Beginning of World War II Immediate Causes of WW
... The Maginot Line was established after World War I. ...
... The Maginot Line was established after World War I. ...
WORLD WAR II 1939-1945
... Civil War in Spain- Hitler & Mussolini help Fascist leader Franco win Hitler and Mussolini’s desire to expand empires/conquer land Mussolini invaded Ethiopia ...
... Civil War in Spain- Hitler & Mussolini help Fascist leader Franco win Hitler and Mussolini’s desire to expand empires/conquer land Mussolini invaded Ethiopia ...
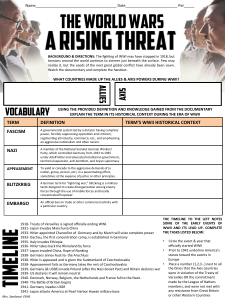
term definition term`s wwii historical context fascism nazi blitzkrieg
... An official ban on trade or other commercial ac9vity with a par9cular country. ...
... An official ban on trade or other commercial ac9vity with a par9cular country. ...
world war ii - mrgilliamsworldhistory
... intentions to occupy the Sudetenland, a highly industrial district of Czechoslovakia • The League of Nations is not empowered to fight the aggression; they issue condemnations that meant nothing • At the Munich Conference, Hitler promises to stop invading if he is given the Sudetenland. The European ...
... intentions to occupy the Sudetenland, a highly industrial district of Czechoslovakia • The League of Nations is not empowered to fight the aggression; they issue condemnations that meant nothing • At the Munich Conference, Hitler promises to stop invading if he is given the Sudetenland. The European ...
Name Date ______ Block _____ World War II Test Study Guide
... During the Lend-Lease program, the United States gave Britain war supplies and old naval warships in return for military bases in Bermuda and the Carribbean. ...
... During the Lend-Lease program, the United States gave Britain war supplies and old naval warships in return for military bases in Bermuda and the Carribbean. ...
Page 1 1. The League of Nations a. proved to be an obstruction to
... a. the code name for the German invasion of Russia b. a new style of warfare which employed massed armor columns supported by air power c. the German term denoting a counteroffensive d. both a and b ...
... a. the code name for the German invasion of Russia b. a new style of warfare which employed massed armor columns supported by air power c. the German term denoting a counteroffensive d. both a and b ...
(Versailles Treaty) failed to provide a “just and secure peace”
... • Mussolini was a strong public speaker who appealed to Italian national pride • By 1921, Mussolini had established the Fascist Party -- Fascism stressed nationalism and militarism and placed the interest of the state above the interests of the individual ...
... • Mussolini was a strong public speaker who appealed to Italian national pride • By 1921, Mussolini had established the Fascist Party -- Fascism stressed nationalism and militarism and placed the interest of the state above the interests of the individual ...
unit #10 review - the world of World History!
... (14) Why did the British & French pursue a policy of appeasement? • To prevent another world war ...
... (14) Why did the British & French pursue a policy of appeasement? • To prevent another world war ...
Failure of post-war (WWI) efforts
... • March, 1936– German troops enters Rhineland, a region in western Germany that the Versailles Treaty banned them from occupying. GB & France take no action. • March, 1938-- Germany took over Austria. • Hitler demands Sudetenland (region of Czechoslovakia). • Chamberlain (GB) & Daladier (France) sig ...
... • March, 1936– German troops enters Rhineland, a region in western Germany that the Versailles Treaty banned them from occupying. GB & France take no action. • March, 1938-- Germany took over Austria. • Hitler demands Sudetenland (region of Czechoslovakia). • Chamberlain (GB) & Daladier (France) sig ...
U.S. History Study Guide Chapters 16/17 – World War II 1
... 6. Also known as ‘Il Duce” he was the leader of Italy? 7. The name of Hitler’s government. 8. This outlawed arm sales or loans to nations at war or in a civil war? 9. What was the first county Hitler took over? 10. The meeting that adopted the policy of appeasement in Hitler’s quest to take over Cze ...
... 6. Also known as ‘Il Duce” he was the leader of Italy? 7. The name of Hitler’s government. 8. This outlawed arm sales or loans to nations at war or in a civil war? 9. What was the first county Hitler took over? 10. The meeting that adopted the policy of appeasement in Hitler’s quest to take over Cze ...
isolationism to involvement
... •The Blitzkrieg was a style of battle, that had never been seen before. •It was extremely successful, it was so overwhelming that no one had a defense to it. •When other nations saw this attack they were not sure if Hitler was THAT good, or was Poland THAT bad…… ...
... •The Blitzkrieg was a style of battle, that had never been seen before. •It was extremely successful, it was so overwhelming that no one had a defense to it. •When other nations saw this attack they were not sure if Hitler was THAT good, or was Poland THAT bad…… ...
World War II - Mrs. Cronin's APUSH
... – He warned that no part of the world was “truly isolated” from the rest ...
... – He warned that no part of the world was “truly isolated” from the rest ...
Class Rules - Denton ISD
... 1935 Italy invades Ethiopia The Italian army, under Mussolini, invaded Ethiopia. The Ethiopian forces could not stop the invasion, and Italy annexed the country in 1936. Hitler and Mussolini soon formed a treaty of friendship known as the Rome–Berlin axis. 1936–1939 Germany and Italy aid nationalist ...
... 1935 Italy invades Ethiopia The Italian army, under Mussolini, invaded Ethiopia. The Ethiopian forces could not stop the invasion, and Italy annexed the country in 1936. Hitler and Mussolini soon formed a treaty of friendship known as the Rome–Berlin axis. 1936–1939 Germany and Italy aid nationalist ...
WHAP Student Copy The Largest Costliest and Deadliest Conflict
... Excerpt from ushmm.org In the early years of the Nazi regime, the National Socialist government established concentration camps to detain real and imagined political and ideological opponents. Increasingly in the years before the outbreak of war, SS and police officials incarcerated Jews, Roma, and ...
... Excerpt from ushmm.org In the early years of the Nazi regime, the National Socialist government established concentration camps to detain real and imagined political and ideological opponents. Increasingly in the years before the outbreak of war, SS and police officials incarcerated Jews, Roma, and ...
Assessments
... The pre-assessment is designed to activate prior knowledge. Students may write anything in the “what I Know” and “what I Want to know” sections. Expected answers from students include references to information learned in the World War I and Interwar Period unit, such as the Treaty of Versailles or e ...
... The pre-assessment is designed to activate prior knowledge. Students may write anything in the “what I Know” and “what I Want to know” sections. Expected answers from students include references to information learned in the World War I and Interwar Period unit, such as the Treaty of Versailles or e ...
World War 2
... is about to begin." Four days later, France surrendered to Germany and they began the invasion of Britain. German air superiority in the south of England was crucial before Hitler could even begin an invasion. Hitler said to the leader of the Luftwaffe, that the RAF must be "beaten down to such an e ...
... is about to begin." Four days later, France surrendered to Germany and they began the invasion of Britain. German air superiority in the south of England was crucial before Hitler could even begin an invasion. Hitler said to the leader of the Luftwaffe, that the RAF must be "beaten down to such an e ...
Review: World War II
... Anschluss. The western democracies took no action. Hitler annexed the Sudetenland, a region in western Czechoslovakia. At the Munich Conference, British and French leaders again chose appeasement. In 1939, Hitler claimed the rest of Czechoslovakia. The democracies realized that appeasement had faile ...
... Anschluss. The western democracies took no action. Hitler annexed the Sudetenland, a region in western Czechoslovakia. At the Munich Conference, British and French leaders again chose appeasement. In 1939, Hitler claimed the rest of Czechoslovakia. The democracies realized that appeasement had faile ...
Topic 6: World War II
... Stalin's use of the media solidified his political power in the Soviet Union B Hitler opposed Communism because it was a threat to German ethnic solidarity. C. Hitler ability to communicate with the public, was his primary political strength. D. Japan's military leaders take over when the Japanese e ...
... Stalin's use of the media solidified his political power in the Soviet Union B Hitler opposed Communism because it was a threat to German ethnic solidarity. C. Hitler ability to communicate with the public, was his primary political strength. D. Japan's military leaders take over when the Japanese e ...
WORLD WAR II
... CAUSES OF THE WAR CONTINUED • ASIA: – Japan’s invasion of Manchuria – Clashes with China (war) – U.S. placed economic sanctions on Japan – Japan’s retaliation of U.S. sanctions by attacking U.S. and European colonies in Southeast Asia ...
... CAUSES OF THE WAR CONTINUED • ASIA: – Japan’s invasion of Manchuria – Clashes with China (war) – U.S. placed economic sanctions on Japan – Japan’s retaliation of U.S. sanctions by attacking U.S. and European colonies in Southeast Asia ...
WWII
... • Pacifism: opposition to all war Why did the Western democracies respond to aggression with a policy of appeasement? The Western democracies wanted to avoid the horrors of another war. ...
... • Pacifism: opposition to all war Why did the Western democracies respond to aggression with a policy of appeasement? The Western democracies wanted to avoid the horrors of another war. ...
World War II (Visuals)
... hold of their respective countries. Countries were too worried about their own country to worry about another country ...
... hold of their respective countries. Countries were too worried about their own country to worry about another country ...
US Hisory
... 5. What was his title? 6. What portion of China was taken control of by Japan between 1931-1933? a. What two treaties did this violate? 7. What were the two competing groups in Japanese politics in the 1920s and 1930s? 8. How did Japan react to the League of Nation’s condemnation of its aggression i ...
... 5. What was his title? 6. What portion of China was taken control of by Japan between 1931-1933? a. What two treaties did this violate? 7. What were the two competing groups in Japanese politics in the 1920s and 1930s? 8. How did Japan react to the League of Nation’s condemnation of its aggression i ...
Mein Kampf (My Struggle)
... • U.S. President–Franklin D. Roosevelt 1933-1945 • Lend-Lease Act - 1940 – U.S. loans weapons and supplies to England ...
... • U.S. President–Franklin D. Roosevelt 1933-1945 • Lend-Lease Act - 1940 – U.S. loans weapons and supplies to England ...
Appeasement

Appeasement in a political context is a diplomatic policy of making political or material concessions to an enemy power in order to avoid conflict.The term is most often applied to the foreign policy of the British Prime Ministers Ramsay Macdonald, Stanley Baldwin and Neville Chamberlain towards Nazi Germany between 1933 and 1939. Their policies of avoiding war with Germany have been the subject of intense debate for more than seventy years among academics, politicians and diplomats. The historians' assessments have ranged from condemnation for allowing Adolf Hitler's Germany to grow too strong, to the judgment that they had no alternative and acted in Britain's best interests. At the time, these concessions were widely seen as positive, and the Munich Pact concluded on 30 September 1938 among Germany, Britain, France, and Italy prompted Chamberlain to announce that he had secured ""peace for our time.""