, and the energy stored in the capacitor. (b) The dielectric is carefully removed, without changing the plate separation nor does any charge leave the capacitor. Find the new value of capa ...
BDTIC www.BDTIC.com/infineon Application Note No. 058
... Third-order distortion increases much more rapidly than described by relation (6) (see Figure 3). Above this power, the AC-modulation of the carrier concentration leads to a depletion of the intrinsic zone in the negative halfcycle and thus to an even stronger non-linear i-v-characteristic. In this ...
... Third-order distortion increases much more rapidly than described by relation (6) (see Figure 3). Above this power, the AC-modulation of the carrier concentration leads to a depletion of the intrinsic zone in the negative halfcycle and thus to an even stronger non-linear i-v-characteristic. In this ...
Design Project 4: Modulator
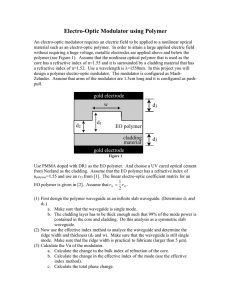
... Electro-Optic Modulator using Polymer An electro-optic modulator requires an electric field to be applied to a nonlinear optical material such as an electro-optic polymer. In order to attain a large applied electric field without requiring a huge voltage, metallic electrodes are applied above and be ...
... Electro-Optic Modulator using Polymer An electro-optic modulator requires an electric field to be applied to a nonlinear optical material such as an electro-optic polymer. In order to attain a large applied electric field without requiring a huge voltage, metallic electrodes are applied above and be ...
Electrical Properties
... electrons or ions) dense solids (no molecules that can reorient). Therefore, the polarizability must come from either ionic and electronic polarizability. Of these two ionic polarizability can make the largest contribution, particularly in a class of solids called ferroelectrics. The ionic polarizab ...
... electrons or ions) dense solids (no molecules that can reorient). Therefore, the polarizability must come from either ionic and electronic polarizability. Of these two ionic polarizability can make the largest contribution, particularly in a class of solids called ferroelectrics. The ionic polarizab ...
Balloon Animals
... Energy in a Capacitor • Work to charge to Q is area of triangle W = 1/2 Q(Q/C) = 1/2 Q2/C • Work to charge to DV W = 1/2 DV (CDV) = 1/2 C(DV)2 DV ...
... Energy in a Capacitor • Work to charge to Q is area of triangle W = 1/2 Q(Q/C) = 1/2 Q2/C • Work to charge to DV W = 1/2 DV (CDV) = 1/2 C(DV)2 DV ...
Three-phase cable: Computation of the dielectric losses
... factor and the insulator permittivity. This example explains how to evaluate the sensitivity of the losses results according to the properties of the electric cable material. ...
... factor and the insulator permittivity. This example explains how to evaluate the sensitivity of the losses results according to the properties of the electric cable material. ...
Appendix A - University of Toronto Physics
... The principle of operation of this device can be explained with the help of Fig. 1(b) and (c). The electromagnetic waves at the rectangular TE10 mode enter from the left side and are transformed into the circular TE11 mode by a gradual transition. The plane of polarization of this circular mode is t ...
... The principle of operation of this device can be explained with the help of Fig. 1(b) and (c). The electromagnetic waves at the rectangular TE10 mode enter from the left side and are transformed into the circular TE11 mode by a gradual transition. The plane of polarization of this circular mode is t ...
Dielectric Materials at Microwave Frequencies
... nant cavity. The resulting characteristics are then measured to compute the dielectric parameters. Since propagation characteristics of electromagnetic waves are influenced by complex permittivity of the medium it propagates through, the material can be characterized by monitoring the reflected and ...
... nant cavity. The resulting characteristics are then measured to compute the dielectric parameters. Since propagation characteristics of electromagnetic waves are influenced by complex permittivity of the medium it propagates through, the material can be characterized by monitoring the reflected and ...
Dielectric Materials Model Questions:
... (c) the potential V as a function of the distance r from the centre of the sphere for 0≤r≤α, assume V(α) = 0. [Ans. For r < R, D=0, E=0, V=Q/4π Є0.R Volt, For r>R, D=Q/4π r2 Coulomb/ m2, E=Q/4π Є0 r2 Volt/m, V=Q/4π Є0.r Volt] 04/C629 ...
... (c) the potential V as a function of the distance r from the centre of the sphere for 0≤r≤α, assume V(α) = 0. [Ans. For r < R, D=0, E=0, V=Q/4π Є0.R Volt, For r>R, D=Q/4π r2 Coulomb/ m2, E=Q/4π Є0 r2 Volt/m, V=Q/4π Є0.r Volt] 04/C629 ...
Analysis of Inhomogeneously Filled Waveguides Using a Bi
... elements are, in principle, frequency independent, so they have to be evaluated only once to obtain the dispersion curves, thus generating a robust and efficient code. This method has been applied to study open dielectric waveguides, as reported in [18] and [19]. Comparisons between our results and ...
... elements are, in principle, frequency independent, so they have to be evaluated only once to obtain the dispersion curves, thus generating a robust and efficient code. This method has been applied to study open dielectric waveguides, as reported in [18] and [19]. Comparisons between our results and ...
HW 4 6340
... The equivalent circuit for a unit cell of this structure is shown below. It consists of a lossless transmission line of length p, with a parallel inductance Lv in the middle and series capacitors 2Cg at the ends to model the gaps. A conductance 2Gg is placed in parallel with the capacitors to model ...
... The equivalent circuit for a unit cell of this structure is shown below. It consists of a lossless transmission line of length p, with a parallel inductance Lv in the middle and series capacitors 2Cg at the ends to model the gaps. A conductance 2Gg is placed in parallel with the capacitors to model ...
The slotted measuring line
... In general, transmission lines can be considered as structures for guiding electromagnetic waves. For this function a multitude of various transmission line types are suitable. The coaxial and two-wire line depicted in Fig. 5.1a) guides transverse electromagnetic waves (TEM waves) and can also be us ...
... In general, transmission lines can be considered as structures for guiding electromagnetic waves. For this function a multitude of various transmission line types are suitable. The coaxial and two-wire line depicted in Fig. 5.1a) guides transverse electromagnetic waves (TEM waves) and can also be us ...
Document
... Example 2. You have 3 capacitors with capacitances 5 nF, 2nF and 2nF. Your circuit needs 6 nF. What do you do? 2nF 5 nF 2nF ...
... Example 2. You have 3 capacitors with capacitances 5 nF, 2nF and 2nF. Your circuit needs 6 nF. What do you do? 2nF 5 nF 2nF ...
Task A. Transmission Line and Discontinuities
... Several different forms of waveguiding structures made from parallel metal strips on a dielectric substrate have found use in microwave and millimeter-wave circuits as well as in high –speed digital circuits. In this section, we will examine in some detail three types, called stripline, microstrip, ...
... Several different forms of waveguiding structures made from parallel metal strips on a dielectric substrate have found use in microwave and millimeter-wave circuits as well as in high –speed digital circuits. In this section, we will examine in some detail three types, called stripline, microstrip, ...
Reed_Frankie_ProjectSummary
... electrical component used to hold charge or store energy in an electric field. Unlike a battery which gives off a constant voltage, the charge held in a capacitor is given off at an exponential rate. The applications of a capacitor can be used to smooth out input. This is done by methods of filterin ...
... electrical component used to hold charge or store energy in an electric field. Unlike a battery which gives off a constant voltage, the charge held in a capacitor is given off at an exponential rate. The applications of a capacitor can be used to smooth out input. This is done by methods of filterin ...
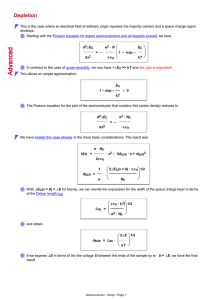
Depletion
... Remember that LDb is a purely material related quality and thus a constant for a given semiconductor. The width of the space charge region can be expressed very simply in terms of LDb, it is always larger by the factor {2eU/kT}1/2 Since kT at room temperature ≈ 1/40 eV, while applied voltages may be ...
... Remember that LDb is a purely material related quality and thus a constant for a given semiconductor. The width of the space charge region can be expressed very simply in terms of LDb, it is always larger by the factor {2eU/kT}1/2 Since kT at room temperature ≈ 1/40 eV, while applied voltages may be ...
Electrical Energy Saving with Improvement of Voltage and Current
... The collection of all necessary data involves power transformers, low and medium voltage General Panels, drawings of electrical installation with the length and the cross-section of all cables, position of supply sub-panels, nominal values of motors, Inverter, Soft Starter, number of cables in each ...
... The collection of all necessary data involves power transformers, low and medium voltage General Panels, drawings of electrical installation with the length and the cross-section of all cables, position of supply sub-panels, nominal values of motors, Inverter, Soft Starter, number of cables in each ...
Waves and Optics - MIT OpenCourseWare
... Typical voltage used to charge the imbedded conductors = 300 Volts Typical spacing between conductors = 2 mm ...
... Typical voltage used to charge the imbedded conductors = 300 Volts Typical spacing between conductors = 2 mm ...
Non-radiative dielectric waveguide
The non-radiative dielectric (NRD) waveguide has been introduced by Yoneyama in 1981. In Fig. 1 the cross section of NRD guide is shown: it consists of a dielectric rectangular slab of height a and width b, which is placed between two metallic parallel plates of suitable width. The structure is practically the same as the H waveguide, proposed by Tischer in 1953. Due to the dielectric slab, the electromagnetic field is confined in the vicinity of the dielectric region, whereas in the outside region, for suitable frequencies, the electromagnetic field decays exponentially. Therefore, if the metallic plates are sufficiently extended, the field is practically negligible at the end of the plates and therefore the situation does not greatly differ from the ideal case in which the plates are infinitely extended. The polarization of the electric field in the required mode is mainly parallel to the conductive walls. As it is known, if the electric field is parallel to the walls, the conduction losses decrease in the metallic walls at the increasing frequency, whereas, if the field is perpendicular to the walls, losses increase at the increasing frequency. Since the NRD waveguide has been deviced for its implementation at millimeter waves, the selected polarization minimizes the ohmic losses in the metallic walls.The essential difference between the H waveguide and the NRD guide is that in the latter the spacing between the metallic plates is less than half the wavelength in a vacuum, whereas in the H waveguide the spacing is greater. In fact the conduction losses in the metallic plates decrease at the increasing spacing. Therefore, this spacing is larger in the H waveguide, used as a transmission medium for long distances; instead, the NRD waveguide is used for millimeter wave integrated circuit applications in which very short distances are typical. Thus an increase in losses is not of great importance.The choice of a little spacing between the metallic plates has as a fundamental consequence that the required mode results below cut-off in the outside air-regions. In this way, any discontinuity, as a bend or a junction, is purely reactive. This permits radiation and interference to be minimized (hence the name of non-radiative guide); this fact is of vital importance in integrated circuit applications. Instead, in the case of the H waveguide, the above-mentioned discontinuities cause radiation and interference phenomena, as the desired mode, being above cutoff, can propagate towards the outside. In any case, it is important to notice that, if these discontinuities modify the symmetry of the structure with reference to the median horizontal plane, there is anyway radiation in the form of TEM mode in the parallel metallic plate guide and this mode results above cutoff, the distance between the plates may be no matter short. This aspect must always be considered in the design of the various components and junctions, and at the same time much attention has to be paid to the adherence of the dielectric slab to the metallic walls, because it is possible that the above-mentioned phenomena of losses are generated. This occurs when in general any asymmetry in the cross section transforms a confined mode into a ""leaky"" mode.