chapter 4 ancient india
... luxury in his palace in northern India. Because he was surrounded with beauty and youth, he had never witnesses old age, sickness, or death. • Then one day, around the age of 30, the prince traveled outside the palace walls. What he saw changed his life. He met a bend and tired old man, a man who wa ...
... luxury in his palace in northern India. Because he was surrounded with beauty and youth, he had never witnesses old age, sickness, or death. • Then one day, around the age of 30, the prince traveled outside the palace walls. What he saw changed his life. He met a bend and tired old man, a man who wa ...
Hinduism and the Rebirth of the Soul
... followers worldwide. Hinduism originated in the Indus River Valley over 3,000 years ago. About 80% of the Indian population regard themselves as Hindu. Hinduism has no single holy book, but Hindu writings like the Vedas, Upanishads, and Bhagavad-Gita provide guidance. Hinduism remains the most popul ...
... followers worldwide. Hinduism originated in the Indus River Valley over 3,000 years ago. About 80% of the Indian population regard themselves as Hindu. Hinduism has no single holy book, but Hindu writings like the Vedas, Upanishads, and Bhagavad-Gita provide guidance. Hinduism remains the most popul ...
Hindu
... events and perspectives in the modern world. I can explain how religious differences have led to conflict throughout history. I can interpret how places and regions serve as meaningful symbols for individuals and societies. ...
... events and perspectives in the modern world. I can explain how religious differences have led to conflict throughout history. I can interpret how places and regions serve as meaningful symbols for individuals and societies. ...
1 - Esamskriti
... Sindhu. This Proto-Indo-Iranian word sindhus literally refers to the “Indus River” and the culture pertaining to its long expansive valley. This is where Hindu culture first developed. (1) Historically, however, at a very early date, Persian explorers entered the Indian subcontinent from the far Nor ...
... Sindhu. This Proto-Indo-Iranian word sindhus literally refers to the “Indus River” and the culture pertaining to its long expansive valley. This is where Hindu culture first developed. (1) Historically, however, at a very early date, Persian explorers entered the Indian subcontinent from the far Nor ...
Death and dying in hinduism
... death and dying have had an extremely long and complex development. What has broadly been called Hinduism is the religion of about 1000 resettled Bhutanese and some Indian migrant in New Zealand. This section aims at describing the customs and rituals relating to death and dying among Hindus who hav ...
... death and dying have had an extremely long and complex development. What has broadly been called Hinduism is the religion of about 1000 resettled Bhutanese and some Indian migrant in New Zealand. This section aims at describing the customs and rituals relating to death and dying among Hindus who hav ...
Jainism Student Outline
... Origin (see timeline in the Resources section) A. Date: 6th century BCE B. Location: India C. Roots: Hinduism (hence, many beliefs/practices similar) Adherents (see statistics in the Resources section) A. Number: 3.7 million B. Location: India Key Figure / Founder: Mahavira (599-527 BC [some date hi ...
... Origin (see timeline in the Resources section) A. Date: 6th century BCE B. Location: India C. Roots: Hinduism (hence, many beliefs/practices similar) Adherents (see statistics in the Resources section) A. Number: 3.7 million B. Location: India Key Figure / Founder: Mahavira (599-527 BC [some date hi ...
Brief
... c. 8000-6000 BCE c. 2500-1500 c. 2000-900 c. 1500 c. 1000-500 BCE c. 400 BCE-200 CE c. 400 BCE-400 CE 200 BCE 100-300 CE c. 600-1800 ...
... c. 8000-6000 BCE c. 2500-1500 c. 2000-900 c. 1500 c. 1000-500 BCE c. 400 BCE-200 CE c. 400 BCE-400 CE 200 BCE 100-300 CE c. 600-1800 ...
universalist approach to religion - Om
... from a single geographical source (thus the popular nineteenth century concept of panBabylonianism, all religious ideas coming from a single source, which was Babylon) vs parallel development, where different ideas developed independently from each other in different cultures. Some scholars had geog ...
... from a single geographical source (thus the popular nineteenth century concept of panBabylonianism, all religious ideas coming from a single source, which was Babylon) vs parallel development, where different ideas developed independently from each other in different cultures. Some scholars had geog ...
Niharranjan Ray et.al. A Sourcebook of Indian Civilization
... In some ways, the back story of this volume is as interesting as the content of the book. It was initially conceived as part of a project designed by the ministry of education to cover historical sources for the ancient, medieval, and modem periods of Indian history. The first volume was completed i ...
... In some ways, the back story of this volume is as interesting as the content of the book. It was initially conceived as part of a project designed by the ministry of education to cover historical sources for the ancient, medieval, and modem periods of Indian history. The first volume was completed i ...
Hinduism Keynote - Westmoreland Central School
... caste beat the impurities out of clothes on the banks of the Yamuna River in Delhi. Life's "unclean" tasks, such as cleaning latrines and digging graves fall to those born into one of the hundreds of Untouchable castes. They face a lifetime of discrimination and brutality—prejudice that endures even ...
... caste beat the impurities out of clothes on the banks of the Yamuna River in Delhi. Life's "unclean" tasks, such as cleaning latrines and digging graves fall to those born into one of the hundreds of Untouchable castes. They face a lifetime of discrimination and brutality—prejudice that endures even ...
Glossary of terms used in Siddhartha
... Maya: a Sanskrit term denoting illusion, the physical world of appearances that surrounds us, blinding us to the reality behind it. Maya is that power in Nature that creates this illusion. The work of spiritual aspirants is to seek and experience the unity behind apparent multiplicity. Nirvana: from ...
... Maya: a Sanskrit term denoting illusion, the physical world of appearances that surrounds us, blinding us to the reality behind it. Maya is that power in Nature that creates this illusion. The work of spiritual aspirants is to seek and experience the unity behind apparent multiplicity. Nirvana: from ...
Hinduism - Relational Concepts
... possible through Christ alone (Romans 3:24, 6:23). Hinduism teaches that all paths lead to God. They believe that some of the great social and political leaders in history were incarnations, such as Jesus and Mahatma Gandhi. The Ganges River of northern India is the most sacred of all holy places. I ...
... possible through Christ alone (Romans 3:24, 6:23). Hinduism teaches that all paths lead to God. They believe that some of the great social and political leaders in history were incarnations, such as Jesus and Mahatma Gandhi. The Ganges River of northern India is the most sacred of all holy places. I ...
The Upanishads and Hindu Religious and Philosophical traditions
... • Between the 6th to 9th centuries CE, bhakti traditions grew in intensity in South India among many poets and mystics, and by the 11th century were widespread in North India. • The worship of Vishnu (Vaishnavism) and Shiva (Shaivism) as the Supreme being were the prominent general forms of religiou ...
... • Between the 6th to 9th centuries CE, bhakti traditions grew in intensity in South India among many poets and mystics, and by the 11th century were widespread in North India. • The worship of Vishnu (Vaishnavism) and Shiva (Shaivism) as the Supreme being were the prominent general forms of religiou ...
Varnas
... was based one the Vedas. There are FOUR Vedas and each had sacred poems and hymns THE OLDEST was the RIGVEDA ...
... was based one the Vedas. There are FOUR Vedas and each had sacred poems and hymns THE OLDEST was the RIGVEDA ...
Chapter 6 Paths to Enlightenment Notes
... Veldic and Upanishadic Period By 1700 BCE, the urban phase of Indus Civilization ended and was replaced by village life, as a result art production gradually ceased for the nest 1000 years. However the religious foundations laid during this time were very important. The religious views were based on ...
... Veldic and Upanishadic Period By 1700 BCE, the urban phase of Indus Civilization ended and was replaced by village life, as a result art production gradually ceased for the nest 1000 years. However the religious foundations laid during this time were very important. The religious views were based on ...
Chapter 6 Paths to Enlightenment: The Art of India - Parkway C-2
... Veldic and Upanishadic Period By 1700 BCE, the urban phase of Indus Civilization ended and was replaced by village life, as a result art production gradually ceased for the nest 1000 years. However the religious foundations laid during this time were very important. The religious views were based on ...
... Veldic and Upanishadic Period By 1700 BCE, the urban phase of Indus Civilization ended and was replaced by village life, as a result art production gradually ceased for the nest 1000 years. However the religious foundations laid during this time were very important. The religious views were based on ...
Hinduism
... Introduction to Hinduism Hindus believe that they work together but only each at a time like most things in life Birth life death Past present future ...
... Introduction to Hinduism Hindus believe that they work together but only each at a time like most things in life Birth life death Past present future ...
or, How to Invent a World Religion
... following an indigenous way of life or dharma. When the British arrived and began to be a dominant political force in the latter half of the eighteenth century the words “Hindu” and “Hinduism” were used in the same way on both sides of the divide—as markers of religious and cultural identity and as ...
... following an indigenous way of life or dharma. When the British arrived and began to be a dominant political force in the latter half of the eighteenth century the words “Hindu” and “Hinduism” were used in the same way on both sides of the divide—as markers of religious and cultural identity and as ...
Courtesy of Metropolitan Museum of Art
... According to the Hindu view, there are four goals of life on earth, and each human being should aspire to all four. Everyone should aim for dharma, or righteous living; artha, or wealth acquired through the pursuit of a profession; kama, or human and sexual love; and finally moksha, or spiritual sal ...
... According to the Hindu view, there are four goals of life on earth, and each human being should aspire to all four. Everyone should aim for dharma, or righteous living; artha, or wealth acquired through the pursuit of a profession; kama, or human and sexual love; and finally moksha, or spiritual sal ...
Courtesy of Metropolitan Museum of Art
... According to the Hindu view, there are four goals of life on earth, and each human being should aspire to all four. Everyone should aim for dharma, or righteous living; artha, or wealth acquired through the pursuit of a profession; kama, or human and sexual love; and finally moksha, or spiritual sal ...
... According to the Hindu view, there are four goals of life on earth, and each human being should aspire to all four. Everyone should aim for dharma, or righteous living; artha, or wealth acquired through the pursuit of a profession; kama, or human and sexual love; and finally moksha, or spiritual sal ...
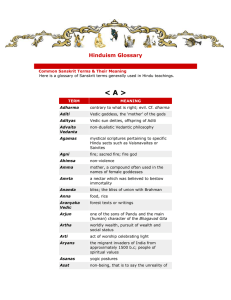
Hinduism Glossary - Vishva Shakti Durga Mandir
... Common Sanskrit Terms & Their Meaning Here is a glossary of Sanskrit terms generally used in Hindu teachings. ...
... Common Sanskrit Terms & Their Meaning Here is a glossary of Sanskrit terms generally used in Hindu teachings. ...
10 NonTheistic-Hinduism
... meditate on God, or your own self, in order to escape the endless cycle of life and death (reincarnation) and obtain moksha. The Rig Veda, dating from 1500-1300 BC, are books of spiritual philosophy – Codified around 600 BC, but the oldest text is 200 BC – Hinduism is more of a philosophy than a hol ...
... meditate on God, or your own self, in order to escape the endless cycle of life and death (reincarnation) and obtain moksha. The Rig Veda, dating from 1500-1300 BC, are books of spiritual philosophy – Codified around 600 BC, but the oldest text is 200 BC – Hinduism is more of a philosophy than a hol ...
Hinduism
... It is said that Hinduism has taught the world both tolerance and universal acceptance. Most Hindus not only believe in universal tolerance of others, but they accept all religions as true. It is said, “As different streams having different sources all mingle their waters in the sea, so different pat ...
... It is said that Hinduism has taught the world both tolerance and universal acceptance. Most Hindus not only believe in universal tolerance of others, but they accept all religions as true. It is said, “As different streams having different sources all mingle their waters in the sea, so different pat ...
Chapter 3: Ancient Indian Civilizations
... esteemed scriptures of Hinduism. The content of the Gita is the conversation between Krishna and Arjuna taking place on the battlefield before the start of the Kurukshetra war. Responding to Arjuna's confusion and moral dilemma, Krishna explains to Arjuna his duties as a warrior and prince. This has ...
... esteemed scriptures of Hinduism. The content of the Gita is the conversation between Krishna and Arjuna taking place on the battlefield before the start of the Kurukshetra war. Responding to Arjuna's confusion and moral dilemma, Krishna explains to Arjuna his duties as a warrior and prince. This has ...